Syllabus of WBCS Examination 2024
WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Exam 2024 : Indicative Advertisement:
https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/indicative-advertisement-wbcs-exe-etc-exam-2024/
WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Exam proposed Syllabus 2024.
https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/wbcs-examination-2025-onwards-change-of-pattern-syllabus-wbcs-2024-in-old-syllabus/
Analysis of Marks obtained by all candidates in WBCS Exam 2021
https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/wbcs-exe-etc-2021-group-a-b-c-d-all-written-and-interview-marks-obtained-by-all-candidates/
To download the detailed scheme and syllabus of WBCS Exam (2023) please go to:
WBCS Exam Scheme Syllabus Notification
Detailed syllabus given below (at the bottom of this page a s a chart).
For detailed structure of the exam etc. you can visit this page too Click here to see it.
Download app (Android /IOS) from this link and go to relevant section. http://on-app.in/app/oc/147006/rrnvu .
In IOS https://apps.apple.com/in/app/myinstitute/id1472483563 and give code RRNVU
Information WBCS 25-26
https://bit.ly/wbcs-exam-expected-pattern-scheme-2025
Details Activities of WBCS MADE EASY –
https://bit.ly/m/wbcs-made-easy
Here is the Extract:
PUBLIC SERVICE COMMISSION, WEST BENGAL
WEST BENGAL CIVIL SERVICE (EXECUTIVE) ETC. EXAMINATION, 2023
SCHEME AND SYLLABUS
The scheme and syllabus of the examination shall be as detailed in the Schedule below :-
1. Scheme of the Preliminary Examination : The Preliminary Examination will consist of only one paper, viz., a paper on “General Studies”. The paper will be of an objective type consisting of 200 multiple-choice questions. The paper will carry 200 marks and will be of 2½ hours duration. The standard of the paper will be of the level of knowledge as expected of a graduate of any faculty of a recognized University. The paper will include questions covering the following fields of knowledge:
(i) English Composition 25 Marks
(ii) General Science 25 Marks
(iii) Current events of National & International Importance 25 Marks
(iv) History of India 25 Marks
(v) Geography of India with special reference to West Bengal 25 Marks
(vi) Indian Polity and Economy 25 Marks
(vii) Indian National Movement 25 Marks
(viii) General Mental Ability 25 Marks
The Preliminary Examination is meant to serve as a Screening Test only for the purpose of selection of candidates for the Main Examination. The marks obtained in this examination by the candidates will not be considered for final selection. Only those candidates who will be declared qualified at the Preliminary Examination in a year shall be eligible for admission to the W.B.C.S.
(Exe.) etc.(Main) Examination of that year.
2. Scheme of the Main Examination : The Main Examination shall consist of six Compulsory papers and one optional subject consisting of two papers (Only for candidates applying for group A and / or B) to be chosen by the candidates from the list of optional subjects given below. There will be two papers of the optional subject of 200 marks each. Each paper, Compulsory or
Optional, will carry 200 marks and will be of 3 hours duration.
Out of six compulsory papers four papers i.e.
(i) General Studies- I,
(ii) General Studies- II,
(iii) The Constitution of India and Indian Economy including role and functions of Reserve Bank of India and
(iv) Arithmetic and Test of Reasoning will be of MCQ Type to be answered in OMR answer sheets and remaining two compulsory papers i.e. Paper – I and Paper – II will be of conventional
type written examination.
Compulsory Papers : Six compulsory papers are as follows:-
Paper I : Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali – Letter writing (within 150 words) / Drafting of Report (within 200 words),
Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from English to Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali
Paper II : English – Letter writing (within 150 words) / Drafting of Report (within 200 words), Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali to English
Paper III : General Studies-I : (i) Indian History with special emphasis on National Movement and (ii) Geography of India with special reference to West Bengal.
Paper IV : General Studies-II : Science and Scientific & Technological advancement, Environment, General Knowledge and Current Affairs.
Paper V : The Constitution of India and Indian Economy including role and functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Paper VI : Arithmetic and Test of Reasoning.
3. List of Optional Subjects :
Literature of Bengali , Hindi , Sanskrit ,English , Pali ,Arabic ,Persian ,French ,Urdu ,Santali ,Comparative Literature ,Agriculture ,Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science ,Anthropology ,Botany ,Chemistry ,Civil Engineering ,Commerce and Accountancy,Computer Science ,Economics ,Electrical Engineering ,Geography ,Geology ,History,Law ,Mathematics ,Management ,Mechanical Engineering ,Medical Science ,Philosophy ,Physiology ,Physics ,Political Science , Psychology ,Sociology ,Statistics ,Zoology .
4. The standard of Arithmetic part of Compulsory Paper – VI(Arithmetic & Test of Reasoning) will be similar to that of the Compulsory Mathematics paper at the Madhyamik Examination of the Board of Secondary Education, West Bengal. Test of Reasoning will cover Analytical Reasoning:Data Sufficiency, Logical Reasoning : (i) Logical Deduction (ii) Forcefulness of the Arguments(iii) Implication of sentences (iv) Inferring from diagrams, Series: (i) Letter series, (ii) Number series, Inferring from Data, Analogy tests, Symbol Interpretation, Mathematical puzzles, Odd man out, Perception test, Non-verbal reasoning & Selecting the correct
sequence.
The standard of other compulsory papers will be of the level of learning expected from a graduate of any faculty of a recognized University.
The two papers of the optional subjects will be of conventional type and the standard of the examination will be approximately that of an Honours Degree Examination as prescribed by the recognized Indian Universities except Law, Medical Science and Engineering subjects which will be that specified for the LLB, MBBS and BE or equivalent courses respectively recognized by Indian Universities /
Institutions.
The Topic ‘Environment’ in paper General Studies II will include the following:-
Bio diversity and Coastal Regulation Zone, Global Warming, Industrial and Environmental Pollution, Ozone Layer and related issues.
The Topic ‘Indian Economy including role and functions of the Reserve Bank of India’ of the compulsory paper- V will consist of the
following:-
Central State relation and devolution of central funds to state, Planning process and objectives of five years plan, Functions of RBI and Monetary policy, Central Finance Commission & State Finance Commission and Fiscal Policy of Government of India.
5. Answers in all the papers, Compulsory and Optional, except the language papers may be written either in English or in Bengali (unless otherwise directed in these rules or in the question papers). Answers in the following optional papers may also be written in Nepali:
Optional : (1) Political Science
(2) Botany
Note : Candidates shall write their answers to all the questions in only one and the same language in any particular paper. Candidates may use the Devanagari or Bengali Script in the answer papers on Sanskrit, the Devanagari Script in the answer papers on Hindi or Nepali, and the Bengali, Arabic, Persian, Urdu in the answer papers on Bengali, Arabic, Persian and Urdu
respectively.Questions for Santali Paper will be set in Olchiki script and answers should also be written in Olchiki.
6. A summary of the group-wise papers in the Main Examination :
Group ‘A’ & ‘B’ Services & Posts : All 6 compulsory papers and one optional subject consisting of two papers.
Group ‘C’ & ‘D’ Services & Posts : All 6 compulsory papers.
7. Personality Test : A number of candidates selected in order of merit on the results of the Main Examination for all the services and posts included in Groups A, B, C and D shall have to appear at a Personality Test. Each candidate will be asked questions on matters of general interest. The object of the test will be to assess the candidate’s personal qualities e.g., alertness of mind, power of clear and logical exposition, intellectual and moral integrity, leadership and also the candidate’s range of interests.
Candidates for Group ‘B’ Service (West Bengal Police Service) will be specially tested at the interviews with regard to their suitability for the service.
Marks for the Personality Test
(i) Group ‘A’ & ‘B’ 200 Marks
(ii) Group ‘C’ 150 Marks
(iii) Group ‘D’ 100 Marks
Note : No separate Personality Test will be held for different groups viz. Group-‘A’, Group-‘B’, Group-‘C’ and Group-‘D’ in respect of a candidate. Marks will be awarded according to different services against allotted full marks for Personality Test. In all the answer papers under examination due credit will be given for proper economy of words combined with clarity,
precision and effectiveness of expression and originality of approach.
8. Deduction of marks : A deduction of 10% of full marks may be made from the total marks secured by a candidate in a particular paper if he / she discloses his / her identity by writing his / her name, roll number or by putting any identifying marks in
the answer script of that paper. There shall be negative marking for each wrong answer to multiple-choice questions (MCQ) type.
9. Discretion of the Commission : The Commission has discretion to fix qualifying marks in any or all the papers/subjects and in the aggregate.
If a candidate fails to secure qualifying marks in any paper / subject, the marks in that paper / subject will not be considered in calculating his / her aggregate.
Abstract Table of Papers / Subjects and Marks Main Examination and Personality Test
Detailed Syllabus:
SCHEME AND SYLLABUS
The scheme and syllabus of the examination shall be as detailed in the Schedule below :-
- Scheme of the Preliminary Examination : The Preliminary Examination will consist of only one paper, viz., a paper on “General Studies”. The paper will be of an objective type consisting of 200 multiple-choice questions. The paper will carry 200 marks and will be of 2½ hours duration. The standard of the paper will be of the level of knowledge as expected of a graduate of any faculty of a recognized The paper will include questions covering the following fields of knowledge:
| (i) | English Composition | 25 Marks |
| (ii) | General Science | 25 Marks |
| (iii) | Current events of National & International Importance | 25 Marks |
| (iv) | History of India | 25 Marks |
| (v) | Geography of India with special reference to West Bengal | 25 Marks |
| (vi) | Indian Polity and Economy | 25 Marks |
| (vii) | Indian National Movement | 25 Marks |
| (viii) | General Mental Ability | 25 Marks |
An outline of the syllabi is given in Appendix – I
The Preliminary Examination is meant to serve as a Screening Test only for the purpose of selection of candidates for the Main Examination. The marks obtained in this examination by the candidates will not be considered for final selection. Only those candidates who will be declared qualified at the Preliminary Examination in a year shall be eligible for admission to the W.B.C.S. (Exe.) etc.(Main) Examination of that year.
Final Merit List will be prepared on the basis of marks obtained in Main Examination and Personality Test taken together.
Scheme of the Main Examination : The Main Examination shall consist of six Compulsory papers and one optional subject consisting of two papers (Only for candidates applying for group A and / or B) to be chosen by the candidates from the list of optional subjects given below. There will be two papers of the optional subject of 200 marks each. Each paper, Compulsory or Optional, will carry 200 marks and will be of 3 hours
Out of six compulsory papers four papers i.e. (i) General Studies- I, (ii) General Studies- II, (iii) The Constitution of India and Indian Economy including role and functions of Reserve Bank of India and (iv) Arithmetic and Test of Reasoning will be of MCQ Type to be answered in OMR answer sheets and remaining two compulsory papers i.e. Paper – I and Paper – II will be of conventional type written examination.
Compulsory Papers : Six compulsory papers are as follows:-
Paper I : Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali – Letter writing (within 150 words) / Drafting of Report (within 200 words), Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from English to Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali
Paper II : English – Letter writing (within 150 words) / Drafting of Report (within 200 words), Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali to English
Paper III : General Studies-I : (i) Indian History with special emphasis on National Movement and (ii) Geography of India with special reference to West Bengal.
Paper IV : General Studies-II : Science and Scientific & Technological advancement, Environment, General Knowledge and Current Affairs.
Paper V : The Constitution of India and Indian Economy including role and functions of the Reserve Bank of India.
Paper VI : Arithmetic and Test of Reasoning.
- List of Optional Subjects : (Vide restriction on choice in Item No.-4 below and syllabi in Appendix-I)
Subject Code
Comparative Literature 11
Agriculture 12
Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science 13
Anthropology 14
Botany 15
Chemistry 16
Civil Engineering 17
Commerce and Accountancy 18
Computer Science 19
Economics 20
Electrical Engineering 21
Geography 22
Geology 23
History 24
Law 25
Mathematics 26
Management 27
Mechanical Engineering 28
Medical Science 29
Philosophy 30
Physiology 31
Physics 32
Political Science 33
Psychology 34
Sociology 35
Statistics 36
Zoology 37
- The standard of Arithmetic part of Compulsory Paper – VI(Arithmetic & Test of Reasoning) will be similar to that of the Compulsory Mathematics paper at the Madhyamik Examination of the Board of Secondary Education, West Bengal. Test of Reasoning will cover Analytical Reasoning:Data Sufficiency, Logical Reasoning : (i) Logical Deduction (ii) Forcefulness of the Arguments(iii) Implication of sentences (iv) Inferring from diagrams, Series: (i) Letter series, (ii) Number series, Inferring from Data, Analogy tests, Symbol Interpretation, Mathematical puzzles, Odd man out, Perception test, Non-verbal reasoning & Selecting the correct
The standard of other compulsory papers will be of the level of learning expected from a graduate of any faculty of a recognized University.
The two papers of the optional subjects will be of conventional type and the standard of the examination will be approximately that of an Honours Degree Examination as prescribed by the recognized Indian Universities except Law, Medical Science and Engineering subjects which will be that specified for the LLB, MBBS and BE or equivalent courses respectively recognized by Indian Universities / Institutions.
The Topic ‘Environment’ in paper General Studies II will include the following:-
Bio diversity and Coastal Regulation Zone, Global Warming, Industrial and Environmental Pollution, Ozone Layer and related issues.
The Topic ‘Indian Economy including role and functions of the Reserve Bank of India’ of the compulsory paper- V will consist of the following:-
Central State relation and devolution of central funds to state, Planning process and objectives of five years plan, Functions of RBI and Monetary policy, Central Finance Commission & State Finance Commission and Fiscal Policy of Government of India.
- Answers in all the papers, Compulsory and Optional, except the language papers may be written either in English or in Bengali (unless otherwise directed in these rules or in the question papers). Answers in the following optional papers may also be written in Nepali:
Optional : (1) Political Science
(2) Botany
Note : Candidates shall write their answers to all the questions in only one and the same language in any particular paper.
Candidates may use the Devanagari or Bengali Script in the answer papers on Sanskrit, the Devanagari Script in the answer papers on Hindi or Nepali, and the Bengali, Arabic, Persian, Urdu in the answer papers on Bengali, Arabic, Persian and Urdu respectively.Questions for Santali Paper will be set in Olchiki script and answers should also be written in Olchiki.
- A summary of the group-wise papers in the Main Examination :
Group ‘A’ & ‘B’ Services & Posts : All 6 compulsory papers and one optional subject consisting of two papers. Group ‘C’ & ‘D’ Services & Posts : All 6 compulsory papers.
- Personality Test : A number of candidates selected in order of merit on the results of the Main Examination for all the services and posts included in Groups A, B, C and D shall have to appear at a Personality Test. Each candidate will be asked questions on matters of general interest. The object of the test will be to assess the candidate’s personal qualities e.g., alertness of mind, power of clear and logical exposition, intellectual and moral integrity, leadership and also the candidate’s range of
Candidates for Group ‘B’ Service (West Bengal Police Service) will be specially tested at the interviews with regard to their suitability for the service.
Marks for the Personality Test
Group ‘A’ & ‘B’ 200 Marks
- Group ‘C’ 150 Marks
- Group ‘D’ 100 Marks
Note : No separate Personality Test will be held for different groups viz. Group-‘A’, Group-‘B’, Group-‘C’ and Group-‘D’ in respect of a candidate. Marks will be awarded according to different services against allotted full marks for Personality Test.
In all the answer papers under examination due credit will be given for proper economy of words combined with clarity, precision and effectiveness of expression and originality of approach.
- Deduction of marks : A deduction of 10% of full marks shall be made from the total marks secured by a candidate in a particular paper if he/she discloses his/her identity by writing his/her name, roll number or by putting any identifying marks in the answer script of that
There shall be negative marking for each wrong answer to multiple-choice questions (MCQ) type.
- Discretion of the Commission : The Commission has discretion to fix qualifying marks in any or all the papers/subjects and in the
If a candidate fails to secure qualifying marks in any paper / subject, the marks in that paper / subject will not be considered in calculating his / her aggregate.
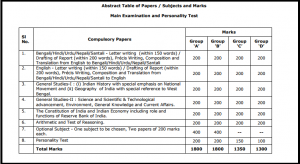
Abstract Table of Papers / Subjects and Marks Main Examination and Personality Test
|
Sl No. |
Compulsory Papers |
Marks | |||
| Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ | Group ‘C’ | Group ‘D’ | ||
| 1. | Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali – Letter writing (within 150 words) /
Drafting of Report (within 200 words), Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from English to Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| 2. | English – Letter writing (within 150 words) / Drafting of Report (within 200 words), Précis Writing, Composition and Translation from Bengali/Hindi/Urdu/Nepali/Santali to English |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| 3. | General Studies-I : (i) Indian History with special emphasis on National Movement and (ii) Geography of India with special reference to West Bengal. |
200 |
200 |
200 |
200 |
| 4. | General Studies-II : Science and Scientific & Technological advancement, Environment, General Knowledge and Current Affairs. | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 5. | The Constitution of India and Indian Economy including role and functions of Reserve Bank of India. | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 6. | Arithmetic and Test of Reasoning. | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 7. | Optional Subject – One subject to be chosen, Two papers of 200 marks each. | 400 | 400 | — | — |
| 8. | Personality Test | 200 | 200 | 150 | 100 |
| Total Marks | 1800 | 1800 | 1350 | 1300 | |
APPENDIX – I
THE SYLLABI MENTIONED BELOW ARE INDICATIVE ONLY. CANDIDATES SHOULD BE PREPARED TO ANSWER ANY QUESTION FROM ESSENTIAL QUALIFICATION/DEGREE MENTIONED IN THE ADVERTISEMENT FOR THE RELEVANT POST.
