Principles Of Holography – Physics Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
হোলোগ্রাফির নীতি – পদার্থবিজ্ঞানের নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
A hologram is a physical structure that diffracts light into an image. The term ‘hologram’ can refer to both the encoded material and the resulting image.Continue Reading Principles Of Holography – Physics Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
A holographic image can be seen by looking into an illuminated holographic print or by shining a laser through a hologram and projecting the image onto a screen.
Other methods of projecting and reflecting images are often described as holographic – or even misleadingly holograms, because they have an optical presence, spatial quality or iridescent colors.
While it the past it there was a clear distinction technology is evolving to create virtual holograms by steering light into an image. Augmented reality systems like the HoloLens often use a Holographic Optical Elements to make a video projection appear at comfortable viewing distance. The virtual objects in augmented reality are a kind of ‘virtual hologram’
& not a hologram – The Pepper’s ghost technique, which uses a partially reflective surface to mix an image with the scene beyond. John Henry Pepper demonstrated the technique in the 1860s with it being used to overlay visual elements (often a figure – ‘ghost’) onto a physical set or stage.
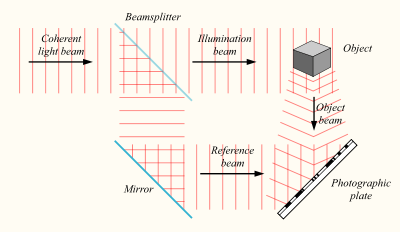
How does holography work?Holography is based on the principle of interference. A hologram captures the interference pattern between two or more beams of coherent light (i.e. laser light). One beam is shone directly on the recording medium and acts as a reference to the light scattered from the illuminated scene.
The hologram captures light as it interests the whole area of the film, hence being described as a ‘window with memory’. By contrast a photograph captures a single small area ‘aperture’ of perspective, the photographic image being created by focusing this light onto film or a digital sensor.
The physical medium of holographic film is photo-sensitive with a fine grain structure1. Common materials used are silver-halide emulsions, dichromate gelatins and photopolymers – each having their own characteristics and require different processing. Holograms can also be embossed ‘stamped into a foil’ with applications including in security identification, such as on passports, credit cards, tickets and packaging, as they are difficult to copy without the master hologram.
The hologram is the recorded interference pattern of constructive (intensity peaks) and destructive (elimination) of the superimposed light-wavefronts (the electromagnetic field). By using a coherent laser light-source and a stable geometry (or short ‘pulse’ duration) the interference pattern is stationary and can be recorded into the hologram’s photosensitive emulsion. The hologram is then chemically processed so that the emulsion has a modulated density, freezing the interference pattern into ‘fringes’.
When looking at the modulated structure under a microscope it does not look like the image encoded within. The density fringes are a distributed pattern of wavefront interference – a frozen distributed recording of the direction, phase and amplitude of light (the visible spectrum of electron-magnetic radiation).
When the hologram is re-illuminated the light is diffracted through these fringes. If the direction and shape (curvature) of the light is the same as the reference beam then the hologram diffracts the light into the shape of the other wavefront, reconstructing the recorded image.
The relationships that can be set up with the holographic image suggest a particular way of considering optical information. While there are a number of ways of making holograms, each having their own aesthetic qualities they all have the same underlying principle. Holography is a way of encoding recording an interference pattern.
On encountering a hologram, what is most surprising is that a surface seems to hold a space. The difference of scale between the optical shaping by the hologram structure and our material sense of it as a surface produces a perception of a virtual form, as if the light holds its own shape.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in