Current Affairs of 9th June 2023 For IAS And WBCS Examination
Environment & Ecology
Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS)

- As per recent UN Report, noise pollution is known to cause significant disturbance to marine wildlife, including migratory species protected under the Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS).
- Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals (CMS):
- CMS, also known as the Bonn Convention, is an environmental agreement maintained by the United Nations Environment Programme.
- It was signed on June 23, 1979, in Bonn, Germany.
- It serves as a global forum for the conservation and sustainable use of migratory species and their habitats.
- CMS is the only global and UN-based intergovernmental organization dedicated solely to the conservation and management of terrestrial, aquatic and avian migratory species throughout their range.
- The parties to the convention acknowledge the importance of conserving migratory species, and the need to pay special attention to species whose conservation status is unfavourable.
- The convention’s signatories recognize the necessity of maintaining migratory species, as well as the need to pay special attention to species whose conservation status is unfavorable.
- CMS Parties’ activities might range from legally binding treaties (known as Agreements) to less formal agreements such as Memorandums of Understanding.
- The Conference of Parties (COP) is the convention’s decision-making body.
- CMS has two appendices: These appendices list the migratory species covered by the Convention.
- Appendix I lists endangered migratory species and specifies prohibitions regarding the take of these species.
- Appendix II identifies species with a ‘unfavorable conservation situation’ (as defined by the Convention) and encourages range states to create range-wide conservation and management agreements for these species.
- CMS and India:Since 1983, India has been a signatory to the CMS.India has also signed a non-legally Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with CMS on the protection and management of Siberian Cranes (1998), Marine Turtles (2007), Dugongs (2008), and Raptors (2016).
Indian Economy
First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG):

- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently approved the framework for the First Loss Default Guarantee (FLDG).
- FLDG:
- FLDG is a lending mechanism between fintech firms and their partner banks and non-banking finance companies where the initial hit on a default is taken by the fintech firm that generated the loan.
- Under these agreements, the fintech originates a loan and assures to compensate the partners up to a predetermined percentage if customers fail to repay.
- Bank/NBFC partners lend through fintech but on their own books.
- Benefits:
- FLDG enables traditional lenders expand their customer base while relying on the fintech’s underwriting capabilities.
- It would also rationalize existing prudential standards for implementing resolution strategies for natural disaster exposures.
- Issues with FLDGs:
- A report by an RBI-constituted working group on digital lending outlined the risks of FLDG agreements with unregulated entities.
- The other concern is that FLDG costs are often passed on to customers.
- FinTech:
- Fintech, a combination of the phrases “financial” and “technology,” is the use of new technical breakthroughs to financial products and services.
- It refers to the use of software and hardware to improve the speed, usability, and security of financial services and operations.
- Payment processing solutions to mobile banking apps are all part of the fintech business.
- Mobile banking, peer-to-peer payment services, automated portfolio managers, and trading platforms are a few examples.
RuPay card

- Context: In an effort to widen the reach of RuPay cards, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently decided to allow banks to issue RuPay Prepaid foreign cards to consumers and to issue such cards abroad.
- RuPay card:
- RuPay (a combination of Rupee and Payment) is a transnational Indian financial services and Payment Service System that was designed and launched in 2014 by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- Its objective is to achieve the Reserve Bank of India’s vision of a domestic, open-loop, and multilateral payments system in India.
- While combining and integrating numerous payment systems in India, NPCI envisioned RuPay as an alternative to Mastercard and Visa. RuPay was initiated with the goal of less a cash-based economy.
- All Indian companies with an annual revenue of more than 50 crore are required to offer RuPay payment choices to their clients.
- It is in the process of enabling electronic payment at all Indian banks and financial organizations.
- Products:
- RuPay provides debit cards, credit cards, prepaid cards, and government plan cards.
- Government scheme cards include debit and credit cards such as the RuPay PMJDY, RuPay Mudra, and RuPay PunGrain debit cards, as well as the RuPay Kisan credit card.
- It also provides combo cards that combine debit and credit, debit and prepaid, or credit and prepaid functions into a single card.
- The following are the advantages of using a RuPay Card:
- As the transaction processing will happen domestically, it would lead to a lower cost of clearing and settlement for each transaction. This reduces transaction costs and encourages the use of cards in the sector.
- As a domestic system, RuPay is committed to developing unique product and service offers for Indian consumers.
- Protection of information related to Indian consumers: Transaction and customer data related to RuPay card transactions will reside in India.