SYLLABI FOR PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION
Questions on English Composition will cover Synonyms, Antonyms, Idioms and Phrases, Vocabulary test, Phrasal Verbs, the same words bearing more than one meaning, use of appropriate and qualifying words etc. Questions on General Science will cover general appreciation and understanding of science, including matters of everyday observation and experience as may be expected of a well-educated person who has not made a special study of any scientific discipline. In History, emphasis will be on broad general understanding of the subject in its social, economic and political aspects. Questions on the Geography of India will relate to Physical, Social and Economic Geography of the country, including the main features of Indian Agricultural and Natural Resources with special reference to West Bengal. Questions of Indian Polity and Economy will test the knowledge of the country’s Political System, Panchayatee Raj, Community Development and Planning in India, Questions on the Indian National Movement will relate to the nature and character of the Nineteenth Century Resurgence, Growth of Nationalism and Attainment of Independence. General Mental Ability will relate to Logical perception, understanding and natural conclusion.
SYLLABI FOR OPTIONAL PAPERS OF MAIN EXAMINATION
| BENGALI : | |
| Paper – I : | Section-A
1) Topics from the History of Bangla Language. a) The chronological track from Proto Indo-European to Bangla (Family tree with branches and approximate dates). b) Historical stages of Bangla (Old, Middle, New) and their linguistic features. c) Dialects of Bangla and their distinguishing characteristics. d) Elements of Bangla Vocabulary. e) Forms of Bangla Literary Prose-Sadhu and Chalit.
2) Process of Phonetic Changes in Bangla Language. Apinihiti (Anaptyxis), Abhishruti (Umlaut), Samibhavan (Assimilation), Svarabhakti / Viprakarsha, Svarasangati (Vowel harmony).
3) Problems of standardization and reform of alphabet and spelling and those of transliteration and Romanization.
Section-B 4) History of Bangla Literature. a) Periodization of Bangla Literature: Old Bangla and Middle Bangla. b) Roots and reasons behind the emergence of modernity in Bangla Literature. c) Evolution of various Middle Bangla forms: Mangal kavyas, Vaishnava lyrics, Adapted narratives (Ramayana, Mahabharata, Bhagavata) and religious biographies. d) Narrative and lyric trends in the nineteenth century Bangla poetry. e) Development of prose. f) Bangla dramatic literature (nineteenth century, Tagore, Post-1944 Bangla drama).
5) Tagore and Post Tagoreans (upto the decade of fifties).
6) Fiction, major authors: Bankimchandra, Tagore, Saratchandra, Bibhutibhusan, Tarasankar, Manik.
7) Women and Bangla Literature. a) Swarna Kumari Devi, b) Ashapurna Devi, c) Mahasweta Devi, d) Rajlakshmi Devi, e) Kabita Singha, f) Nabanita Deb Sen |
| Paper – II : | Section – A
1) Vaishnava Padavali (Calcutta University Publication). Phases (Parjayas): Gourchandrika, Purvaraga, Abhisar, Mathur, Prarthona.
2) Chandimangal: Kalketu episode by Mukunda (Sahitya Akademi).
3) Meghnadbadh Kavya by Michael Madhusudan Dutta – 1st, 2nd and 3rd cantos.
4) Rajani by Bankimchandra Chattopadhyay.
5) Kapalkundala by Bankimchandra Chattopadhyay.
6) Samya and Bangadesher Krishak by Bankimchandra Chattopadhyay.
7) Punascha by Rabindranath Tagore.
8) Bichitra Prabandha by Rabindranath Tagore.
9) Chacha Kahini by Sayed Muztaba Ali.
Section-B
10) Chandragupta by Dwijendralal Roy.
11) Grihadaha by Saratchandra Chattopadhyay.
12)Adhunik Bangla Kabita Selected Poems: i) Saswati by Sudhindranath Dutta ii) Rabindranath by Achintya Kumar Sengupta iii) Aami Kabi Jata Kamarer by Premendra Mitra iv) Bandir Bandana by Buddhadeb Basu v) Amar Koifiat by Kazi Nazrul Islam |
|
13) Prabandha Samgraha by Pramatha Choudhuri: Selected Essays: Bharatchandra, Birbal, Boipara
14) Pather Panchali by Bibhutibhusan Bandyopadhyay
15) a) Ekaler Galpo Sanchayan – Vol.- 1 & 2 (Calcutta University Publication). b) Selected Stories: i) Payomukham by Jagadish Gupta ii) Haraner Natjamai by Manik Bandyopadhyay iii) Fossil by Subodh Ghosh iv) Tope by Narayan Gangyopadhyay v) Adab by Samaresh Bose vi) Aswamedher Ghora by Dipendranath Bandyopadhyay
16) Shrestha Kavita by Jibanananda Das.
17) Jagori by Satinath Bhaduri.
18) Ebam Indrajit by Badal Sircar. |
|
| HINDI : | |
| Paper – I : | SECTION-A
1. Hindi Linguistic and Grammatical References i. Definition of Language ii. Difference between learning and parole iii. Elements of Communication of Language iv. Different aspects of Language v. Units of language – Phonemes, Morphemes, Syntax, Discourse, Sementics.
2. History of Hindi language and Nagari Lipi i. History of Development of Hindi language (Short study) ii. Development of Khari Boli Hindi as literary language and Lingua Franka (Special context to Indian Freedom struggle and post Independent India) iii. Area of Hindi Language iv. Prominent Hindi dialects and inter relationship between the dialects v. Grammatical structure of standard Hindi vi. Scientific features of Nagari lipi vii. Development of Hindi as a global language in the modern context
SECTION-B
History of Hindi Literature: 1. Tradition of writing History of Hindi Literature 2. Literary trends of following four periods of Hindi Literature: a) Adikala b) Madhya Kala : i) Purva Madhyakala (Bhakti kala) (ii) Uttar Madhyakala (Riti Kala) c) Adhunika Kala
A. ADIKALA- Prominent Poets and their works: i) Sarhapa and Goraknath ii) Chand Vardai and Narapati Nalha iii) Svambhu iv) Abdur Rahman and Amir Khusro
B. PURVA MADHYAKALA (Bhakti kala) – Prominent Poets and their works: i. Sant Kavyadhara – Kabir and Sahjo Bai ii. Sufi Kavyadhara – Jayasi iii. Krish Kavyadhara – Surdas and Meerabai iv. Ram Kavyadhara -. Tulsidas
C. UTTARMADHYAKALA (Ritikala) – Prominent Poets and their works : i. Ritibadh – Keshavdas ii. Ritisiddha – Bihari iii. Ritimukta -Ghananda
D. ADHUNIK KALA 1. Trends of Navajagran (Renaissance) 2. Development of Hindi Prose and contribution of Bhartendu Mondal |
| 3. Contribution of Mahavir Prasad Divedi towards the development of Hindi Prose
4. Prominent trend of Modern Hindi Poetry- Chahayavad, Pragtivad, Prayogvad, Nai Kavita, Samakalin Kavita and Ghazal, Sanavadi Kavita 5. Prominent Poets – Maithili Sharan Gupta, Prasad, Nirala, Mahadevi, Dinkar, Agyeya, Muktibodh, Nagarjun, Dushyant Kumar.
KATH SAHITYA i) Development of Hindi Novels and short stories ii) Prominent writers-Premchand, Jainendra, Prasad, Renu, Bhishma Sahani, Yaspal, Chitra Mudgal, Mohan Rakesh and Krishna Sobti
DRAMA AND THEATRE 1. Development of Hindi Drama and Stage 2. Prominent Dramatists-Bhartendu, Prasad, Mohan Rakesh, Lakshmi Narayan Lal 3. The development of Hindi Theatre
CRITICISM 1. Development of Hindi Criticism 2. Prominent Critics -Ramchandra Shukla, Hazari Prasad Divedi, Ram Vilas Sharma |
|
| Paper – II : | (Textual studies of the prescribed text. This paper will test the critical and analytical aptitude of the candidates)
SECTION-A 1. Kabir – Kabir Vani, ed. by Parasnath Tiwari, first 25 padas 2. Surdas – Bhramar Gitsar, ed. Ramchandra Sukla, first 25 padas 3. Tulsidas-Vinay Patrika-Geeta Press, first 15 padas 4. Bihari -Ritikavya Sanghra ed. Jagadish Gupta, first 25 dohas 5. Prasad -Kamayani (Shraddha and Ira Sarga) 6. Nirala -Saroj Smriti, Jago Phir Ek Bar 7. Mahadevi Varma – Mai Neer Bhari Dukh ki Badli, Ravindra ke Mahaprasthan Par 8. Agyeya-Asadhya Vina, Hamne Poudhey se kaha 9. Nagarjun-Bahut Dino Ke Bad and Pret ka Byan. 10. Dhumil-Mochiram, Roti Aur Sansad 11. Sarveshvar Dayal Saxsena -Tumhare Sath Rah Kar, Soundryabodh 12. Muktibodh – Mai Dur Hun, Bhool Galati
SECTION-B 1. Bharatendu – Andher Nagri 2. Mohan Rakesh – Ashad Ka Ek Din 3. Ramchandra Shukla-Shraddha Aur Bhakti, Krodha 4. Premchand-Godan (Novel), Paush ki Raat, Badey Ghar ki Beti, Ahuti, Mukti Marg, Idgah (Stories) 5. Prasad – Dhruswamini 6. Phanishwar Nath Renu – Tisari Kasam, Panchlight, Rasapriya(Stories) 7. Manu Bhandari – Mahabhoj 8. Bhairv Prasad Gupta-Ganga Maiyya 9. Harishankar Parasai – Matadin Chand Par, Viklanga Shraddha ka Dor 10. Hazari Prasad Divedi-Vasant A Gaya, Devdar |
| SANSKRIT : | |
| Paper – I : | (a) Sanskrit Linguistics:-.
(i) Indo European family of languages (ii) Phonetic Laws-Grimm’s Law, Verner’s Law, Grassmann’s Law, Collitz’s Law (iii) Phonetic Tendencies (iv) Development of Sanskrit- Vedic and Classical Sanskrit, Non-Aryan Influence in Sanskrit, Contribution of Sanskrit in Linguistic Studies
(b) Sanskrit Grammar- Siddhanta Kaumudi-Karaka and Samasa
(c) Translation from Vedic texts into English:- Agnisukta-1.1 Indrasukta-2.12 Suryasukta-1.115 Aksasukta-10.34 Hiranyagarbha Sukta-10.121 Devisukta-10.125
(d) (i) Translation from Sanskrit into English Or (ii) Translation from English into Sanskrit |
| (e) Paragraph in Sanskrit | |
| Paper – II : | (a) History of Vedic and Classical Sanskrit Literature:-
(i) Vedic- Samhita, Brahmana, Aranyaka, Upanisad, Vedanga (ii) Classical- Ramayana, Mahabharata, Asvaghosa, Bhasa, Kalidasa, Sudraka, Visakhadatta, Bhavabhuti, Bharavi, Bhotti, Magha, Dandi, Banabhatta. (iii) Philosophical – Fundamental ideas of orthodox systems of Indian Philosophy (iv) Technical – Chandas, Arthasastra, Architecture, Medicine, Mathematics
(b) Texts (Meant for general acquaintance and not for minute study) (i) Kalidasa’s Abhijnanasakuntalam and Bhavabhuti’s Uttararamacaritam (ii) Kalidasa’s Kumarasambhavam (Canto I – V ) and Bharavi’s Kiratarjuniyam (Canto I – V ) (iii) Manusamhita (Ch. VII Sl. I-144) (iv) Isavasyopanisad |
| ENGLISH : | |
| Paper – I : | In Section A, candidates will have to write an essay. Texts for detailed study in Sections B and C are given below.
SECTION-A : An essay on a literary topic
SECTION-B 1. William Shakespeare- -Macbeth -As You Like It 2. Christopher Marlowe – Edward II 3. John Donne- – ‘Canonization’; -‘ Death be not proud’; -‘The Good Morrow’ 4. Andrew Marvell-‘To His Coy Mistress’; -‘The Garden’ 5. John Milton-‘Lycidas’; -Paradise Lost, Book I 6. Alexander Pope – The Rape of the Lock 7. William Wordsworth- -‘Ode on Intimations of Immortality’; -‘Tintern Abbey’ 8. Samuel Taylor Coleridge -‘Kubla Khan’; -‘Dejection: an Ode’ 9. Percy Bysshe Shelley- – ‘Ode to the Westwind’ ; -‘ Ozymandias’ 10. John Keats- -‘Ode to a Nightingale’ -‘Ode on a Grecian Urn’ 11. Alfred Tennyson-‘Ulysses’; -‘The Lotus Eaters’; -‘Tithonus’ 12. Robert Browning-‘The Last Ride Together’ 13. Elizabeth Barrett Browning-‘ How do I love thee!’
SECTION-C 1. Jane Austen- Pride and Prejudice 2. Charles Dickens-Great Expectations 3. Thomas Hardy-The Mayor of Caster bridge 4. Mark Twain-The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn 5. Emily Bronte-Wuthering Heights 6. Mary Shelley-Frankenstein |
| Paper – II : | In Section A, candidates will have to respond critically to an Unseen Passage. Texts for detailed study in Sections B and C are given below.
SECTION-A Critical analysis/response to an unseen passage in prose/verse
SECTION-B 1. W. B. Yeats-‘Easter 1916’; -‘Sailing to Byzantium’; -‘Leda and the Swan’ 2. T. S. Eliot- -‘The Love Song of J. Alfred Prufrock’; -‘The Journey of the Magi’; -‘Burnt Norton’ 3. W.H. Auden- -‘In Memory ofW.B.Yeats’; -‘Lay your sleeping head, my love’; -‘The Shield of Achilles’ 4. John Osborne-Look Back in Anger 5. Samuel Beckett-Waiting for Godot 6. Sylvia Plath – -‘Mirror’; – ‘Nick and the Candlestick’ 7. Henry Louis Vivian Derozio-‘To India My Native Land’; -‘My Country’ |
| 8. Kamala Das -‘ An Introduction’
SECTION-C 1. D.H. Lawrence-The Rainbow 2. Raja Rao-Kanthapura 3. Amitava Ghosh-The Shadow Lines 4. Chinua Achebe-Things Fall Apart 5. James Joyce -A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man 6. Rabindranath Tagore – ‘Crisis in Civilization’ 7. Virginia Woolf – ‘A Room of One’s Own’ |
|
| PALI : | |
| Paper – I : | Candidates shall have to answer five questions taking atleast one question from each group. Answer to questions on Group-B, Group-D and Unit 3 of Group-C must be written in Pali language either in Bengali or in Roman script. The remaining questions must be attempted in Pali or in Bengali or in English but in only any one of these languages.
A) PALI LINGUISTICS : Unit 1 – Concepts of Linguistics, Languages and Phonetic Laws. Unit 2 – Concept of Homeland of Pali, Features of Pali, Pali as M.I.A., Pali & Sanskrit, Pali & Prakrits. Unit 3 – Short notes on Phonetic Tendencies.
B) PALI GRAMMAR : Unit 1 – Sandhi, Samasa, Itthipaccaya. Unit 2 – Karaka Vibhakti, Paccaya-Kita & Taddhita. Unit 3 – Conjugation, Declension, Make Sentences.
C) TRANSLATIONS : Unit 1 – Pali to English (unseen passages from poetry) with grammatical notes on any two words. Unit 2 – Pali to English (unseen passages from prose) with grammatical notes on any two words. Unit 3 – English to Pali.
D) ESSAY IN PALI consisting of 200 words on any one of the following topics: Gotama Buddha, Tipiţaka, Dhamma – Vinaya, Sammāsambuddha, Paccekabuddha, Bodhisatta, Majjhima paţipadā, Ariyaaţţhangikamagga, Cattāriariyasaccāni, Dukkha, Paţiccasamuppāda, Nibbāna, Dukkhanirodhagāminīpaţipadā, Tilakkhana, Anicca, Anattā, Kammavāda. |
| Paper – II : | Candidates shall have to answer any three questions from Section -A and any two from Section-B. Answers of questions belonging to Section-B must be answered in Pali language in Bengali or in Roman script. The remaining three questions must be attempted in any one of the following three languages – Pali, Bengali, English.
SECTION – A
A) History of Canonical Literature : Vinayapitaka, Suttapitaka & Abhidhammapitaka.
