Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function – General Science Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
অ্যাডেনোসিন ট্রাইফোসফেট (এটিপি) ক্রিয়া – সাধারণ বিজ্ঞান নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
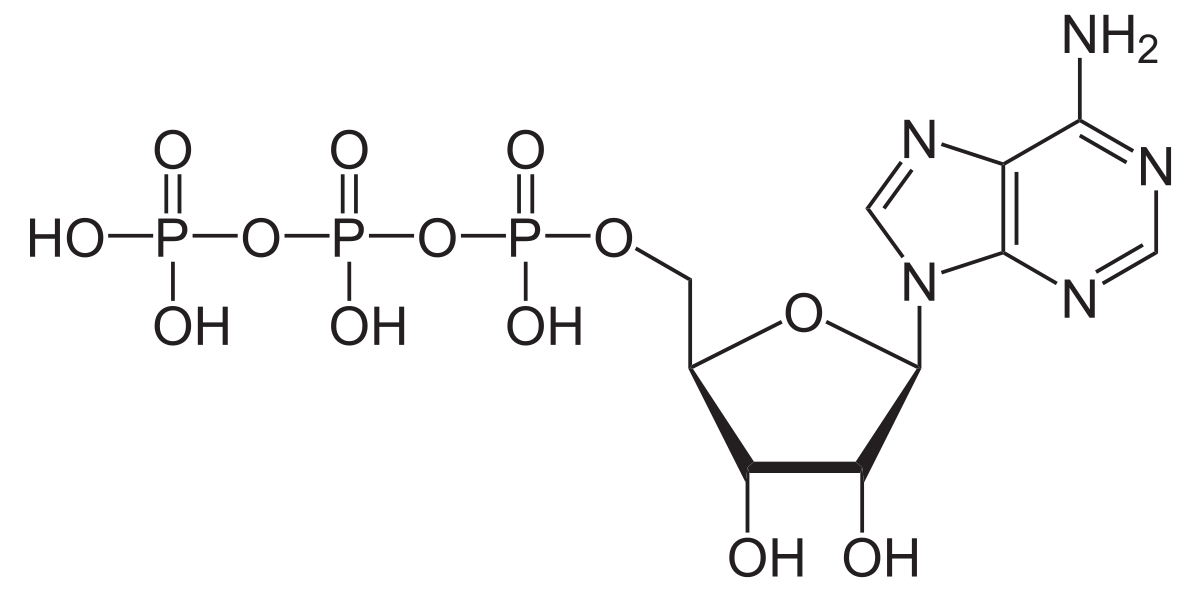
ATP is the main source of energy for most cellular processes. The building blocks of ATP are carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and phosphorus. Because of the presence of unstable, high-energy bonds in ATP, it is readily hydrolyzed in reactions to release a large amount of energy.Continue Reading Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Function – General Science Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
The enzymatic removal of a phosphate group from ATP to form ADP releases a huge amount of energy which is used by the cell in several metabolic processes as well as in the synthesis of macromolecules such as proteins. The removal of a second phosphate group from ATP results in further energy release and the formation of adenosine monophosphate (AMP).
When energy is not needed by the organism, the phosphate group is added back to AMP and ADP to form ATP – this can be hydrolyzed later as per required. Thus, ATP functions as a reliable energy source for cellular pathways.
Functions of ATP in cells
ATP finds use in several cellular processes. Some important functions of ATP in the cell are briefly discussed below:
Active Transport
ATP plays a critical role in the transport of macromolecules such as proteins and lipids into and out of the cell. The hydrolysis of ATP provides the required energy for active transport mechanisms to carry such molecules across a concentration gradient. Transport of molecules into the cell is called endocytosis whilst transport out of the cell is known as exocytosis.
Cell Signaling
ATP has key functions both in intracellular and extracellular signaling. It is easily recognized by purinergic receptors in mammalian tissues – its release from synapses and axons activates purinergic receptors that modulate calcium and cyclic AMP levels inside the cell.
In the central nervous system, adenosine modulates neural development, the control of immune systems, and of neuron/glial signaling.
ATP is also involved in signal transduction – its phosphate groups are used up by kinases in phosphate transfer reactions which activate a cascade of protein kinase reactions.
Structural Maintenance
ATP plays a very important role in preserving the structure of the cell by helping the assembly of the cytoskeletal elements. It also supplies energy to the flagella and chromosomes to maintain their appropriate functioning.
Muscle contraction
ATP is critical for the contraction of muscles; it binds to myosin to provide energy and facilitate its binding to actin to form a cross-bridge. ADP and phosphate are then released and a new ATP molecule binds to myosin. This breaks the cross-bridge between myosin and actin filaments, thereby releasing myosin for the next contraction.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in