- The National Payments Corporations of India:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Indian Banks’ Association (IBA) established the National Payments Corporations of India (NPCI) in 2008 under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- NPCI is a non-profit company that promotes and facilitates electronic payment acceptance in India.
- The NPCI, which is regulated by a consortium of banks, aims to build a strong payment and settlement systems.
- Ten major banks, including the State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, Citibank, Bank of Baroda, and HSBC, are supporting NPCI. In 2016, the shareholding was expanded to 56 member banks in order to attract additional banks from different sectors.
- The NPCI can operate payment systems like as the National Financial Switch (NFS), Immediate Payment System (IMPS), Aadhaar-enabled Payments System (AEPS), and National Automated Clearing House (NACH).
- NPCI has also introduced RuPay, the Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), the Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM), and the Unified Payments Interface (UPI).
- NPCI provides the following services:
- United Payments Interface (UPI) is a real-time payment system that connects bank accounts to mobile phone UPI platforms.It eliminates the requirement for a third-party wallet and allows for direct transfers of funds from one bank account to another.
- BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money): BHIM is a UPI-enabled app. It enables customers to make payments quickly and easily by utilizing only a registered mobile number or a virtual payment address (VPA).
- NPCI’s *99# services are powered by USSD, which stands for Unstructured Supplementary Service Data.These services aim to provide traditional and modern financial alternatives to Indian individuals who may lack smartphones, internet access, or traditional bank accounts.
- IMPS / Immediate Payment Service: This technology operates around the clock and offers payments to be transferred instantaneously. Current advancements such as UPI are made feasible via IMPS. Unlike NEFT and RTGS, IMPS does not rely on traditional banking hours nor does it adhere to public holidays.
- BBPI / Bharat Bill Payment Interface: It functions as the single platform that consolidates payments for bill payers and aggregators.
International News
Turkmenistan–Afghanistan–Pakistan–India (TAPI) Pipeline
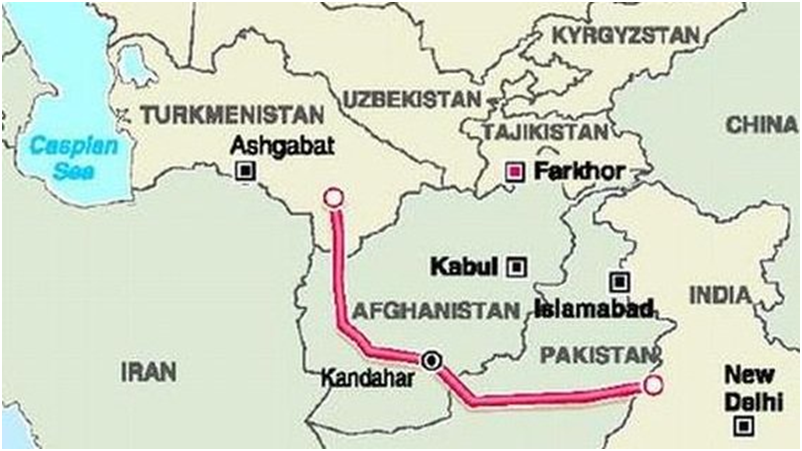
- Context:Pakistan and Turkmenistan recently signed a Joint Implementation Plan (JIP) to expedite work on the Turkmen, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India (TAPI) gas pipeline project and complete the feasibility study as soon as possible.
- TAPI Pipeline:
- It is a 1,814-kilometer pipeline that will carry 33 billion cubic meters of gas from Turkmenistan to Afghanistan, Pakistan, and finally India.
- It is also known as ‘Peace Pipeline’.
- Route:
- It will begin from the Galkynysh gas field in Turkmenistan.
- It will then go through Afghanistan and Pakistan before arriving in the Indian town of Fazilka (close to the Indo-Pak border).
- The pipeline will go from Turkmenistan’s Mary area to Afghanistan, covering a total distance of 214 kilometers. The Afghanistan section will be built along the highway.
- The pipeline will extend approximately 774 kilometers through Afghanistan’s Kandhar and Herat highways. It will go 826 kilometers through Pakistan, passing through the cities of Quetta and Multan before ending in Fazilka at the Indo-Pakistan border in the Punjab region of India.
- Funding:
- The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is funding the TAPI project and also serving as the development’s transaction adviser.
- In December 2016, Turkmenistan received a $700 million loan from the Islamic Development Bank to fund the project.
- The remaining three countries contributed $200 million to the TAPI initiative.