B) Non-Canonical Literature : Extra-Canonical (Anupitaka), Commentaries (Atthakathas), Vamsa Literature.
C) History of Early Buddhism : Pre-Buddhist India, Life of Buddha, Royal Patronage, Origin of Samgha.
D) Development of Buddhism : Buddhist Councils (1st, 2nd, 3rd & 4th); Buddhist Schools and Sects; Spread and Decline of Buddhism.
SECTION – B
E) CRITICAL STUDY OF SELECTED PALI TEXTS UNIT-I POETRY TEXTS DHAMMAPADA – Yamakavagga, Appamadavagga, Cittavagga, Maggavagga, Buddhavagga SUTTANIPATA – Pabbajja Sutta, Padhana Sutta, Karaniya Mettasutta, Khaggavisanasutta, Parayanavagga – Vatthugatha.
THERAGATHA – Kaccayana, Talaputa, Silava |
|
THERIGATHA – Ambapali, Subha Jivakambabanika, Kisagotami UNIT-II PROSE TEXTS
Dhammacakkapavattana Sutta, Mahaparinibbana Sutta, Ariyapariyesana Sutta, Singalovada Sutta, Kutadanta Suttanta. How women were admitted to the Sangha, Milindapanha-Bahirakatha, Marriage of Visakha, Annihilation of the Sakiyas, Sibi Jataka, Dasaratha Jataka
Explanation of Pali quotations from the prescribed texts in Pali language. Ref.: www.vipassanaresearchinstitute.com for Pali texts
Ref.: B.A. Pali Selection, Prose & Poetry, Calcutta University Publication B.A. Pali (Hon.) Selection, Calcutta University Publication M.A. Pali Selection, Prose & Poetry, Calcutta University Publication F) CRITICAL STUDY OF CHANDA AND ALAMKARA (Answers to be written in Pali language) UNIT-I – VUTTODAYA _ – Samavutta Chanda UNIT-II – SUBODHALANKARA – Yamaka, Upama, Rupaka, Vyatireka, |
|
| ARABIC : | |
| Paper – I : | (a) Arabic linguistics; (b) Arabic grammar; (c) Translation from Arabic into English; (d) Translation from English into Arabic; (e) Arabic rhetoric and prosody. |
| Paper – II : | (a) History of Arabic literature; (b) Texts (meant for general acquaintance and not for minute study) : (1) Diwan-Ibn-ul-Fariz; (2) Sab’a Mu’allaqa; (3) Sirat-Ibn-i-Hisham; (4) Muqaddama-Ibn-i-Khaldun. |
| PERSIAN : | |
| Paper – I : | (a) Persian linguistics (Persian and Indo-European family of languages; Aryan or Indo_Iranian branch, evolution of Persian language, Old Persian, Avestan language, Middle Persian or Pahlavi, Modern Persian, Iranian dialects, Persian influence on Indian languages); (b) Persian grammar; (c) Translation from Persian into English; (d) Translation from English into Persian; (e) Persian rhetoric and prosody. |
| Paper – II : | (a) History of Persian literature (Origin of Persian poetry, Early poets, Development of poetic forms- qasida, ghazal, masnavi,, etc. Growth of poetic themes or trendsepic, romantic, mystical, philosophical, ethical, etc. Survey of prose-works-historical, mystical, ethical, biographical, etc. Literary progress in different periods of Iranian history. Contributions of eminent poets and writers. Modern poetry, Modern prose, Indo-Persian literature); (b) Texts (meant for general acquaintance and not for minute study) : (1) Shahnama of Firdausi; (2) Chahar Maqala of Nizami Aruzi; (3) Qasaid-i-
Khaqani; (4) Diwan-i-Hafiz; (5) Masnavi of Jalaluddin Rumi; (6) Naldaman of Fayzi. |
| FRENCH : | |
| Paper – I : | Translation from French into English, Translation from English into French, French Grammar. |
| Paper – II : | History of French Literature, Texts, Texts (meant for general acquaintance and not for minute study) :
(1) Prose-Ronsard : Deveres choisies (Classique Larosusse) – 2 volumes, Pierre Loti; La roman d’um enfant; (2) Poetry-Ronsard : Poesies choisies (Classique Larosusse)-2 volumes. Musset : Poesies nouvelles. Drama-Moliers : L’Avare, Corneilles : La Cid. |
| URDU : | |
| Paper – I : | (Answer must be written in Urdu)
Section – A
1. Development of Urdu Language :- a) Development of Indo-Aryan i) Old Indo-Aryan ii) Middle Indo Aryan iii)New Indo Aryan
b) Western Hindi and its dialects :- i) Brij Bhasha, Maghrabi Hindi Aur Uski Mukhtalif Boliyan & Haryanvi ii) Theories about the origin of Urdu Language
c) Daccani Urdu origin and Development, its significant linguistic feature. |
| d) Fort William College and its contribution to Urdu Literature.
Section – B
1. Genres and their development :-
A. Poetry :- i. Ghazal, Qasida, Masnavi, Marsia, Nazm and Rubai.
a) Ghazal :- i) Wali :- Intekhab-e-wali compiled by Nurul HasanHashmi – (First five Ghazals)
ii) Mir :- Intekhab-e-Mir compiled by Maulvi Abdul Haq – ( First five Ghazals)
iii) Ghalib :- Diwane-Ghalib ( First five Ghazals)
Faiz Ahmed Faiz :- Naqsh-e-Faryadi, (first five Ghazals) Nasir Kazmi :- Barg-e-Ne ( first five Ghazals) Shaharyar :- Hijr ke Mausam ( First five Ghazals)
Qasida : Dar Tazhik-e-Rozgar – Sauda. Masnavi : Sahrul Bayan – Mir Hasan Marsia; i) Jab Badban-e-Kashti Shahe Umam Gira – Mir Anis ii) Kis Sher ki Amad hai Ke Run Kanp Raha hai – Mirza Dabir Nazm; Banjara Nama – Nazir Akbarabadi Masjide Qartaba – Iqbal
Tanhai – Faiz Ahmed Faiz
Ek Ladka – Akhtarul Iman Taslise Hayat – Pervez Shahedi
Rubai; i. Khenche Huwe Sar Ko Kahan jata hai – Mir Anis
ii.Ek Fitna hai Naqeson Mein Kamil hona – Josh Malihabadi iii.Aa Ae Mani-e-Kayenat Mujh Mein Aaja – Firaq Gorakhpuri 2. Significant features of :-
a) i) Lucknow School
ii) Delhi School
b) i) Sir Sayed Movement
ii) Progressive Movement
iii) Modernism |
|
| Paper – II : | Answer must be written in Urdu
(This paper will require first hand reading of the texts prescribed and will be designed to test the candidates critical ability)
Section – A
1. Bagho Bahar Mir Aman Dehalvi 2. Abe Hayat (Dibacha) Md. Hussain Azad 3. Ood-e-Hindi Asadullah Khan Ghalib 4. Ghubar-e- Khatir Maulana abul Kalam Azad 5. Godan Munshi Prem Chand 6. Lajwanti Rajindra Singh Bedi 7. Toba Tek Singh Sa’adat Hassan Manto 8. Maqualate sir syed (Ta’asub, Sir Syed Ahmed Khan Tahzib, Rasm-o-Rewaj ki Pabandi Ke Nuqsanat, Khushamad) 9. Ganjhaye Giramaya Rasheed Ahmed Siddiqui (Maulana Md. Ali Johar, Mukhtar Ahmed Ansari, Md. Aqbal, Ayub Abbasi, |
| Asghar Gondavi)
10. Safaid Khoon Agha Hashr Kashmiri Section – B Literary criticism and its development with reference to :- i. Muqaddama sher-o-shaeri – Altaf Hussain Hali ii. Tanquidi Nazaryat – Ehtasham Hussain iii. Urdu Tanquid Per Ek Nazar – Kalimuddin Ahmed iv. Adab aur zindagi – Majnu Gorakhpuri v. Tanquidi Afkar – Shamsur Rahman Farooqui
Section – C
Essay writing (Compulsory, covering literary and imaginative topics). |
|
| SANTALI : | |
| Paper – I : | Question Papers are to be set in ‘OLCHIKI’ script and Answers should also be given in ‘OLCHIKI’ script.
Section – A
1. Topic from the History of Santali Language:
a) The chronological track from Austro-Asiatic-Austric to Santali (Family tree with branches and approximate dates);
b) Historical stages of Santali (Old, Middle and New) and their Linguistic features with Santali grammar (Ranor);
c) Santali languages and its Dialects and their distinguishing characteristic;
d) Elements of Santali Vocabulary;
e) Forms of Santali literary prose (Relevant with personal relations);
2. Process of Phonetic changes in Santali languages and necessity of ‘OLCHIKI’ script.
3. Problems of standardization and reform of alphabet and spelling and those of transliteration and inevitability of ‘OLCHIKI’ Script. Ill effects of use of other script in writing Santali excepting ‘OLCHIKI’ script.
Section – B
4. History of Santali literature:
a) Periodization of Santali literature: Old and Middle Santali literature;
b) Roots and reasons behind the emergence of modernity in Santali literature;
c) Evolution of Santali oral literatures like ‘Binti’, ‘Bankher’, ‘Thuti’, Serwa Sereng (Traditional songs) and the ‘Jamsimbinti’- the scripture of SARIDHARAM religion;
d) Narrative and lyric trends in the nineteenth century Santali poetry;
e) Development of Santali prose;
f) Santali dramatic literature (Nineteenth century, Pandit Raghunath Murmu, Sadhuram Chand Murmu and Post 1946 Santali drama);
5. Majhi Ramdas Tudu (Reska), Sadhuram Chand Murmu and Pandit Raghunath Murmu (Upto 1950). 6. Fiction – Major Authors : Majhi Ramdas Tudu (Reska), Sadhuram Chand Murmu, Pandit Raghunath Murmu, Paul Jujar Saren, Narayan Saren (Toresutam), Sarada Prasad Kisku (Totko Malang), Nayke Mongal Chandra Saren, Domon Sahu Samir. |
| Paper – II : | Question Papers are to be set in ‘OLCHIKI’ script and Answers should also be given in ‘OLCHIKI’ script.
Section – A
1. SADHURAM CHAND ANOLMALA (A total collection of Sadhuram Chand Murmu) – April, 1997, Department of Information & Cultural Affairs, Govt. of West Bengal:
i) Marang Buru Dharam Sari Page – 19 ii) Ana terang horko Dusao Kana Page – 11 iii) Deban tengon adibasi bir Page – 61
(All from ol daha anarhe) |
|
iv) Bhorom nasao Page – 85 v) Jati Milan Page – 93 vi) Kolkata renah bharak Page – 155 vii) Bah julung Page – 151
(All from ‘Aldaha anarhe’)
viii) Jamsimbinti Page – 204 ix) Dharti Dhasao Page – 208 x) Manmi Reah Bad Borket Page – 283 – 304 (Jat hating)
(All from Lita Godet)
2. (HORKOREN MARE HAPRAM KOREYAH KATHA) Rev. L. O. Skrefsud:
i) AAD KHON MANOA REAH BIBORAN – Page – 1-19
ii) DHARAM AAR SERWOA – Page – 203-249
3. Kherwal Bansha Dharam Puthi – Rajhi Ramdas Tudu (Reska) Karmu ar kharmu reyah – Karambinti Galmarao – Page – 68-102 4. Sansar Phend – A Drama by Sadhuram Chand Murmu
5. Bidu Chandan – A Drama by Pandit Raghunath Murmu
6. Sidu Kanu Santal Hool – A Drama by Pandit Raghunath Murmu
7. The Jamsim Binti By Nayke Mongal Ch. Saren
Section – B
8. Pandit Raghunath Murmu (Biography) By Ramchanda Murmu
9. Santal Folk Tales (Collected) Vol-I By P. O. Bodding
10. a) SAOHEND MOHANK – A collection of selected Essays By Subodh Hansda and Debdulal Murmu
b) AYO AARANG TE OLOH – Pandit Raghunath Murmu
c) SANTARI PARSI AARSAOHET – Sarada Prasad Kisku
d) SANTARI TULAJAKHA SAOHET – Gomosta Prasad Saren
11. a) SAI SERMA RENAH ANORHE – A collection of Santali Poems of 100 year with Bengali Translation
b) NIDA YUNTA – Sarada Prasad Kisku
c) DHARAM GE SARIYA – Mondal Hembram
d) MAYAJAL – Narayan Saren (Tore Sutaru)
12. MIT GEL HOR KAHNI SALAH MIT SAI MIT KAHNI – A collection of Ten Santali Folk Tales and 101 short stories.
13. ‘Paschimbangla’ (Sadhu Ramchand Murmu Memorial Edition – Govt. of West Bengal).
14. Saotal Bidraher 150 Bochhor – ‘Paschimbanga’ special issue. |
|
| COMPARATIVE LITERATURE : | |
| Paper – I : | (a) Theories of Literature : Dates terms and Concepts.
(b) Literature of the Ancient World; (i) Indian, (ii) Western (c) Bangla Sahitya : 1 (Baishnab Padabali theke Bankimchandra) (d) Bangla Sahitya : 2 (Rabindranath o Uttorkaal) (e) Bengali Literature in Translation (f) Indian Literature other than Bengali in Translation |
| Paper – II : | Western Literature –
(a) 800 – 1400 A.D. (including Song of Ronald, Tristan and representative writings of Troubadour Minnesang, Dante, Petrarch, Boccaccio and Chaucer).
(b) 1400 – 1616 A.D. (including representative writings of Villon, Ronsard, Spencer, Machiavelli, Rableis, Montaigne and Shakespeare). |
| (c) 1616 – 1749 A.D. (including representative writings of Moliere, Racine, Swift, Voltaire and
Defoe). (d) 1749 – 1832 A.D. (including representative writings of Goethe, Schiller, Heine, Wordsworth, Coleridge, Shelley, Keats, Scott, Rene, Lamartine, Vigny, Hugo and Musset).
(e) 1832 – 1910 A.D. (including representative writings of Whitman, Baudelaire, Verlaine, Laforgue, lbsen, Balzac, Tolstoy, Maupassant and Chekhov).
(f) 1910 to the Present times (including representative writings of Yeats, Eliot, Frost, Rilke, Mayakovsky, Eluard, Neruda, Hervert, Kafka, Marquez and lonesco). |
|
| AGRICULTURE : | |
| Paper – I : | Agro-ecological factors- plant growth and distribution. Distribution of crops according to region. Role of climate and weather of crop production, weather forecasting including modern methods. Greenhouse effect and global warming. Precision farming- Remote Sensing (RS) and Geographic Information system (GIS).
Cropping pattern and cropping system-distribution, objectives, types and impact on high yielding varieties, scope and limitations. Package and practices of cereals (rice, wheat, maize), pulses (green gram, black gram, red gram, lentil and peas), oil seeds (mustard, sesamum, ground nut, linseed, sunflower); fibre crops (Jute, sunhemp, mesta); sugarcane and forage crops (Sorghum, napier, para, berseem, Lucerne, ricebean, cowpea, oat, dinanath grass). Weeds- definition, characteristics, dessimination and control. Agroforestry-Definition of forest, scope of various types of forest – social forest, rural forest, urban forest, farm forestry; forest products. Aforestation. Conservation. Soil- definition, process and factors of soil formation, soil properties and soil conservation. Soilfertility – problems of soil and their reclamation. Nutrition- essential elements, role of nutrients on plants, integrated nutrient management and biofertilizers. Water use efficiency and dryland farming- water use efficiency in relation to crops production. Criteria for scheduling irrigation. Methods and systems of irrigation. Rainwater harvesting. Dryland farming – definition, prospects and problems. Techniques for establishment and management. Farm management – scope, importance and characteristics, farm planning, farm budgeting and farm operations. Agro-economics – function and crop insurance. Agril-extension – importance and role, methods of evaluation of extension programme. Role of KVK in technology transfer. Role and scope of Information Technology in Indian Agriculture. Livelihood management through agriculture (Self Help Group in agriculture). Marketing – its channels, pricing, marketing intelligence, storage with special references to cold storage and wirehouse. Distribution- public distribution system. |
| Paper – II : | Crop improvement- Cell structure and functions, law of heredity, chromosome structure and aberrations, polyploidy. Mutation breeding.
