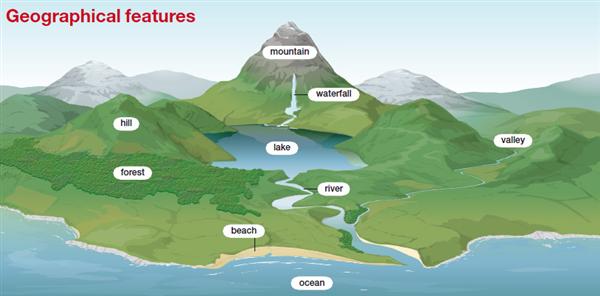
Geography Notes On – Critical Geographical Features – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Geography as a subject assumes a significant part in all competitive examination.It has a prominent role in Prelims and General studies Papers. It is an interesting subject. If aspirants are profound of this subject, no doubt you can choose this as your optional subject for W.B.C.S. mains Exam. It is an endless subject which deals with the spatial association between individuals, places, and the earth and it broadly covers all sphere. This is very easy and scoring optional if approached rightly. Many candidates has cracked W.B.C.S. examination by opting geography as their optional subjects.Continue Reading Geography Notes On – Critical Geographical Features – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
- Environment Education Awareness and Training (EEAT) is an established central sector scheme of the Environment ministry continuing since 1983-84.
- It aims to promote environmental awareness and mobilize student’s participation for environment conservation.
- Under the scheme, National Green Corps (NGC) ‘Ecoclub’ programme was initiated in 2001-2002 with the objective to impart knowledge to school children through hands on experience, about their immediate environment, interactions within it and the problems therein.
- The programme aims to inculcate proper attitude towards environment and sensitize children on issues related to environment and development.
- The scheme is continuing to build young cadres of students and trigger their sensitivity towards environment protection and conservation.
- It is envisaged that number of Ecoclubs shall be enhanced from about 1.5 lakh at present to 2 lakh in the ensuing year 2020-21.
Two major decisions are at the heart of the European Green Deal. The Green Deal includes sectoral plans to achieve these two overall targets and proposals for the policy changes that would be required. They are:
1) Climate neutrality
- The EU has promised to bring a law, binding on all member countries, to ensure it becomes “climate neutral” by 2050.
- Climate neutrality, sometimes also expressed as a state of net-zero emissions is achieved when a country’s emissions are balanced by absorptions and removal of greenhouse gases from the atmosphere.
- Absorption can be increased by creating more carbon sinks like forests, while removal involves technologies like carbon capture and storage.
- The EU is now the first major emitter to agree to the 2050 climate neutrality target. It has said it would bring a proposal by March next year on a European law to enshrine this target.
2) Emission reduction
- The second decision pertains to an increase in its 2030 emission reduction target.
- In its climate action plan declared under the Paris Agreement, the EU was committed to making a 40 per cent reduction in its emissions by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
- It is now promising to increase this reduction to at least 50 per cent and work towards 55 per cent.
- Even at 40 per cent, the European Union had the most ambitious emission reduction targets among the developed countries.
Why such move by EU?
- The 28 EU member countries are together the third-largest emitter of greenhouse gases in the world after China and the United States,
- The EU also happens to be only one among major emitters to retain the 1990 baseline for emission cuts originally mandated under the Kyoto Protocol for all developed countries.Also Read , Psychology Notes On – Item Response Theory – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Significance
- The European Union, as a whole, has been doing better than other developed countries on reducing emissions.
- In 2010, the EU had pledged to reduce its emissions by at least 25 per cent by 2020 from 1990 levels.
- By 2018, it claimed to have achieved 23 per cent reduction in emissions.
- In terms of emission reductions, it probably is on track to meet the 2020 target, unlike any developed country outside the EU.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in