- Capacity: During the 30-year commercial operations period, the pipeline will transport 33 billion cubic meters (bcm) of natural gas annually from TKM to respective consumers in AFG (5%), PAK (47.5%), and IND (47.5%).
- The Project entails the purchase, installation, and operation of a pipeline and associated infrastructure in Afghanistan and Pakistan.
- Timeline:
- The initiative was conceived in the 1990s, and the heads of four member nations signed an inter-governmental agreement in 2010.
- In December 2010, a Gas Pipeline Framework deal was signed, and in May 2013, a bilateral gas selling deal was signed.
- A groundbreaking ceremony for Afghanistan’s segment of the TAPI gas pipeline was held in the western Afghan city of Herat in February 2018.
- Benefits of the TAPI pipeline:
- The pipeline is projected to allow a high level of trade and cooperation across the area, while also promoting peace and security among the four nations.
- More than 1.5 billion people in Afghanistan, Pakistan, and India are expected to benefit from the project’s long-term energy security.
- Furthermore, the project is intended to increase Turkmenistan revenue through the sale of gas.
- Transit fees will aid Afghanistan and Pakistan as well.
- However, political instability and violence in Afghanistan slowed its progress.
Science & Technology
Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT)

- Context: PUNE-BASED researchers recently identified two new Millisecond Pulsars (MSP) – rotating neutron stars — utilizing an indigenously designed unique technique , which was applied during an ongoing sky survey conducted by the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT).
- GMRT (Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope):
- The GMRT is a low-frequency radio telescope that aids in the investigation of various radio astrophysical problems spanning from close solar systems to the observable universe’s edge.
- It is located in Khodad, Maharashtra, around 80 kilometers north of Pune.
- It is a project of the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), operating under the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR).
- The National Centre of Radio Astrophysics (NCRA) operates the telescope. NCRA is a division of the TIFR in Mumbai.
- It comprises of 30 fully- steerable dish-type antennas of 45-meter diameter each, spread over a 25-km region.
- Currently, the GMRT is the world’s largest radio telescope operating at meter wavelength.
- It has been recently updated with additional receivers, and it is now referred to as the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT).
- Pulsars:
- Pulsars are revolving neutron stars observed to have pulses of radiation at very regular intervals that typically ranging from milliseconds to seconds.
- Pulsars have extremely powerful magnetic fields that funnel jets of particles out along their two magnetic poles.
- These accelerated particles produce extremely intense light beams.
- Because the magnetic field is not always aligned with the spin axis, those particle and light beams are swept around as the star rotates.
- Pulsars are among the rare astronomical objects that emit circular polarised light.
- Astronomers presently recognize three primary classes of pulsars based on the source of the electromagnetic radiation:
- rotation-powered pulsars: loss of rotational energy of the star provides the power
- accretion-powered pulsars: the gravitational potential energy of accreted matter serves as the power source (generating X-rays visible from Earth),
- Magnetars: the decay of an extremely strong magnetic field provides the electromagnetic power.
Defence News
Agni Prime Missile

- The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) recently successfully flight-tested the New Generation Ballistic Missile ‘Agni Prime’ from Dr APJ Abdul Kalam Island.
- Agni Prime Missile:
- It is the most recent and sixth variant of the Agni series missiles (developed under the IGMDP – Integrated Guided Missile Development Program).
- It is a short-range ballistic missile with a range of 1000 to 1500 kilometers.
- It is a surface-to-surface missile capable of carrying a 1,000 kg payload or a nuclear warhead.
- It has innovative propulsion systems, composite rocket motor casings, and improved navigation and guiding systems.
- Other Agni Missiles:Range of other Agni Missiles:
- Agni I: Range of 700-800 km.
- Agni II: Range more than 2000 km.
- Agni III: Range of more than 2,500 Km
- Agni IV: Range is more than 3,500 km and can fire from a road mobile launcher.
- Agni-V: The longest of the Agni series, an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km.
- IGMDP (Integrated Guided Missile Development Program):
- Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam developed the IGMDP (Integrated Guided Missile Development Program) to help India achieve self-sufficiency in missile technology. It received approval by the Indian government in 1983 and completed in March 2012.
- This program’s five missiles (P-A-T-N-A) are as follows:
- Prithvi: A surface-to-surface ballistic missile with a short range.
- Agni: Ballistic missiles with different ranges, such as Agni (1,2,3,4,5).
- Trishul is a low-level, short-range surface-to-air missile.
- Nag is a third-generation anti-tank missile.
- Akash: Surface-to-air missile with a medium range.