History of plant breeding. Mode of reproduction, selfing and crossing techniques. Crop genetic resources – conservation and utilization. Application of principles of plant breeding. Breeding methods. Heterosis,somatic hybridization. Molecular markers, DNA finger printing and genetically modified crops. Principles of plant physiology; absorption, translocation, photosynthesis and respiration (definition, process, factors affecting and significance). Growth and development, photoperiodism, plant growth substances (definition, classification and role).Stress-physiology. Seed production, testing, certification and storage. Cultivation practices of major commercial fruits, vegetables, flowers, plantation and spices, medicinal and aromatic crops. Landscaping- principles, features and designs. Postharvest technology. Protected cultivation of horticultural crops. Pests and diseases of commercially important fruit, vegetables, flowers, plantation & spices, medicinal and aromatic crops. IPM. Food and nutrient security. Scope for export of agricultural products. |
| ANIMAL HUSBANDRY AND VETERINARY SCIENCE : | |
| Paper – I : | 1. ANIMAL NUTRITION
1.1 Livestock Feeds : Common feeds and fodder and their classification. Proximate analysis of feed stuff.
1.2 Energy Nutrition : Energy sources, Measures of food energy and their application such as Gross Energy, Digestible Energy, Metabolisable Energy, Net Energy, Total Digestible Nutrients. Energy requirement for maintenance, growth, pregnancy and lactation in milk producing livestock.
1.3 Protein Nutrition: Biological value of protein, Protein efficiency ratio, digestible crude protein. Use of NPN in ruminants, bypass protein. Protein requirements for maintenance, growth, pregnancy and lactation in milk producing livestock. Improvement of poor quality roughages. |
| 1.4 Mineral and Vitamin Nutrition : Major and trace minerals, their sources, physiological functions and deficiency symptoms. Role of vitamins, their sources and deficiency symptoms.
1.5 Feed Additives: Role of probiotics, prebiotics, antibiotics, enzymes, antioxidants, buffers, mould inhibitors and methane inhibitors. Antinutritional and toxic factors present in livestock feed and fodder.
1.6 Storage & Conservation of Feeds and Fodders: Storage of feed ingredients. Conservation of fodder through hay and silage making and their use in livestock feeding.
1.7 Computation of Ration: Balanced ration, Formulation of ration and feeding of dairy cattle and buffaloes during different phases of growth and production (young, pregnant, lactating and dry animals). Formulation of ration and feeding of sheep,goat, pig and poultry.
2. LIVESTOCK PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT 2.1 Breeds : Various indigenous breeds of livestock including poultry; Exotic breeds experienced in India; Origin, distribution and breed descriptor of important breeds.
2.2 Farm Animal Practices : Dentition and ageing of animals. Disbudding, marking of animals, Grooming, Dipping, Castration, Isolation, quarantine, Disinfection and disposal of carcasses. Drug administration, Vices of animals, their prevention and care.
2.3 Dairy Farming : Opportunities in dairy farming, Dairying under mixed and as specialized farming. Management of calves, heifer, pregnant, lactating and dry animals, bulls and bullocks. Housing systems, Layout and design of different buildings for dairy animals. Methods of milking and precautions. Factors affecting quality and quantity of milk. Organic Livestock Production.
2.4 Fodder Production : Importance of grasslands and fodders in livestock production. Feed and fodder requirements of individual animal. Supply of greens throughout the year. Scarcity fodder, Recycling of animal wastes and washings for fodder production.
2.5 Sheep and Goat Farming : Homestead farming vs. Commercial farming, Goat as poor man’s cow. 2.6 Poultry Production : Economic Importance of commercial poultry farming, Backyard poultry farming. Brooding management. Incubation and hatching, Management of broilers, layers and breeder flock. Designer egg.
3. ANIMAL GENETICS AND BREEDING 3.1 Principles of Genetics : Mitosis and Meiosis. Mendelian inheritance, deviation to Mendelian genetics. Expression of genes. Linkage and crossing over. Sex linked, sex influenced, and sex limited characters. Cytoplasmic inheritance, chromosomal aberrations, Gene and its structure, DNA as a genetic material, genetic code and protein synthesis, Recombinant DNA technology, Transgenesis.
3.2 Population Genetics : Quantitative and qualitative traits. Gene and genotype frequency, Hardy- Weinberg Law and its application. Inbreeding and methods of estimating inbreeding coefficient. Heritability, repeatability, genetic and phenotypic correlations and environmental interaction.
3.3 Animal Breeding : Basis of selection such as individual, pedigree, family, progeny testing. Methods of Selection. Methods of breeding – Inbreeding, out breeding, upgrading, cross breeding. Crossing of inbred lines for commercial production. Sire index.
4. ANIMAL REPRODUCTION 4.1 Hormone in reproduction : Hormones related to reproduction, mechanism of action, control of secretion and negative feed back mechanism of hormonal regulation. Releasing and tropic hormones of reproduction.
4.2 Andrology : Puberty, sexual maturity and libido. Factors causing infertility in males. Components of semen, physical and chemical properties of semen. Preservation of semen and artification insemination. Deep freezing of semen.
4.3 Gynaecology : Symptoms of heat, detection of oestrus and time of insemination for optimal conception. Anoestrus and repeat breeding. Silent heat. Management of buffaloes in summer for better conception.
5. LIVESTOCK PRODUCTS TECHNOLOGY 5.1 Milk and milk products : Milk industry in India. Composition and nutritive value of milk. Physico-chemical properties of milk Quality testing of raw milk. Processing, packaging, storing, distribution and marketing of milk. Pasteurized, standardized, toned, doubled toned, homogenized, reconstituted, recombined and flavoured milk. Various milk products such as Cream, Butter, Ghee, Khoa, Channa, Cheese, Condensed, evaporated and dried milk. Preparation of cultured milk such as yoghurt, Dahi, Lassi and Srikhand.
5.2 Meat and meat products : Meat industry of India.Ante mortem care and management of food animals, stunning, slaughter and dressing. Meat inspection. Physical and chemical characteristics of meat. Method of meat preservation such as curing, canning, irradiation, packaging.
5.3 Poultry products Technology : Composition and nutritive value of poultry meat and eggs. Slaughtering techniques. Grading of eggs. Structure, composition and nutritive value of eggs. |
| 5.4 Milk and meat hygiene : Clean milk production. Hygienic method of handling meat and meat products. Adulteration of milk and its detection. Legal standards of milk.
6. EXTENSION EDUCATION 6.1 Concept of Sociology : Man and animal relationship, Society, Community, Association and Institution. Social groups, its types and function.
6.2 Principles of Extension : Basic philosophy, objective and concept. Methods adopted to educate farmers under rural condition, generation of technology, its transfer and feedback. Animal Husbandry Programmes for rural development. |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. VETERINARY ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY AND BIOCHEMISTRY
(i) VETERINARY ANATOMY
Osteology, arthrology and myology: Classification, physical properties and structure of long bones, joints and muscle. Study of skeleton of Pectoral, Pelvic gardles, Skull and vertebral bones of ox/buffaloes.
Splanchology : Gross morphology and topography of visceral organs of thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavity.
Neurology and asthesiology : Basic structural organization of nervous system (CNS, PNS, ANS), Eye and ear.
Anatomy of fowl : Parts of female reproductive tracts of fowl and their role in egg formation. Organs of digestive system.
(ii) PHYSIOLOGY
Blood : Constituents of blood, blood cell formation, haemoglobin synthesis, coagulation of blood, hemorrhagic, disorders, anticoagulants. Biochemical tests for assessing liver and kidney function.
Circulatory System : Haemodynamics of circulation, physiology of heart function, Cardiac Cycle, regulation of cardiac output, coronary circulation and ECG, blood pressure and hypertension, osmotic regulation, shock.
Excretion : Structure and function of nephron, formation of urine. Regulation of electrolyte and acid-base balance, sweat glands and their function.
Respiration: Mechanism of respiration, Transport and exchange of gases in lungs and tissues. Neural control of respiration and hypoxia.
Environmental Physiology : Climate change, climatological variables and their importance in animal ecology and behaviour. Effect of environmental stress on health and production.
Physiology of Milk Production : Hormonal control of mammary growth, lactogenesis and galactopoiesis. Letting down and holding up of milk. (iii) BIOCHEMISTRY Biochemistry of carbohydrate, protein, lipids, enzymes, co-enzymes, co-factors and their role in metabolism; Biochemistry of blood and body fluids.
2. PHARMACOLOGY AND TOXICOLOGY
Pharmacology : Principles of drug activity such as pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Concept of drug and receptor. Does response relationship. Adverse drug reaction, drug interaction. Biopharmaceuticals and gene therapy Antimicrobials, antifungal and principles of chemotherapy in microbial infections.
Toxicology : Fundamentals and scope of toxicology. Toxicity due to insecticides, organo phosphates, heavy metals, non-metals, micotoxins and their ameliorative measures. Toxic plants.
3. BASIC VETERINARY MICROBIOLOGY, PATHOLOGY AND PARASITOLOGY
Microbiology: Marphology and classification, cultivation and identification of microbes related to animal diseases. Transmission of infections, sterilization and disinfactants. Pathology: Pathogenesis and Pathognomic lesions in important microbial diseases of livestock. Parasitology: Morphology and pathogenesis of important helminthic and protozoal diseases in livestock like ascariasis, facioliasis, Trypanosomiasis etc.
4. ANIMAL DISEASES:
Infectious diseases : Etiology, symptoms, diagnosis and control of important bacterial, protozoal and viral diseases of domestic livestock and poultry, such as Anthrax, HS, BQ, Brucellosis, FMD, Hog Cholera, PPR, Goat Pox, Rabies, RD, IBD, Trypanosomiasis, Babesiosis, Coccidiosis etc.
Production/metabolic diseases : Etiology, symptoms, treatment and control of important |
| metabolic diseases such as milk fever, ketosis, pregnancy toxaemia, hypomagnesemia of domestic animals.
Systemic states and diseases : Fever, hyperthermia, hypothermia, toxaemia, septicaemia, bloat, impaction, diarrhoea, dehydration and snake bite.
Herd health Management : Herd immunity, disease free zones, chemotherapeutics and chemoprophylaxis for herd health. Vaccination and deworming schedule of livestock and poultry.
Surgical intervention : Diagnosis and surgical intervention in fracture, hernia, choking, ruminotomy, castration and Caesarian section.
5. VETERINARY PUBLIC HEALTH AND EPIDEMIOLOGY Epidemiology : Principles and applications of epidemiological measures in the study of diseases and their control. National and international regulations on livestock diseases.
Zoonoses : Socio-economic importance of zoonotic diseases. Role of animals in transmission of zoonotic diseases. Occupational zoonotic diseases.
Animal Welfare and Jurisprudence : Role of veterinarian in animal welfare. Animal Welfare Board of India. Role and function of Committee for the Purpose of Controlling and Supervising Experiments in Animals (CPCSEA), Common offences against animals. Examination of living and dead animals in criminal cases.
6. WILD / ZOO / LAB ANIMAL HEALTH CARE Method of handling and restrant of Wild animals. Conservation of wild life. Management and feeding practice and housing of Wild, Zoo and Laboratory animals. |
|
| ANTHROPOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | 1. Introducing anthropology: Meaning and scope of anthropology. Major branches of anthropology:
1.1 Main branches of Anthropology, their scope and relevance : (a) Social-cultural Anthropology, (b) Biological Anthropology, (c) Archaeological Anthropology, (d) Linguistic Anthropology.
1.2 Brief outline of the growth of anthropology. Enlightenment. Colonialism and anthropology.
2. Human evolution and Hominization process :
2.1 Theories of organic evolution. Human evolution and emergence of Man :
(a) Biological and Cultural factors in human evolution, (b) Theories of Organic Evolution (Pre-Darwinian, Darwinian and Post-Darwinian), (c) Synthetic theory of evolution; Brief outline of terms and concepts of evolutionary biology.
2.2 Neutral theory of molecular evolution.
2.3 Concept of evolutionary biology: Skeletal changes, (skull, vertebral column, pelvic girdle, hind limb).
2.4 Characteristics of primates, Primate classification (general), Features and distribution of New World Monkey, Old World Monkey, Asian and African Apes.
2.5 Theories of human origin.
2.6 Geological time scale with special reference to Pleistocene epoch.
2.7 Distribution, characteristics and phylogenetic status :
(a) Parapithecus (b) Dryopithecus, Sivapithecus (c) Australopithecus africanus, Australopithecus afarensis, Homo habilis (d) Homo erectus (Java Man, Peking Man) (e) Archaic Homo sapiens (f) Neanderthal Man – La-chapelle-Aux-Saints, Tabun Man (g) Anatomically Modern Homo sapiens – Cromagnon, Grimaldi, Chancelade
3. Human Genetics : 3.1 Methods – Mendelism, Twin-study, Cytogenetics, Population genetics.
3.2 Biological basis of inheritance: DNA structure and replication, Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP), Variable Number of Tandem Repeat(s) (VNTRs), Short Tandem Repeat(s) (STRs) protein synthesis, gene, allele, cell division.
3.3 Concept of Human Genome : nuclear genome, mitochondrial genome, Chromosome and chromosomal aberrations in man (Numerical and structural aberrations, point mutation), Satellite DNA. |
| 3.4 Patterns of inheritance – autosomal, sex-chromosomal, multifactorial, polygenic, sex determination, sex influenced.
3.5 Application of human genetics – consanguinity, inbreeding, genetic load, genetic counselling, forensic anthropology, personal identification, paternity identification, DNA fingerprinting, dermatoglyphics.
4. Human variation : 4.1 Concept of Race, racism.
4.2 Basis of variation – Morphological (hair, eye) metric (stature, head shape), Polymorphic (genetic marker) – blood group (ABO, Rh), Hb, PGM, HP, Y-chromosome STR, mtDNA.
4.3 Concept of Human physique and somatotype. 4.4 Concept of ethnic groups – Mongoloid, Caucasoid, Negroid, Australoid.
5. Human Growth and Nutrition : 5.1 Concept of human growth, stages of growth – Pre-natal, Post-natal, Adolescent.
5.2 Factors affecting the growth and development – genetic, environmental, nutritional, socio- economic.
5.3 Methodology of growth study.
6. Concept of Health and disease : 6.1 Concept of Communicable and Non-Communicable diseases. (Malaria and Type-2 diabetes respectively). Nutrition Deficiency related diseases.
6.2 Nutrition – concept of Macro and Micro nutrients and Deficiency.
7. Human adaptation : 7.1 Concept of Human adaptation and acclimatization – hot, cold and high altitude. Bergman’s and Allen’s Rules.
7.2 Anthropometry and its uses in understanding human adaptation (BMI and CI), Physiological variable (blood pressure, pulse rate), Body composition (fat patterning). 8. Cultural evolution :
8.1 Tool typology and technology of tool manufacturing.
8.2 Excavation, Exploration, Site survey, Application of GIS
8.3 Concept of Dating: Absolute (C14, K-Ar) Relative (Dendrochronology and Stratigraphy).
8.4 Features and distribution of prehistoric cultures with reference to India and Europe : (a) Paleolithic (b) Mesolithic (c) Neolithic (d) Chalcolithic (e) Iron Age.
9. Theories and concept of culture and society : 9.1 Brief outline of Anthropological Theories: Evolutionism, Diffusionism, Functionalism, Structuralism, Symbolism and Interpretative Approach, Post-structuralism and Post-modernism – Hermeneutics and Phenomenological Anthropology.
9.2 Concept (brief outline): Social structure, Social organization, Gender, Institution, Group, Community.
10. Culture and civilization : 10.1 Definition and features of culture and civilization.
10.2 Cultural relativism, Acculturation, Enculturation, Diffusion, Cultural lag, World view, Symbol.
10.3 Anthropological approaches to the study of civilization.
11. Elements of social organization : 11.1 Family – Definition, Types, functions, recent changes.
11.2 Marriage – Definition, Types, functions, recent changes. Marriage payments (dowry and bride wealth). Incest regulation, Preferential and prescribed forms of marriage.
11.3 Kinship – Definition of kinship system. Importance, Types of kinship systems, kin term classification. |
|
11.4 Rules of Descent and alliance, Rules of residence, Descent groups. 12. Economic Anthropology :
12.1 Concept and approaches.
12.2 Major ways of subsistence – Hunting-gathering, Pastoralism, Horticulture and Settled Agriculture.
12.3 Production, Distribution (Reciprocity, Market exchange, Re-distribution), Consumption, Gift exchange.
12.4 Peasant.
13. Political anthropology :
13.1 Definition and approach.
13.2 Power, authority, social control, law, social sanction, governance.
13.3 Concepts of Band, Tribe, Chiefdom and State. 13.4 Political movement – Approaches of study, Types of socio-political movements (Revitalization, Messianic, Social solidarity, regional and Ethnic).
13.5 Ethnicity – Definition, concept of ethnic boundary.
14. Anthropology of religion :
14.1 Definition of religion, functions of religion.
14.2 Approaches to the study of religion (intellectual, psychological, functional, interpretative).
14.3 Concepts: Myth, magic, witchcraft, sorcery, taboo, totem, divination, rituals, symbolism in religion.
14.4 Religious specialists – shaman, witch-doctor, priest.
15. Social stratification :
15.1 Definition and features.
15.2 Theories/approaches.
15.3 Types – Caste and class.
15.4 Concepts: Status, role, age-set/age-grade, social mobility.
16. Ecological anthropology :
16.1 Definition, scope and approaches/methods of ecological anthropology.
16.2 Concept of culture ecology.
17. Emerging fields of social-cultural anthropology :
17.1 Development anthropology – Definition and scope, development, globalization.
17.2 Legal anthropology and Human Rights.
17.3 Anthropology of communication – visual anthropology, mass media, popular culture.
17.4 Anthropology of gender.
18. Basic methods of data collection and interpretation :
18.1 Qualitative and quantitative approaches, ethnography, fieldwork.
18.2 Basic methods/techniques of data collection – observation (special reference participant observation), interview, case study, schedule, questionnaire, genealogy, PRA and RRA.
