Origin And Growth Of Settlements – Geography Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
জনবসতির উৎস এবং বৃদ্ধি – ভূগোল নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
Throughout India, there are many villages, 75 percent of India’s population live in villages. Villages in India are small there are only about a couple hundred people that live in each village. Agriculture is the main thing that takes place in these villages. People living in these villages make a living by being farmers and survive by trying to feed themselves and their country. India is mostly rural but it also has many populated cities.Continue Reading Origin And Growth Of Settlements – Geography Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Urban growth is more populated than rural growth and it is even becoming over populated. Manufacturing and the commercialization of agriculture industries have increased India’s population in these urban areas. Most of these places are in the western, southern, and northwestern part of India. This is where the agriculture is most prosperous. In the city areas, it is very congested and becoming a problem.
Traffic is a huge problem within the cities. Overpopulation has taken place and the growth rate just keeps on growing. Because of the overpopulation the people do not have clean water. 53 percent of children under the age of five are malnourished and 15 million people in just the city of Mumbal are homeless (Grinnell.edu, 2003). 1.273 billion people live in India and if the population still continues to grow with all of these problems their will be even more homeless and malnourished children. India is the seventh largest country and the second most populated country with China beating them.
Five Historical Turing Points
- The Mughal Empire came to be in 1526 and this affected India’s population of the movement of Muslims into India.
- In 1858 the British overthrow the Mughal Empire and take control of India
- The first census of population 1881 the population grew 10 percent in the first decade.
- In 1920, India’s population was steady and did not grow due to human lives being killed in wars, famines and epidemics.
- The Independence of Britain breaking away from India in 1947 lead to a growth increase in India; however, more than 500,000 people were killed in the violence between the Hindu and Muslim.
- Human Settlement is a form of human habitation which ranges from a single dwelling to large city. In other words, it is a process of opening up and settling on a previously uninhabited area by the people. Here, we are giving ‘Summary on the Settlements and Urbanization in India’ which is very useful as GK study material for the preparation of competitive examinations like UPSC-prelims, SSC, State Services, NDA, CDS, and Railways etc.
Summary on the Settlements and Urbanisation in India
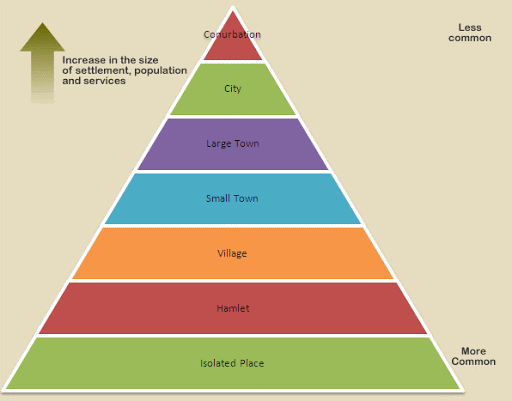
1. Types of the settlement are determined by the extent of the built-up area and inter-house distance. In India settlements are broadly classified into two major categories rural settlements and urban settlements.
2. Rural settlements in India can be broadly classified as clustered, agglomerated or nucleated, semi-clustered or fragmented, helmeted and dispersed or isolated.
3. Clustered settlements are generally found in fertile alluvial plains and in the North-Eastern states.
4. Semi-clustered settlements are found mainly in Ganga-Yamuna doabs, Khadar plains, etc.
5. Dispersed settlement or isolated settlement pattern in India appears in the remote jungles or on small hills with farms or pasture on the slopes.
6. Census of India 2011, defines the urban areas as statutory towns and Census towns.Statutory towns are all places with a municipality, corporation, and cantonment board or notified the town area committee, etc.
Dichotomy of Human Geography
7. Census towns are places having a minimum population of 5000, at least 75% of the male main working population engaged in non-agricultural pursuits and a density of population of at least 400 per sq. km.
8. Urban agglomeration is a continuous urban spread constituting a town and its adjoining out-growths and the agglomeration must consist of at least a statutory town with a population not less than 20,000 as per census 2001. Ex. Greater Mumbai UA, Delhi UA, etc.
9. In India, urban places with population exceeding 1,00,000 are called class-I towns or cities by convention and these are 468 in number and constitute 70% of total urban population. Population by 50,000 to 99,999 is called class-II, populations between 20,000 to 49,999 are called class-III, populations of 10,000 to 19999 are called class-IV, populations of 5,000 to 9,999 are called class-V and populations below 5000 are called class-VI towns.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in