- Ballistic missile:
- Ballistic missiles are launched directly into the Earth’s upper layers of atmosphere.
- They travel outside the atmosphere, where the missile’s warhead detaches and falls to a specified target.
- They are self-guided rocket-propelled weapons systems that may carry conventional or nuclear munitions. They can be launched from planes, ships, and submarines, as well as from land.
Important One-Liner:
- The Union Cabinet has approved the third BSNL revival package, totaling Rs. 89,047 crore. The authorized capital of BSNL will be increased from Rs. 1,50,000 crore to Rs. 2,10,000 crore as part of this revival package.
- World Accreditation Day (#WAD2023) is celebrated on June 9th, 2023, as part of a global initiative launched by the International Laboratory Accreditation Cooperation (ILAC) and the International Accreditation Forum (IAF) to emphasize the importance of accreditation. The theme for WAD 2023 is “Accreditation: Supporting the Future of Global Trade”.
- Shantanu Gupta, a well-known author who has written two best-selling books about Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath, has released a new graphic novel titled “Ajay to Yogi Adityanath” for young readers.
- In a landmark victory for India’s defense capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) successfully conducted the first pre-induction night launch of the new-generation ballistic missile ‘Agni Prime.’
- The Federal Bank has initiated a unique campaign in Chennai, titled ‘I am Adyar, Adyar is me,’ to celebrate the rich culture and stories of the local community. The campaign turns an entire bank branch into a museum of local stories, highlighting the hardships and accomplishments of the people who make Adyar special.
- The Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) is an important government commission in India that is in charge of assuring the safety of railway travel and operations. The CRS was established during the British era and has evolved over time to become an independent authority under the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA).
- NTPC Kanti has launched the Girl Empowerment Mission (GEM)-2023 as part of their CSR initiative, a four-week residential workshop program targeted at uplifting 40 impoverished rural girls from the Kanti block. This program, organized for the first time by NTPC Kanti, seeks to provide academic training, skill development, and overall personality enhancement to the participants.
- Alby D’Cruz, one of Kerala’s proud Defence personnel who always maintained a low profile despite being the first Keralaite to be conferred the Ashoka Chakra, passed away.
- The non-profit organisation Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) released its yearly statistics compilation, ‘State of India’s Environment 2023: In Figures,’ on the eve of World Environment Day. The report includes statistics on various aspects of the environment, including climate and extreme weather, health, food and nutrition, migration and displacement, agriculture, energy, waste, water, and biodiversity. According to the report, Telangana is the best-performing state in terms of total environmental performance.
- Farmers Fresh Zone (FarmersFZ), a Kerala-based startup, has been chosen for the United Nations’ ‘Accelerator Programme’ hosted by the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), making the country proud.
- Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath launched the Nand Baba Milk Mission with a Rs 1,000 crore funding. Its goal is to increase milk production and empower milk farmers by allowing them to sell their milk at reasonable prices through dairy co-operative societies.
- As a measure to manage inflation and increase supply, the Indian government eliminated restrictions on the maximum amount of specific pulses that can be purchased. The limits on the procurement of tur, urad, and masoor under the Price Support Scheme operations for the 2023-24 period have been lifted. This decision ensures that these pulses can be purchased from farmers at the minimum support price without any restrictions.
- Sanjay Swarup is set to become the new Chairman & Managing Director (CMD) of Container Corporation of India (CONCOR), a PSU under the Ministry of Railways.
- The Karnataka government has advised the women to apply for Shakti smart cards to avail the free travel in state run buses, starting from June 11. The government has already issued a set of guidelines on the ‘Shakti’ scheme, which is one of the major poll promises by the Congress party in Karnataka.
- For the year 2023, Director of Gulf of Mannar Marine National Park Jagdish S Bakan will get the Michel Batisse Award from the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for his accomplishments in Biosphere Reserve Management.
- V Anantharaman, a seasoned banker with extensive experience in the banking industry, has been appointed as the non-executive chairman of credit bureau TransUnion CIBIL.
- According to Mercer’s Cost of Living survey, Mumbai is the most costly city in India for expatriates in India. The survey analyzed 227 cities across five continents to determine the cost of living for expats. Following Mumbai, New Delhi and Bengaluru ranked second and third respectively on the list.


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in






































































