18.3 Application of statistical principles – Descriptive statistics – central tendency (mean, median, mode), standard deviation, standard error, Testing of hypothesis: t-test, chi-square test. |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. History and Development of Anthropology in India :
1.1 Colonialism and Anthropology in India. |
|
1.2 Phases of development and major trends of Anthropology in India. 1.3 Idea of Indian tradition of Anthropology. Contribution of Indian scholars : S.C.Roy, N.K. Bose, M.N. Srinivas, D.N. Majumdar, T.C. Das, S.C. Sinha and S.S. Sarkar.
2. Evolution of Indian culture and civilization :
2.1 Prehistoric cultures: Palaeolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Chalcolithic, Iron age.
2.2 Indus Valley Civilization (origin, distribution, features with special reference to architectural, socio-economic and religious; decline; Indus script.)
2.3 Vedic society (early and late): Society, economy and polity.
2.4 Contribution of tribal cultures to Indian civilization.
2.5 Ethnoarchaeology in India with special reference to mortuary practices and megalithic burials. 3. Emergence of man in India and contemporary variation :
3.1 Fossil remains in India: Ramapithecus, Narmada man.
3.2 Classification of Indian population: H.H. Risley, B.S. Guha and S.S. Sarkar.
3.3 Contemporary classification based on morphology, anthropometry and genetic markers (ABO, Hb, HP, mtDNA).
4. Demographic Profile of India :
4.1 Demography: concept, theories and methods.
4.2 Structure and features of Indian population; Rates and Ratios : Fertility, Mortality; Factors influencing fertility and mortality. Dynamics of demography in rural, urban and tribal contexts. Migration and effects of migration.
4.3 Linguistic elements in Indian population (Grierson and S.K.Chatterjee).
5. Anthropological approaches to Indian civilization :
5.1 Cultural categories of ancient India :Varnashram, Purushartha, Karma and Rebirth.
5.2 Caste system – origin, features, functions and change in caste system, Dominant Caste, Jajmani system.
5.3 Structure of Indian civilization: Theoretical understanding (R.Redfield, N.K.Bose).
5.4 Concepts for understanding Indian civilization: Sanskritization, Universalization-Parochialization, Tribe-peasant & Tribe-caste continuum, State Formation and Sacred Complex.
5.5 Idea of folk and folk culture, folkloric elements in Indian culture (proverbs, folksong, folkart with special reference to West Bengal), folklore and identity, performances.
5.6 Impact of Buddhism, Jainism, Islam, Christianity on Indian society.
6. Aspects of Indian village :
6.1 Development of village study in India and its significance.
6.2 Types of village, social organization of Indian village (agricultural).
6.3 Concepts developed through village studies in India.
6.4 Changes in rural society in post-Independent India.
7. Weaker sections :
7.1 Concepts of SC, ST, OBC, minority, women, children, aged – status, constitutional provisions, problems, programmes of development. 7.2 Linguistic minority and its problems.
8. Tribal situation in India :
8.1 Ethnic strains in Indian population, Geographical, Economic and linguistic distribution of Indian tribes.
8.2 Major problems of Indian tribes with special reference to issues of land and forest.
8.3 Plan and programmes for the development of the STs; problems/critique of tribal development; five year plans and Indian tribes – a review. |
|
8.4 Constitutional safeguards for STs, 5th and 6th Schedules. 8.5 Socio-economic changes in tribal millieu – Impact of urbanization, industrialization, forest policy, development projects on tribal people. Changes in tribal society in colonial and post-Independent periods. Impact of modern democratic institutions on traditional political system.
8.6 Tribal movement (Nature and distribution), Emergence of Ethnicity, Issues of Identity, Tribe and Nation-State, Indian National Movement and Indian tribes, Regionalism, Jharkhand movement, Santal movement.
9. Anthropology of development:
9.1 Critique, approaches, issues of women development, cultural factors of development, displacement and rehabitation, sustainable development, alternative to development.
9.2 Role of NGO in development. 9.3 Role of anthropology in development.
10. Emerging issues in Indian Anthropology:
10.1 Human Rights and advocacy of anthropology in the contexts of women, children, health and education.
10.2 Social-cultural dimensions of health: Bio-medical, medical anthropology and ethno medicine.
10.3 Issues in context: Sect, Cult, Religions pluralism in India, Visual image and Indian society, Public Culture in India, Refugee, Civil Society, Violence, Traditional Knowledge. |
|
| BOTANY : | |
| Paper – I : | Microbiology:
Plant virus- types – TMV- Physicochemical characteristics and Multiplication, One step growth curve, Lytic cycle (T4 phage) and Lysogenic cycle (Lambda phage), Significance of lysogeny, Viroids and Prions. Bacteria – Distinguishing features of Archaea and Bacteria, Flagella (ultrastructure) and Pilli, wall – chemical structure and differences between Gram +ve & Gram –ve bacteria, Bacterial genome and plasmid, Endospore – formation, structure and function. Genetic Recombination (Transformation, Transduction & Conjugation) Application in Medicine and Industry.
Plant Pathology: Terms and Definitions: Disease concept, Symptoms, Etiology and causal complex, Endemic, Epidemic, Pandemic and Sporadic diseases, Disease triangle, Disease cycle (monocyclic, polycyclic and polyetic) with special reference to Late Blight of Potato, Brown Spot of Rice and Citrus Canker. Host – Parasite Interaction. Pathotoxin (Definition, criteria and example), Phytoalexin, Resistance. Plant Disease Management- Symptoms, Causal organism, Disease cycle and Control measures.
Cryptogams: ALGAE: General account. Ultrastructure of cell. Diatom: Cell structure, Cell division, Auxospore formation in Centrales and Pennales. Economic Importance: Food, Phycocolloid (Agar-agar, Algin, Carrageenan), Diatomite, Algal Biotechnology – potential of microalgae for SCP, β-carotene, Biofertilizer, Biodiesel; Principles of mass cultivation of microalgae; Algal toxins.
FUNGI & LICHEN: General Account: Hyphal forms, Fungal spore forms and mode of liberation, Sexual reproduction and degeneration of sex, Homothallism and heterothallism, Life cycle patterns, Anamorphic fungi and parasexuality, Mycotoxins with emphasis on aflatoxin. Mycorrhiza: Role in Agriculture & Forestry. Fungal Biotechnology: Mushroom, Cheese and Ethanol- Industrial production (brief outline), Fungal sources and uses of Mycoprotein, Enzyme (Cellulase), Amino acid (Tryptophan), Vitamin (Riboflavin), Antibiotic( Griseofulvin), Pharmaceuticals (Cyclosporin-A). Lichen : Types, Reproduction , Economic and ecological importance.
BRYPOPHYTES : General Account and Origin of Alternation of Generations (Homologous and Antithetic theory), Evolution of Sporophytes (Progressive and Regressive concept). Importance: Role of bryophytes in Plant succession and Pollution Monitoring.
PTERIDOPHYTES: General Account: Colonisation and rise of early land plants. Fossil Pteridophytes: Structural features, Geological distribution and Evolutionary significance. Telome concept and its significance in the origin of different groups of Pteridophytes. Heterospory and Origin of Seed habit. |
| Economic importance as food, medicine and Agriculture.
Palaeobotany & Palynology: Plant Fossil: Types, Different modes of preservation, Nomenclature and Reconstruction, Importance of fossil study. Geological time scale with dominant plant groups through ages. Palynology: Pollen aperture types, NPC classification (Erdtman). Pollen wall- Sporopollenin, Stratification and Ornamentation (sculpturing), Applied Palynology:- Palaeopalynology,.Aeropalynology , Forensic palynology, Melissopalynology.
Phanerogams: GYMNOSPERMS : Progymnosperms: Phylogenetic importance. Fossil gymnosperms: Structural features of Cycas, Pinus, Lyginopteris, Williumsonia oldhamia and Geological distribution of reconstructed genera. Economic Importance of fossils with reference to Wood, Resins, Essential oils, and Drugs.
MORPHOLOGY OF ANGIOSPERMS: Inflorescence types with examples. Flower: Corolla- forms, aestivation; Stamen- types; Placentation- types; Ovule – structure and forms. Fruit – types with examples.
TAXONOMY OF ANGIOSPERMS: Components of Systematics: Nomenclature, Identification, Classification; Taxonomy and its phases – Pioneer, Consolidation , Biosystematic and Encyclopaedic ; alpha- and omega- taxomony . Nomenclature: Herbaria and Botanical Gardens – their role; important Indian Herbaria and Botanical Gardens; Dichotomous keys – indented and bracketed, Phenetics. Brief idea on Phenetics, Numerical taxonomy; Cladistics; Monophyletic, polyphyletic and paraphyletic groups; Plesiomorphy and apomorphy. Data sources in Taxonomy: Supportive evidences from: Phytochemistry, Cytology and Anatomy. Diagnostic features, Systematic position of Economically important plants (parts and uses) with special reference to the families Poaceae, Orchidaceae, Brassicaceae, Fabaceae, Solanaceae and Malvaceae.
Embryology: Pre-fertilisation changes: Microsporogenesis and Microgametogenesis, Megasporogenesis. Post- fertilization changes. Embryogenesis and Development of Endosperm, Apomixis, Apospory and Apogamy, Polyembryony.
Anatomy: Ultrastructure and chemical composition of cell wall. Stomata: Types, Ontogeny of Trachea and Sieve- tube. Stele: Stelar types & evolution/ Secondary growth with special reference to the abnormal growth in Dracaena, Boerhaavia and Bignonia. Mechanical tissues and the Pinciples governing their distribution in plants. Organisation of shoot apex (Tunica–Corpus) and Root apex (Korper-Kappe), Adaptive anatomical features of Hydrophytes and Xerophytes. Ecology: Habitat and Niche, Ecotone and edge–effect, Carrying capacity. Community ecology: Community- Characteristics and diversity, Ecological succession –Primary and secondary, Seral stages (with reference to Hydrosere), autogenic and allogenic succession. Plant indicators (metallophytes); Phytoremediation. Conservation of Biodiversity (In-situ & Ex-situ).
Plant Geography: Phytogeographical regions; Endemism; Endemic types and Factors; Age & Area hypothesis and Epibiotic theory; Endemism in Indian flora with special emphasis on Sunderban and Eastern Himalayas. |
|
| Paper – II : | Cell & Molecular Biology
CELL BIOLOGY: Cell and its types (prokaryotic and eukaryotic), structure and functions of the major cell organelles (nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, ribosome, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies, microbodies), cell division (mitosis and meiosis), significance of cell division, Cell cycle, structure of a typical chromosome, nucleosome model of chromosome, chromosomal aberrations (deletion, duplication, translocation and inversion), Concept of RNA world. MOLECULAR BIOLOGY: Chemical structure and nature of the nucleic acids, concept of gene, replication of DNA, concept of genomic DNA and cDNA, split genes, overlapping genes, oncogenes, genetic code, protein synthesis in prokaryotes and eukaryotes, central dogma, basic of recombinant DNA technology (restriction enzymes, vectors, molecular cloning, application of R DNA technology and its social ethics). Genetics, Plant Breeding, Biometry & Evolution Biology: GENETICS: Mendelian principles (Mendel’s monohybrid and dihybrid experiments and laws), concept of linkage and crossing over, polyploidy, multiple alleles, point mutation, sex-linked inheritance, cytoplasmic |
| inheritance and basic population genetics.
PLANT BREEDING: Objective of plant breeding, methods of propagation in relation to breeding methods, methods of plant breeding (selection, hybridization, concept and causes of heterosis). Maintenance of germplasm, Heterosis and hybrid seed production, Molecular Breeding (use of DNA markers in plant breeding). Maintenance of germplasm, Mass selection and pure line selection, Heterosis and hybrid seed production, Molecular Breeding (use of DNA markers in plant breeding).
BIOMETRY: Random sampling, Frequency distribution, Central tendency– Arithmetic Mean, Mode and Median, Measurement of dispersion – Standard Deviation, Standard error of Mean, Test of significance: ‘t’- test; chi square test for goodness of fit. Probability, Measurement of gene frequency (Hardy- Weinberg equilibrium). Overview of Bioinformatics, nature of biological data, literature databases (searching and downloading), introduction and overview of biological databases, nucleic acid sequence databases, GenBank, Protein sequence databases, introduction to BLAST series.
EVOLUTION BIOLOGY: Concept of biological evolution, evidence of organic evolution (taxonomic, geological, morphological and anatomical); Lamarckism, Darwinism and mutation theories of de Vries.
Physiology and Biochemistry: Plant-water relations, Stomatal physiology-mechanism of opening and closing, Organic Translocation Photosynthesis, Photochemical reaction centres, Cyclic and noncyclic electron transport, Water splitting mechanism, photophosphorylation, Z-scheme, Calvin cycle – Biochemical reactions and stoichiometry, Photosynthetic efficiency of C3 and C4 plants and crop productivity, Photorespiration, Crassulacean acid metabolism. Respiration- EMP pathway, TCA cycle, ETS and oxidative phosphorylation, Oxidative pentose phosphate pathway and its significance, ß-oxidation of fatty acids and significance. Nitrogen Metabolism (symbiotic and non-symbiotic), structure and function of di-nitrogenase complex, ETS of di-nitrogenase, basic concept of nif and nod genes. Plant Growth Regulators (Auxin, Gibberellin, Cytokinin, Ethylene and Abscisic Acid). Photoperiodism and plant types, Phytochrome, Vernalisation, Concept of biological clock and biorhythm. Seed dormancy, Physiology of Senescence and Ageing. Stress Physiology.
Biochemistry as the molecular logic of living organisms, axioms of living organisms, the major compounds of living beings; pH, buffers and basic bioenergetics, chemical structure and properties of water molecule, ionization of water, Henderson-Hasselbalch equation, titration curve and the concept of preparation of any buffer solution; biomolecules: general structure, properties, classification and metabolic importance of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and nucleic acids; enzymes, basic structure (holoenzyme, apoenzyme, cofactor, coenzyme and prosthetic group), nomenclature and classification of enzymes according to IUBMB, mechanism of enzyme action (concept of active site of an enzyme, activation of free energy, principles of enzyme action, Fisher’s and Koshland’s models), enzyme kinetics (Michaelis-Menten equation and Lineweaver-Burk plot), reversible and irreversible enzyme inhibition, allosteric enzyme regulation and covalently modulated enzyme regulation, basic concept of ribozymes, abzymes and isozymes. Pharmacognosy : Pharmacognosy and its importance in modern medicine , Crude drugs, Drug evaluation Secondary metabolites, Interrelationship of basic metabolic pathways with secondary metabolite biosynthesis with special reference to Cinchona, Ipecac, Adhatoda and Curcuma longa.
Plant Biotechnology & Instrumentation: Plant tissue culture and Micropropagation. Plant Genetic Engineering: Brief concept of different gene transfer methods. Transgenic plants. Principles and applications of simple, compound, confocal and electron microscopy, colorimetry, visible and UV-visible spectrophotometry, deferential centrifugation, PCR, RT-PCR, Gel Electrophoresis, Blotting (Southern, Northern and Western) and ELISA. |
|
| CHEMISTRY : | |
| Paper – I : | Group A
1. Atomic Structure: Bohr theory of hydrogen atom, Mosley’s experiment. Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle; Schrodinger wave equation; Interpretation of wave function, particle in a one-dimensional box; quantum numbers; hydrogen atom wave functions; shapes of s, p and d-orbitals.
2. Chemical Bonding: Ionic bond: characteristics of ionic compounds, lattice energy, Born-Haber cycle. Covalent bond and its general characteristics: polarities of bonds in molecules and their dipole moments; shapes of molecule, VSEPR theory. Valence bond theory, concept of resonance and resonance energy; molecular orbital theory (LCAO |
| method); bonding in H +, H , He + to Ne , NO, CO, HF, and CN–, comparison of valence bond and
2 2 2 2 molecular orbital theories, bond order, bond strength and bond length.
3. Acid-Base & Redox Reactions Theory of acids and bases; pH, buffer solution; solubility product and salt hydrolysis. Nernst equation (without derivation). Influence of complex formation, precipitation and pH on redox potentials; formal potential. Feasibility of a redox titration, redox potential at the equivalence point, redox indicators. Redox diagram (Latimer and Frost diagrams) of common elements and their applications. Disproportionation and comproportionation reactions (typical examples). 4. Chemical Periodicity: Periodic table, group trends and periodic trends in physical properties. Effective nuclear charge, screening effect, Slater’s rules, atomic radii, ionic radii (Pauling univalent), covalent radii. Ionization potential, electron affinity and electronegativity (Pauling, Mulliken and Allred- Rochow scales) and factors influencing these properties. Comparative studies of hydrides, halides, oxides of s- and p- block elements. Structure and bonding of B2H6, (SN)x, Phosphazenes and inter-halogens. d-block elements; electronic configuration, ionization energies, oxidation states, variation in atomic and ionic radii, magnetic and spectral properties.
Group-B 5. Gaseous State and Transport Phenomenon Maxwell distribution of molecular speeds, intermolecular collisions, collisions on wall and effusion; thermal conductivity and viscosity of hard sphere gases. van der Waals equation of state, inter-molecular interactions, critical phenomena and liquefaction of gases,
6. Liquid State Viscosity, Poiseuille equation, temperature dependence. Surface tension and surface energy, wetting and contact angle, interfacial tension and capillary action; Laplace equation.
7. Solid State Crystal systems; designation of crystal planes, lattice structure and unit cell; Miller indices, Bragg’s law; X-ray diffraction by crystals; close packing, radius- ratio rules, calculation of some limiting radius-ratio values; structures of NaCl, KCl; stoichiometric and non-stoichiometric defects, impurity defects, semi- conductors.
8. Thermodynamics Work, heat and internal energy; first law of thermodynamics. Second law of thermodynamics; entropy as a state function, entropy change in various processes, reversibility and irreversibility, free energy functions; thermodynamic equation of state; Maxwell’s relations; temperature, volume and pressure dependence of thermodynamic functions; J-T effect and inversion temperature; criteria for equilibrium, relation between equilibrium constant and thermodynamic quantities; Nernst heat theorem. Definitions and interrelations among Kp, Kc and Kx ; Van’t Hoff equation, Le Chatelier principle.
Group – C 9. Aromaticity Aromaticity and anti-aromaticity; benzene, naphthalene, annulene, azulene, tropolones, fulvenes, sydnones. Electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution. Synthesis and reactions of heteroaromatic compounds (pyrrole, furan, thiophene, pyridine).
10. Study of Mechanisms General methods (both kinetic and non-kinetic) of study of mechanism of organic reactions: isotopic method, cross-over experiment, intermediate trapping, stereochemistry; energy of activation; thermodynamic control and kinetic control of reactions. Reactive intermediates: Generation geometry, stability and reactions of carbonium ions and carbanions free radicals, carbenes, benzynes and nitrenes.
11. Organic Reaction Types |
| Substitution Reactions: SN1, SN2 and SNi mechanisms; neighbouring group participation.
Elimination Reactions: E1, E2 and E1cb mechanisms; orientation in E2 reactions-Saytzeff and Hoffmann; pyrolytic syn elimination – Chugaev and Cope eliminations. Addition Reactions: Electrophillic addition to C=C and CºC; nucleophilic addition to C=O, C=N, conjugated olefins and carbonyls. Rearrangements: Pinacol-pinacolone, Hoffmann, Beckmann, Baeyer-Villiger, Favorskii, Fries, Sclaisen, Cope, Stevens and Wagner-Meerwein rearrangements.
12. Organic Spectroscopy: Principle and applications in structure elucidation: Infra-red: typical functional group identification UV-vis: Singlet and triplet states; n-p* and p-p* transitions; application to conjugated double bonds and conjugated carbonyls – Woodward–Fieser rules; charge-transfer spectra. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR): Basic principle; chemical shift and spin-spin interaction and coupling constants. Mass Spectrometry: Parent peak, base peak metastable peak, McLafferty rearrangement. |
|
| Paper – II : | Group-A
1. Coordination Chemistry – I Bonding theories of metal complexes; valence bond theory, crystal field theory and its modifications; application of theories in the explanation of magnetism and electronic spectra of metal complexes.
2. Coordination Chemistry – II Isomerism in coordination compounds; IUPAC nomenclature of coordination compounds; stereochemistry of complexes with 4 and 6 coordination numbers; chelate effect and polynuclear complexes; trans effect and its theories; kinetics of substitution reactions in square-planer complexes; thermodynamic and kinetic stability of complexes.
3. Bio-Inorganic Chemistry Metal ion in biological systems and their role in ion transport across the membranes (molecular mechanism), oxygen-transport proteins: hemoglobin, myoglobin, hemerythrin; electron-transport proteins: cytochromes and ferrodoxins.
4. Organometallic Chemistry EAN rule, synthesis, structure and reactivity of metal carbonyls; carboxylate anions, carbonyl hydrides and metal nitrosyl compounds.
Complexes with aromatic systems; synthesis, structure and bonding in metal-olefin, -alkyne and – cyclopentadienyl complexes; coordinative unsaturation, oxidative addition reactions, insertion reactions, fluxional molecules and their characterization; compounds with metal-metal bonds and metal atom clusters.
Group – B
5. Phase-equilibria and solutions Gibbs phase rule and its significance. Clapeyron equation; Clausius – Clapeyron equation; phase diagram for a pure substance; phase-equilibria in binary systems, partially miscible liquids, upper and lower critical solution temperatures; properties of dilute solutions; Raoult’s and Henry’s law. Partial molar quantities, their significance; excess thermodynamic functions.
6. Surface phenomena, catalysis and polymers Adsorption from gases and solutions on solid adsorbents: Langmuir and B.E.T. adsorption isotherms; determination of surface area, characteristics and mechanism of reactions on heterogeneous catalysts.
Number and weight average molecular weight, their determination. Kinetics of polymerization.
7. Chemical Kinetics Differential and integral rate equation for zeroth, first, second and fractional order reactions; rate equations involving reverse, parallel, consecutive and chain reactions; branching chain and explosion; effect of temperature and pressure on rate constant; collision theory and transition state theory.
8. Photochemistry and spectroscopy : Fluorescence & phosphorescence, Jablonsky diagram, Franck-Condon principle, Lambert-Beer law. Laws of photochemistry, quantum yield, photo-stationary state, photosensitized reaction. Rotational spectra of diatomic molecules: Rigid rotator model, selection rule, determination of |
| bond length.
Vibrational spectroscopy of diatomic molecules: SHO model, selection rule, determination of bond energy.
Group – C
9. Configuration and conformation
Representation of molecules in three dimension Fischer, Saw-horse and Newman projection; configuration (R and S) of chiral carbon, priority rule.
Conformation of acyclic and alicyclic molecules; gauche-butane interaction; chair-boat in cyclohexane.
10. Chirality and stereoselectivity
Chirality: asymmetric carbon, axial and planar chirality. Optical activity; resolution of optically active compounds; enantioselective and diastereoselective synthesis; enantiomeric excess; Prelog’s rule for configuration determination; Cram’s rule.
11. Organic Synthetic methods Condensation reactions; Aldol, Claisen, Diemann, Perkin, Knoevenagel, Stobbe, Acyloin Oxidation; epoxidation, dihydroxylation, periodate, chromate, permanganate, lead tetraacetate, allylic oxidation.
Reduction; catalytic hydrogenation, metal hydrides, dissolving metal reduction.
Organometalic, catalysis; palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction and allylic substitution; Wilkinson catalyst; alkene metathesis.
12. Pericyclic and photochemical reactions
Photochemical reaction; singlet and triplet state; Norrish Type I and Type II. Patterno-Buchi. Photochemical generation of radicals.
Pericyclic reaction; conservation of orbital symmetry; electrocyclic reactions; cycloaddition reactions, sigmatropic rearrangements. |
|
| CIVIL ENGINEERING : | |
| Paper – I : | Strength of Materials :
Stress-strain, elastic modulus, shear force and bending moment diagrams of determinate beams, deflection of beams by different methods.
Structural Analysis :
Application of Area moment theorem & Conjugate beam method, Castigliano’s theorems I & II, Slope deflection & Moment distribution method. Introduction of Matrix method of analysis : force and displacement method. Application of displacement method to truss, beam & frame structure, Introduction of plastic analysis.
Design of steel structures :
Concept of design by working stress method and Limit state method. Application of Limit state method : Design of tension and compression member, design of flexure members : Beams – rolled section and plated beam. Design of column for axial and eccentric loads. Design of connection : Bolted and welded.
Design of concrete structures :
Concept of working stress method and limit state method. Application of limit state method to design of singly reinforced rectangular, T and L beams, doubly reinforced beam, column for axial and eccentric loads, isolated footing.
Geotechnical Engineering :
Type of soils. Weight-volume relationship. Grain size distribution. Index properties – Attergb’s limit, relative density, identification and classification of soils. |
| Water in soils, Effective pressure, Pore water pressure, Permeability – laboratory and field tests, Seepage, Quick sand condition.
Shear strength – Mohr–Coulomb failure criteria, pole, Determination of shear strength parameters – laboratory and field tests. Compressibility and consolidation – normally consolidated and over consolidated soils, compression and swelling indices. Determination of coefficient of Consolidation. Settlement Computation. Soil stabilization – Compaction, Laboratory test, field methods and uses of admixtures. Soil exploration – Spacing, depth and number of exploratory borings. Methods of boring & sampling. Standard penetration test, Static cone penetration test, Seismic refraction method. Earth pressure theories – Rankine and Coulomb, Different types of back fill. Determination of earth pressure. Stability of retaining walls. Sheet piles, Braced excavation. Shallow Foundations – Estimation of bearing capacity and settlement. Allowable bearing pressure. Effect of ground water table. Field tests. Types of footing – Isolated, combined, strip, grid and raft foundations. Deep foundations – Types of piles, material, suitability and uses. Determination of pile capacity. Negative skin friction, Testing of piles. |
|
| Paper – II : | Construction: Materials, Planning & Management :
Physical Properties of Cement and cement concrete, stone, bricks and mortars, Stress-strain behaviour of reinforcing steels, Nondestructive tests – Rebound Hammer, Ultrasonic Pulse velocity tests, Construction activities schedules, organization for construction industry. Quality assurance principles. Network analysis, CPM & PERT analysis: their use in construction monitoring, Cost optimization and resource allocation.
Surveying : Chain surveying; Principles, Methods of linear measurement; Instruments for Chaining; Chaining tape corrections including sag corrections; Chain triangulation; Selection of stations, locating ground features; Plotting of chain survey. Compass survey; Use of prismatic compass; Measurement of bearing, Computations of angles from bearings, Chain and Compass traversing, Plotting compass traverse; Plane table survey; Introduction and method; Errors in plane tabling; Leveling; Adjustment of dumpy level; Reciprocal leveling and profile leveling; Countering and interpretation of contour maps; Theodolite Surveying and Traversing. Uses of Total Station. Basic elements of Remote sensing and photogrammetry
Transportation Engineering : Principles of Highway Planning. Functional classification of road. Highway alignment, Geometric design – Cross section, Camber, Superelevation, Horizontal and Vertical curve, Pavement structure and Materials – Subgrade soil, Sub base, Base materials, aggregates & bitumen. Pavement design – flexible and Rigid by IRC and other methods. Construction method of WBM, Bituminus work and cement concrete roads. Highway drainage system.
Traffic surveys and their application in traffic planning. Design of intersection, rotary signals. Standard traffic signs and marking.
Water Resources Engineering : Concept of storm and unit hydrograph, type of aquifers, Ground Water: Specific yield, storage coefficient, coefficient of permeability, confined and unconfined aquifers, aquitards, radial flow into a well under confined and unconfined conditions. Flood-flow estimation. Rainfall-frequency distribution and analysis. Water requirements of crops, Canals : rectangular and trapezoidal, design of lined and unlined canal, Types of dam, design, principles of design of rigid gravity & earth dams including statistical analysis, River training : Objectives and methods.
Environmental Engineering : Water Demand, Population estimate. Water quality : Physical, Chemical and bacteriological. Water treatment principle and design of coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation and filtration. Principle of Chlorination and softening. Waste water : Types and characteristics, BOD, COD estimation, Design of separate and combined sewer. Wastewater treatment: Grit chamber, setting tank, activated sludge process, stabilization pond.
Solid waste : Composting and land fill methods
Air Pollution : Types, sources and effects, control measures – ventury, wet scrubber, Electrostatic precipitator, Cyclone.
Noise Pollution : Equivalent noise level, Determination of Leq. |
| COMMERCE & ACCOUNTANCY : | |
| Paper – I : | Financial Accounting: Accounting as a Financial Information System, Basic Concepts & Conventions, |
| Accounting Standards, Final Accounts of Profit-seeking and Non-profit seeking organisations.
Corporate Accounting: Issue, Forfeiture & Re-issue of Shares, Redemption of Preference Shares & Debentures, Buy-back of Shares, Company Final Accounts, Reconstruction of Companies, Preparation of Consolidated Balance Sheet. Cost & Management Accounting: Cost Concepts, Terms & Classification of Costs, Elements of Cost, Accounting for Material, Employee Cost and Overhead, Job costing, Process costing, Activity-based costing, Marginal Costing – CVP Analysis & Decision Making, Standard Costing, Budgetary Control, Funds flow & Cash Flow Statement, Accounting Ratios. Taxation: a) Income Tax – Definitions, Residential Status & Incidence of Tax of Individual, Computation of Total Income of an individual (various heads of income and deduction from Gross Total Income), Set off & Carry Forward.
b) Indirect Tax i) WB VAT Act, 2003: Basic concepts, features, determination of tax payable, registration of dealer. ii) Central Sales Tax, 1956: Definition, incidence and levy of tax, exemption and exclusion, determination of turn over and tax payable, registration of dealer. |
|
| Paper – II : | Indian Financial System – Role of finance in an economy, components (instruments, markets, etc.), role of financial intermediaries, structure of Indian financial system, role of RBI, Commercial Banks and other Financial Institutions(LICI,UTI, SIDBI, SFCs, NABARD)
Money Market – structure of Indian money market, discount houses, call money market, recent trends of Indian money market Capital Market – primary and secondary market, functionaries of stock-exchanges, concept of DMAT, role of SEBI.
Business Laws i) Indian Contract Act, 1872 – Offer & Acceptance, Consideration, capacity of parties, free consent, void & voidable agreements, discharge of contracts. ii) Consumer Protection Act, 1986 – Rights of consumers; definition of consumer, manufacturer, complaints, unfair trade practices; composition and jurisdiction of District Forum, State Commission and National Commission. iii) Companies Act, 1956 – Types of companies, Memorandum and Articles of Association, Prospectus, Promotion and Incorporation of Companies, Directors, Company Meeting, Winding up. iv) Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 – Nature, Causes, and settlement of industrial disputes, workers’ participation in management and collective bargaining.
Auditing – Auditing procedures and techniques; internal control and internal audit; company audit – divisible profit, dividend and depreciation; Audit of Bank, Insurance and NGOs; Audit Report.
Organisation Behaviour – Nature and Concept of Organisation; organisation structure; modern concepts of organisation theory; Leadership – theories and styles; Motivation – concept & theories; Quality of Work Life – meaning and impact. |
| COMPUTER SCIENCE : | |
| Paper – I : | Algorithms and Problem solving : Number systems and Arithmetic : Theory of Counting : Graphs and Algorithms : Boolean Algebra : Models of Computer Machines : Numerical Algorithms : Operations Research : Circuit and Network Theory : Basic Electronics : Instruments : Digital Logic and Systems : Data Communication : Data Structure. |
| Paper – II : | Operating System : System Analysis and Design : Object oriented Programming, Computer Architecture and Organization : Micro Processor : Computer Networks : Database Management : Assembler, Loader and Linker : Compiler : Graphics and Multimedia. |
| ECONOMICS : | |
| Paper – I : | 1. Microeconomic Theory
2. Macroeconomic Theory 3. International Trade Theory 4. Public Finance 5. Statistics and Econometrics
1. Microeconomic Theory i. Consumer Theory ii. Production and cost- returns to scale, short run and long run costs iii. Market Structure-Perfect competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition, Oligopoly |
| iv. General Equilibrium and Welfare (optimality of perfect competition)
v. Marginal Productivity Theory of Distribution 2. Macroeconomic Theory i. National Income Accounting ii. Economy in the long run, economy in the short run, Fiscal and Monetary policy using IS-LM, Growth Theory—Harrod-Domar Model, Solow Model, Endogenous Growth.
3. International Trade Theory i. Classical — Ricardo, Neoclassical – Hecksher- Ohlin ii. Imperfect competition and trade , Intra-industry trade iii. Trade Policy—Tariff, Quota iv. Current and Capital Account in Balance of Payments, Fixed and Flexible exchange rate systems v. Open economy macroeconomics — Mundell-Fleming model
4. Public Finance a. Theory of externality and market failure b. Public Goods and Role of the Public Sector c. Budget — Different concepts d. Tax—indirect and direct, VAT, subsidy and transfers e. Public debt and its burden
5. Statistics & Econometrics 1. Measures of Central Tendency & Dispersion 2. Theory of Probability 3. Sampling Theory 4. Inference 5. Econometrics—Classical Linear Regression Model |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. Development
2. The Indian Economy (a) Pre-independence period (b) Post-independence pre-liberalisation period (c) Post-liberalisation period (d) The West Bengal Economy 1. Development (a) Process of development Lewis Model Harris Todaro Model Demographic change and occupational transformation (b) Trade and Development Trade as an engine of growth (c) Planning vs. Market Model of Development Poverty and Inequality (d) Capability and Human Development including issues of Gender (e) Environment and development
2. The Indian Economy (a) Pre-independence Land system Commercialisation of agriculture Deindustrialisation Drain Theory Development of Indian Railways
(b) Post-independence Planning models and experience till Seventh Plan Change in composition of national income—Agriculture, Industry & Services. Agriculture—Green Revolution Industry—Role of Public Sector
(c) Post-Liberalisation Changing role of Planning (from centralised to indicative, participatory and decentralised planning.) Salient features of NEP Progress in Reforms—1st and 2nd generation Reforms Role of WTO & IMF Monetary and Fiscal Policies Poverty and inequality (d) The West Bengal Economy-A historical perspective |
| i. Brief economic history of the colonial period.
ii. Economic & demographic consequences of Partition. iii. Evolution of Land and Tenancy Reforms (1950-1980) and its economic consequence iv. Changing composition of SDP v. Social development indicators-health, education, environment vi. West Bengal: in relation to other major States of India. |
|
| ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING : | |
| Paper – I : | Electrical Circuits and Network :
Circuit components, network graphs, KCL, KVL.
Circuit analysis methods : nodal analysis/mesh analysis, basic network theorems and applications. Transient analysis : RL, RC and RLC circuits. Sinusoidal steady state analysis, resonant circuits and applications. Coupled circuits and applications. Balanced 3-phase circuits. Two-port networks. Signals & Systems :
Representation of continuous-time and discrete-time signals & systems, Analysis of signals & systems by Laplace Transform and Z-Transform, Poles & Zeroes, Fourier Transform, Sampling and Reconstruction of Signals, analysis of discrete time signals by DFT and FFT.
Field Theory :
Electric Field : Gauss’s Integral Law, Electric Dipole Fields, Electric Polarisation and its relation to the Permittivity of Di-electric media. Gauss’s Law in differential form. Poisson’s and Laplace Equations in different co-ordinates. Energy stored in Electric Field.
Magnetic Field : Ampere’s Law and Biot-Savart’s Law, Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction, Self & Mutual Inductance, Energy in Magnetic Field, Force due to Magnetic Field.
Maxwell’s equations, Wave propagation in bounded media. Boundary Conditions. Reflection and Refraction of Plane Waves, Distributed Parameter circuits.
Analog & Digital Electronics :
Characteristics and equivalent circuits (large and small-signal) of Diode, BJT, JFET and MOSFET. Diode circuits : Clipping, clamping and rectifiers. Biasing and bias stability of BJT.
Amplifiers : Single and multi-stage, differential, operational, feed-back and power. OPAMP circuits, Active Filters. Sinusoidal oscillators : transistor and OPAMP configurations. Function generators and wave-shaping circuits. Boolean algebra; minimization of Boolean functions; logic gates. Digital IC families (TTL,MOS,CMOS). Combinational circuits : Arithmetic circuits, code converters, multi plexers and decoders. Sequential circuits : latches and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers. Comparators, timers, multivibrators. Sample and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs. Semiconductor memories. Logic implementation using MUX / DMUX and programmable devices (ROM, PLA, FPGA).
Measurement and Instrumentation : |
|
Error analysis, measurement of current, voltage, power, energy, power-factor, resistance, inductance, capacitance and frequency, bridge measurement, Use of CT and PT.
Electronic measuring instruments : multimeter, CRO, digital voltmeter, frequency counter, Q-meter.
Transducers : Thermocouple, thermistor, RTD, LVDT, strain-gauge, piezo-electric crystal, use of transducers in measurements of non-electrical quantities.
Data acquisition systems.
Control System :
Elements of control systems, block-diagram representation, open-loop & closed-loop systems, principles and applications of feed-back.
LTI systems : time-domain and transform-domain analysis.
Stability : Routh Hurwitz criterion, root loci, Nyquist’s criterion, Bode plots. Design of lead-lag compensators. Proportional, PI, PID controllers.
State-variable representation and analysis of control systems. Principles of discrete-control system. Microprocessors and Microcontrollers :
Microprocessor architecture, Address/Data and Control lines, Timing Diagram, Internal Registers, Interrupt mechanism (hardware/software), Memory interfacing, I/O interfacing, Programmable Peripheral devices, Microcontrollers and Embedded Processors – its architecture. |
|
| Paper – II : | Electrical Machines :
Principles of electromechanical energy conversion : Torque and emf in rotating machines.
DC machines : characteristics and performance analysis, starting and speed control of motors. Transformers : principles of operation, analysis, regulation, efficiency. 3-phase transformers. 3-phase induction machines and synchronous machines : characteristics, performance analysis, starting, speed control and braking.
Special machines : Stepper motors, brushless DC motors, permanent magnet motors, single-phase induction motors, AC series motors.
Power Electronics & Electric Drives :
Semi-conductor power devices : diode, transistor, thyristor, triac, GTO and Power MOSFET – static characteristic and principles of operation.
Diode rectifiers, phase control rectifiers, triggering circuits. Bridge converters: fully-controlled and half-controlled. Principles of choppers and inverters.
Basic concepts of speed control of dc and ac motor drives. Linear power supplies and SMPS.
Power Systems and Protection :
Construction and parameters of overhead lines and underground cables, p and T models of lines, principles of active and reactive power transfer, per unit representation, load flow analysis, control of voltage, active and reactive power, frequency control, tie-line control, economic operation, analysis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults.
Concept of power system stability : rotor angle stability and voltage stability, swing equation, equal area criterion.
Line compensation, static VAR system, basic concepts of HVDC transmission and Flexible AC Transmission System (FACTS).
Power system protection : principles of overcurrent, differential and distance protection, protection of |
| lines, transformers, busbars and generators.
Circuit breaker : principles of current interruption and arc quenching, restriking voltage, making capacity and breaking capacity, different types of circuit breakers.
Introduction to energy control centre : SCADA and RTUs.
Distribution system : radial and ringmain systems, calculation of voltage drop.
Analog & Digital Communication :
Signals and Spectra: properties of Signals and Noise.
Power Spectral Density and Autocorrelation, Random Signals, Random Process. Analog modulation Techniques : AM, FM and PM. Pulse Amplitude modulation and digital communication : PAM, Delta, ASK, FSK, PSK, MSK. Performance of communication systems corrupted by Noise : signal-to-noise ratio, C/I ratio.
Energy Sources :
Present Electrical Power Scenario of West Bengal & India (Generation & Utilisation). Main components of Thermal and Hydel Power Plant. Basic theory of small Hydropower, Solar (thermal and photovoltaic), Wind & Bio-energy and other renewable sources.
Pollution from energy sources. Energy Conservation & Storage. Energy Management and Audit.
Electrical Utilisation & Illumination Engineering :
Electric heating. Resistance, Arc & Induction Furnaces – basic principles and application, Dielectric Heating – principles & application.
Radiometric and Photometric quantities, Laws of Illumination, Photometry.
Lamps : incandescent, discharge and solid-state types, their efficacies, features and applications.
Magnetic choke and glow starter operation in TL circuit. Difference between electronic and magnetic ballast.
Luminaire – its functions.
General indoor lighting design by Lumen method. |
|
| GEOGRAPHY : | |
| Paper – I : | PRINCIPLES OF GEOGRAPHY (GROUP – A : PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY)
Geomorphology Nature and composition of earth’s crust; Structure of earth’s interior; Origin, distribution and permanency of Continents and Ocean Basins; Theories of isostasy, continental drift, and plate tectonics; Earth movements – types and effects; Fundamental concepts in geomorphology; Gradational processes – weathering and masswasting; Landforms due to fluvial. glacial. aeolian, coastal and karst processes; Evolution of landscape – cyclic and non-cyclic models; Global hydrological cycle.
Climatology Atmosphere – nature, composition and structure; Elements and factors of weather and climate; Insolation and Heat-budget; General circulation of winds, Jet Streams and Monsoons; Condensation and Precipitation; Airmass and fronts; Tropical and Extra- tropical cyclones; Thunderstorm and tornado; Climatic classification – principles and application(Koppen, Thorntwaite, Trewartha); Global climatic changes.
Oceanography Origin of continents and ocean basins; Bottom topography of ocean basins: Indian, Pacific & Atlantic Oceans; Nature, origin and characteristics of continental shelves and slopes, submarine canyons and coral reefs and atolls; Ocean currents: Indian, Pacific and Atlantic oceans; Physical and Chemical properties of ocean water: temperature, salinity and |
| density; TS Diagram and Watermass; Ocean Deposits; Marine Resources.
Environmental Geography Nature and composition of Biosphere; Concepts relating to Ecosystem – production and decomposition, homoeostasis, energy environment, productivity, food chain, food web, trophic structure, ecological niche, ecological pyramids, and ecological crisis; Ecosystem – principles and components; Components, Bio-energy Cycles and Biogeochemical cycles; Major Ecosystems of the world; Environmental degradation and conservation; Environmental pollution – land, water, air and noise; Natural hazards and natural disaster characteristics, mitigation and global efforts.
Cartography The Earth as a Cartographic Problem – size and shape; co-ordinate system; scale and map projection; Principles and properties of Polar Zenithal. Conical. Cylindrical and Conventional projections (all normal case); Thematic mapping – types and techniques; Principles of Surveying and Levelling with Chain, Plane Table, Dumpy level and GPS; Remote Sensing nature and principles; Geographical Information System – evolution, components, and functionality.
GROUP – B : HUMAN GEOGRAPHY Economic Geography Concepts and theories of resources; Locational analysis of agriculture (intensive subsistence in monsoon lands, extensive commercial farming in temperate lands, plantation farming in the tropics and dairy farming in the temperate grasslands), lumbering, fishing, mining (coal, petroleum and iron ore), power production (hydel and nuclear) and manufacturing (iron & steel, aluminium, and cotton textile); Economic models – landuse (Von Thunen), industry (Weber, Hoover, Pred). Economic systems and economic landscape – characteristics and evolution (Rostow, Myrdal, and Isard). Global economic blocks – patterns and functions.
Population Geography Factors and measures of population growth; Malthus, Neo-Malthusianism, Optimum, Social and economic, Biological and natural and Demographic transition theories of population growth; Pattern of World population growth; Migration – nature, theories and consequences on society; Population distribution – density and global pattern; Global patterns and trends of population composition (age-sex structure and occupational structure).
Social & Political Geography Concept of space: absolute & relative; Social structure: stratification and differentiation; Social Processes; segregation, adaptation, assimilation and integration; Heartland and Rimland theories; Principles of boundaries and frontiers
Settlement Geography Origin and Growth of Settlements; Function, morphology, types and patterns of Rural settlements; Urban growth and urbanization; Classification, functions, and morphology of towns and cities; Models of urban growth – Burgess, Hoyt, Harris and Ullman, Mann. Urban gradients and densities; Residential areas – patterns and processes; The Central Business District – characteristics, delimitation and changes; The Central Place Theory and the Ranksize rule, The Urban field and inter-urban movement.
Regional Development and Planning Regions – concepts, types and methods of regionalization; Regional diversity and disparities in development; Regional development – role of resource base, technology and information system, agriculture and industry, transport and communication, trade and commerce; Regional development theory – Perroux and Isard; Regional planning – basic principles and types; Environmental issues in regional planning and planning for sustainable development; Planning regions – concepts and delineation; State as a planning unit and micro-level planning with special reference to India. |
|
| Paper – II : | REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY GROUP – A: GEOGRAPHY OF INDIA
Physical Geography Location and space relationship with neighboring countries; structure and Relief; Climate and Drainage; Soil and Natural Vegetation Resource Base Distribution, utilization and Conservation of Land (soil), Water (freshwater), Water Disputes interstate and neighboring countries, Mineral (iron ore, manganese, bauxite, |
| mica), Energy (coal, oil, natural gas, and Non – Conventional sources like wind, tidal and solar power) and Biotic Resources
Economy Indian agriculture – nature and characteristics; Development of Agriculture during the Plan periods; Green Revolution; Distribution and characteristics of cultivation of rice, wheat, jute cotton, tea, and coffee; Agricultural Regions, Industrial development and industrial policy during the Plan Period; Locational Dynamics, Growth and Development of the Iron & Steel, Aluminum, Engineering, Oil Refining, Cotton Textile, Jute, Sugar, Paper, cement and automobile industries; Growth and Development of Transport and Communication System (Road, Rail, Water, and Air); Nature and Development of Trade – national and foreign specially with the SARC and ASEAN countries; Trade Balance.
Population Population as a Resource; Relation between Population and Socio-economic Development; Population Growth – spatial and temporal variations; Population Distribution and population – resource relationships; Population Composition and social implications age, sex, literacy, religion, and caste; Urban Growth and Urbanization – characteristics and patterns, factors and processes; Population Problems and Population Policy during the Plan periods. GROUP – B: GEOGRAPHY OF WEST BENGAL
Physical Geography Location with Geographical Personality; Physiographic Divisions – structure and relief; Climate – seasonal weather conditions; Agro-climatic regions; Drainage systems and problems; Soil – types and fertility, erosion and conservation; Natural Vegetation – types and distribution, deforestation and afforestation.
Resource Base Distribution, utilization and Conservation of Land, Water, Mineral, Energy (both Conventional and Non – Conventional) and Biotic Resources Economy Landuse – characteristics and correlates; Irrigation and Agriculture – development during the Plan periods; Rice, jute, and tea – cultivation, crop ecology, production and problems; Crop Combination Regions; Impact of Green Revolution; Industrial Regions – growth, development and problems; Trade and Transport – nature and status of development; issues of development
Population Population as a Resource; Relation between Population and Socio-economic Development; Growth and Distribution (absolute, and density – crude, physiological and habitational); Population Composition – age, sex, literacy, occupation, religion, and caste; Urban Growth and Urbanisation – characteristics, patterns and factors; Population Problems and Population Policy during the Plan periods |
|
| GEOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | I. General Geology:
Composition of the planets and meteorites. Abundance of elements in the universe and earth. Origin of the Earth. Internal constitution of Earth. Heat flow and geothermal gradient. Gravity, gravity anomalies on earth and Isostasy. Earth as a magnet, magnetic anomalies. Earth’s internal processes, volcanism and global distribution of volcanoes. Earthquakes: causes, effects, earthquake belts. Seismic zones of India. II. Structural Geology: Stress and strain- basic concepts, analysis of stress-strain in two-dimension, stress and strain ellipse. Behavior of rocks under stress. Stress-strain relationships of elastic, plastic and viscous materials. Unconformity: different types and their recognition Fold and Fault: geometry and classifications, mechanisms. Fold and thrust belt. Shear zones and shear sense markers. Classification of joints, foliation, lineation and their relations with folds. III. Geomorphology and Remote Sensing: Basic concept of geomorphology, common landforms related to action of wind, river and glacier; coastal landforms. Geomorphology and its relation to structure and lithology. Aerial photographs and their interpretations. The Electromagnetic spectrum. Orbiting satellites and sensor systems. Indian remote sensing satellites. Applications of remote sensing in geology. Basic concepts of GIS and GPS. |
| IV. Geotectonics:
Continental drift and sea-floor spreading hypotheses, linear magnetic anomalies. Plate tectonics- types of plate-boundaries and their characteristic features. Island arc, continental rift system, active and passive continental margins. Palaeomagnetism. Mountain building and orogeny. V. Palaeontology: Definition, types and significance of fossils. Modes of preservation of fossils. Species concept in biology and binomial nomenclature. Index fossils and their significance. Description of hard-part morphology of brachiopoda, cephalopoda, pelecypoda and gastropoda. Evolutionary trend in Hominidae, Equidae and Proboscidae. Description and importance of Siwalik fauna, Gondwana flora and fauna. VI. Stratigraphy: Geologic time scale, Principles of determination of absolute and relative ages of rocks and geological events. Importance of unconformities in stratigraphy. Lithostratigraphic, biostratigraphic, magnetostratigraphic, chronostratigraphic and geochronologic units and their inter-relations. Geological evolution of Precambrian terrains of Dharwar, Singbhum and Rajasthan. Evolution of Proterozoic Cuddapah and Vindhyan basins. Geological evolution of the following Phanerozoic basins/ successions of India: Gondwana, Spiti, Kutch, Siwalik, Assam and Bengal. VII. Hydrology and Engineering Geology: Hydrologic cycle, vertical distribution of groundwater, porosity, permeability, hydraulic conductivity, transmissivity and storage coefficient. Aquifers: properties and classifications. Exploration for groundwater, groundwater recharge, rainwater harvesting. Groundwater provinces of India and West Bengal. Engineering properties of rocks. Geological investigations for dams, tunnels and reservoirs. Landslides: classification, causes and prevention. |
|
| Paper – II : | I. Mineralogy:
Elements of crystal symmetry, Hermann-Mauguin symmetry notation. Crystal classes, crystal systems, crystallographic axes- interfacial angle and axial ratio. Crystal faces and linear directions, their nomenclature and interrelationship. Crystal forms in different crystal classes and crystal habits. Twining. Concept of space lattice, space group and unit cell.
Physical properties of minerals. Classification of minerals on the basis of chemical composition. Crystal chemistry: bonding, coordination principles, isomorphism, polymorphism, solid solution, exsolution. Elementary thermodynamics. Structural classification of silicate minerals. Physical, chemical and optical properties of pyroxene, amphibole, feldspar and carbonate groups. Optically isotropic, uniaxial and biaxial characters of minerals. Pleochroism, birefringence, extinction angle, double refraction, interference figures and optic sign.
II. Igneous Petrology: Forms of igneous rock bodies. Description and origin of common structures and textures of igneous rocks. Phase rule and its derivation; concept of the liquidus; one-, two- and three-component systems. Diopside-anorthite, forsterite-silica, albite-anorthite, diopside-forsterite-silica systems. Bowen’s reaction series. Processes of diversification of igneous rocks: differentiation, assimilation, and partial melting. Basis of classification of igneous rocks and different classification schemes– CIPW norm; IUGS classification. Petrography and petrogenesis of: granite, basalt, anorthosite, alkaline and , ultramafic rocks.
III. Metamorphic Petrology: Agents and types of metamorphism. Texture of metamorphic rocks, metamorphic crystallization. Classification of metamorphic rocks. Concept of metamorphic grade and metamorphic facies, facies series. Prograde and retrograde metamorphism. Metamorphism and tectonics. ACF, AKF diagrams. Regional metamorphism of pelitic and mafic rocks, and contact metamorphism of impure carbonate rocks. Metasomatism and granitisation. Migmatites. Granulite terrains of India.
IV. Sedimentology: Processes of formation of sedimentary rocks, provenance, diagenesis and lithifaction. Textural components; Textural parameters- porosity, permeability. |
| Classification of sedimentary rocks-terrigenous and chemogenic. Types of fluid. Aqueous fluid flow- current and wave.
Primary sedimentary structures, their processes of formation and significance. Flow regimes, bed forms, their internal structures and fields of stability. Facies, facies association and facies models- fluvial, deltaic and beach-barrier bar systems. Sandstone, conglomerate and limestone: definition, composition, classification.
V. Environmental Geology: Natural hazards – earthquake, tsunami, volcanic eruption, landslides, floods, and droughts. Impact of human activities on wetlands and forests, use of fertilizers on land. Pollution of groundwater, surface water and ocean. Composition of air, air pollution, effects of air pollution on human health. Impact of mining on atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere and hydrosphere. Industrial and radioactive waste disposal. Environmental Protection, legislative measures, processes of mitigation.
VI. Economic Geology: Classification of ore deposits, protore, ore, gangue, tenor and grade. Ore forming processes: magmatic, sedimentary, metamorphic, hydrothermal and supergene. Controls of ore localization, ore textures and structures. Metallogenic provinces and epochs. Geology of important metallic deposits of India: chromite, copper, iron, lead-zinc, manganese and uranium-thorium. Geology of important non-metallic deposits of India: bauxite, mica, phosphates, barite, diamond and graphite. Rock as construction material. Raw materials used in iron and steel, cement, refractories, fertilizer industries. Coal: its origin, chemical, macroscopic and microscopic constituents, ranks, classification, grade and utilization. Distribution of coal in India. Petroleum and natural gas deposits with special reference to their origin, migration and accumulation. Distribution of petroleum and natural gas in India. Methods of mineral prospecting (geological, geophysical and geochemical), mineral beneficiation and ore dressing. |
|
| HISTORY : | |
|
Paper– I : |
ANCIENT AND MEDIEVAL INDIA UNIT A
1. Sources :
Archaeological Sources: Exploration, Excavation, Epigraphy, Numismatics, Monuments.
Literary Sources: Indigenous, Biography, Religious Literature, Creative Literature, Scientific Literature, Literature in Regional Languages.
Foreign Accounts: Greek, Roman, Chinese and Arab Writers.
2. The Harappan Civilization : Third to Second Millenium B.C.E
Origin, Date, Extent, Characteristics, Decline, Survival and Significance, Art and Architecture.
3. The Iron Age in India, Vedic Society and the Megalithic Culture: 1500 B.C.E to 6th Century B.C.E.
Distribution of pastoral and farming cultures outside the Harappan orbit. Early Vedic Society, Polity and Economy. Changes in the later Vedic period.
4. Period of Mahajanapadas :
Formation of territorial States (Mahajanapada): Republics and Monarchies; Spread of Jainism and Buddhism; Rise of Magadha and the Nandas. Iranian and Macedonian invasions and their impact.
5. The Mauryan Empire:
Foundation of the Mauryan Empire, Chandragupta, Kautilya and Arthasastra; Asoka; Concept of Dharma; Edicts; Polity, Administraton; Economy; Art, Architecture and Sculpture; External contacts; Religion; Spread of religion; Literature. Disintegration of the Empire.
6. Post-Mauryan Period
Northern India: The Sungas and the Kanvas, The Indo-Greeks, Sakas, Kushanas, Western Kshatrapas, Contact with the outside world; The Deccan and Southern India: The Satavahanas, Tamil |
| States of the Sangam Age: Administration, Economy: land grants, trade guilds and urban centres; Social conditions. Culture and Religion: Rise of Mahayana Buddhism and Buddhist Centres; Literature and culture; Art and architecture and science.
7. Guptas, Vakatakas and Vardhanas:
Samundra Gupta, Chandragupta-II: Gupta Polity and administration, Economic conditions, land grants, Caste system, Position of women, Education and educational institutions; Nalanda, Vikramsila and Valabhi, Creative Literature, scientific literature, art and architecture.
Decline of the Gupta Empire; changes in Trade network, Decline of urban centres, Indian Feudalism.
8. The Post Gupta Period and the Rise of Regional States
The Kadambas, Pallavas, Chalukyas, Palas, Senas, Rashtrakutas, Paramaras, Cholas, Hoysalas, Pandyas.
Regional Polities and Administration, Local Government, Land administration, Economy, Trade Guilds.
Religion: Proliferation of Religious Sects in Buddhism, Vaishnava and Saiva religions. Tamil Bhakti Movement, Shankaracharya; Vedanta.
Cultural Aspects, Regional Languages and texts, Literature, Growth of art and architecture, Sculpture, Temple Architecture; Education and Literature, major philosophical thinkers and schools, ideas in Science and Mathematics.
Arab conquest of Sind; Alberuni.
UNIT B
1. Major political developments in India during 13th to 15th Centuries:
Campaigns of Mahmud Ghazni, Muhammad of Ghor — The foundation of the Delhi Sultanate and the early Turkish Sultans ‒ Qutbuddin Aibak to Balban — The Khalji revolution ‒ Alauddin Khalji, conquests and economic reforms — , Muhammad‒bin‒Tughlaq and his projects — Firuz Tughlaq— agrarian measures, public works‒ Decline of the Tughlaqs.
Provincial Kingdoms — Bengal under the Iliyas Shahi and Hussain Shahi Dynasties—Bahmani and Vijaynagar Empires — Kashmir and Gujarat.
2. Society, Culture and Economy during 13th and 15th centuries:
Social and Cultural Assimilation — Sufi and Bhakti Movements—Kabir, Nanak, Chaitanya, Namdeva, Growth of Regional Languages and Literature — Nature of the State — agriculture, revenue system (iqta) trade and Commerce — art and architecture.
3. Major Political Developments in India during 16th and 18th Centuries:
Coming of the Mughals —Babur and the foundation of the Mughal Empire, — Afghan — Mughal Contest for supremacy—Humayun and Sher Shah — Consolidation of the Mughal Empire— Akbar, Jahangir and Nur Jahan, Shah Jahan and Aurangzeb — The Mughal Central State and regional powers— Rajputs, Afghans, Marathas, Sikhs, Deccan, Awadh and others. Peasants in Revolt — Jat, Satnami etc. Later Mughals — Fall and Disintegration of the Empire —Rise of the Regional States ‒ Bengal, Hyderabad, Awadh and the Marathas.
4. Society, Culture and Economy during 16th and 18th centuries:
Administrative System- Sher Shah to Akbar, Jagir and Mansabdari systems, — Evolution of religion under the Mughals — Sulh-i-Kul and Din-i-Ilahi — Mughal art, architecture, painting, music and literature, Mughal economy and Society—Condition of the peasants — urbanisation —trade and commerce and the mercantile classes ‒ Coming of the European merchants and ‘trade revolution’. |
|
| Paper – II : | MODERN INDIA AND THE WORLD UNIT A
1. European Penetration and Rise of British power in India:
• The early European Settlements in India in the 17th and 18th centuries – The Anglo – French rivalry.
• The British East India Company and the Bengal Nawabs – the EIC as sovereign ruler of Bengal (From Plassey to Buxar), Grant of Dewani. |
|
• British relations with and subjugation of the other principal Indian powers – Oudh, Hyderabad, Marathas, the Sikhs, and Mysore. 2. Indian economy under the British Colonial Rule:-
(A) Impact of Colonial rule on Indian agrarian economy:-
• Land revenue settlements‒ Permanent, Ryotwari and Mahalwari Settlements.
• Economic Impact of revenue settlements – Commercialization and its consequences.
• Rural Indebtedness and growth of landless labour.
• Famine and poverty.
(B) Changing nature of India’s trade and industry under the colonial rule:-
• Dislocation of traditional trade and commerce
• De-industrialization – decline of village industries and town handicrafts
• Railways
• Growth of Foreign capital and rise of modern industries.
3. Indian Society in transition: Cultural Encounter and Socio-cultural changes:
• Introduction of western education and modern ideas
• Reform movements – Ram Mohan Roy, Brahmo Samaj, Young Bengal, Vidyasagar, Arya Samaj, Vivekananda and Ramkrishna Mission.
• Women’s Question and Indian Reformers
• The Growth of modern vernacular literature, press and public opinion, growth and spread of scientific ideas.
• The Faraizi and Wahabi movements; The Aligarh movement, Deoband School.
• Social Reform movements in the late 19th and early 20th centuries (including depressed caste movements) – a broad overview.
4. Resistance to the British rule:
• Early uprisings against the British rule in 18th and 19th centuries (1757 – 1856) with special reference to Bengal and eastern India.
• The Revolt of 1857 – genesis, course, character, causes of its failure and its impact.
• The Act of 1858 and the establishment of the British Raj.
5. Growth of Nationalism (1858 – 1918):
Factors leading to birth of Indian Nationalism – Early Political Associations – The foundation of the Indian National Congress (1885) – The Safety-valve thesis – Programme and objectives of the early Congress – Economic Nationalism and Drain Theory – The moderates and the extremists – the Partition of Bengal (1905) – The Swadeshi Movement in Bengal and other provinces – the economic, cultural and political aspects of Swadeshi movement.
6. Gandhian Era (1919 – 1947):
Rise of Gandhi – Character of Gandhian nationalism – the Rowlatt Satyagraha – The Khilafat – the Non Co-operation movement – Simon Commission, Nehru Report and Round Table Conferences – Civil Disobedience Movement – Quit India Movement.
The Left: The Left within the Congress and Jawaharlal Nehru – Subhas Chandra Bose and the INA – the Congress Socialist Party – the Communist Party of India – other left parties. The Peasant Movement. The Working Class and Trade Union Movements. Women’s organisations, development of women issues and the role of women in nationalist movement. The Peoples’ Movement in Princely States. The Post – War upsurge Growth of Muslim Separatism – Rise of Muslim League – Demand for Pakistan Hindu Nationalism |
| Depressed Classes and caste politics with special reference to the role of B. R. Ambedkar. Communalism, British Policy, Partition and Independence.
7. The Constitutional Developments (1773 – 1947):
The Regulating Act, Pitt’s India Act and the Charter Acts.
The Acts of 1861 and 1892 – the Morley Minto Reforms (1909) – the Montague-Chelmsford Reforms (1919) – Government of India Act (1935) – Working of Provincial Ministries – Cripps Mission, Wavell Plan and Cabinet Mission – Act of Indian Independence (1947).
8. Consolidation as a Nation after 1947:
Framing of the Indian Constitution – Integration of Princely States – the question of National Language – the linguistic reorganisation of States, making of India’s foreign policy – Non-alignment and the Third World – India and her neighbours.
UNIT B
01. Enlightenment and Modern Ideas:
(i) Major ideas of enlightenment ; and its impact (ii) French Revolution and its aftermath: 1789 – 1815 (iii) The American War of Independence (1776). The American civil War
02. Industrialization:
(i) Industrial Revolution in England: causes, nature, impact. (ii) Industrialization in other countries: USA, Germany, Russia, Japan.
03. Nationalism:
(i) Rise of nation states in Europe: Italy & Germany.
04. Imperialism, Colonialism and War:
(i) Capitalism, imperialism, scramble for colonies. (ii) Origins and impact of the First World War (iii) Making of the Russian Revolution & establishment of a Socialist State.
05. World history from 1919 to 1945:
(i) League of Nations, collective security. (ii) Rise of Nazism and Fascism : Germany, Italy & Japan. (iii) Second World War: Causes and consequences.
06. Asia and Africa after World War II: (i) Chinese Revolution of 1949 (ii) Nationalist movements and decolonization in South and South East Asia. (iii) Changes in Africa: Egypt and South Africa, End of Apartheid.
07. Cold War & Global scenario:
(i) Origins and Growth of cold War (ii) UNO and global disputes – Korea, Congo, Cuban crisis. (iii) Emergence of Third World and NAM
08. Collapse of Soviet Union
(i) Disintegration of the Soviet Union: Causes & Consequences (ii) End of the Cold War (iii) Political Changes in Eastern Europe. |
|
| LAW : | |
| Paper – I : | Constitutional Law of India :International Law : Jurisprudence. |
| Paper – II : | Law of Crimes and Torts : Law of Contracts and Mercantile Law : Indian Evidence Act. |
| MATHEMATICS : | |
| Paper – I : | Paper-I
(1) Linear Algebra: Vector spaces over R and C, linear dependence and independence, subspaces, bases, dimension; existence of basis for finite dimensional vector spaces; deletion and replacement theorem. Linear transformations, rank and nullity, matrix of a linear transformation. Algebra of Matrices; Row and column reduction, Echelon form, congruence’s and similarity; Rank of a matrix; Inverse of a matrix; Solution of system of linear equations; Eigenvalues and eigenvectors, characteristic polynomial, Cayley-Hamilton theorem. Euclidean space, Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization. Symmetric, skew-symmetric, Hermitian, skew- |
| Hermitian, orthogonal and unitary matrices and their eigenvalues. Quadratic forms, diagonalization of symmetric matrices.
(2) Real Analysis I: Real number system as an ordered field with least upper bound property; Sequences, limit of a sequence, Cauchy sequence, completeness of real line; Series and its convergence, absolute and conditional convergence of series of real and complex terms, rearrangement of series. Open sets, limit points, closed sets. Bolzano-Weierstrass theorem.
Functions of a real variable, limits, continuity. Intermediate value theorem. Differentiability, Rolle’s theorem, mean-value theorem. Higher order differentiation, Leibnitz’ formula, Taylor’s theorem with remainders. L’Hospital’s rule. Maxima and minima; asymptotes; envelopes.
(3) Real Analysis II: Compact sets. Nested interval theorem. Heine Borel theorem. Uniform continuity of functions, properties of continuous functions on compact sets.
Riemann Integration. Riemann’s definition of definite integrals; Darboux theorem; Indefinite integrals; Fundamental theorems of integral calculus. Improper integrals.
Sequences and series of functions. Uniform convergence. Term by term differentiation and integration. Power series. Cauchy-Hadamard test. Weierstrass approximation theorem (statement only). Fourier series.
(4) Analytic Geometry: Cartesian and polar coordinates in two and three dimensions. Transformation of rectangular axes. Straight lines.
Conic sections: Circle, parabola, ellipse, hyperbola and pair of straight lines. Second degree equations in two variables, reduction to canonical forms and classification of conics. Tangents and normals to conic sections.
Planes in three dimension; shortest distance between two skew lines. Second degree equations in three variables, reduction to canonical forms. Sphere, cone, cylinder, paraboloid, ellipsoid, hyperboloid of one and two-sheets: tangent planes and normals. Surfaces of revolution. (5) Differential Equations: Formulation of differential equations; Equations of first order and first degree, integrating factor; Orthogonal trajectory; Equations of first order but not of first degree, Clairaut’s equation, singular solution.
Second and higher order linear equations with constant coefficients, complementary function, particular integral and general solution.
Second order linear equations with variable coefficients, Euler-Cauchy equation; Determination of complete solution when one solution is known using method of variation of parameters.
Laplace and Inverse Laplace transforms and their properties; Laplace transforms of elementary functions. Application to initial value problems for 2nd order linear equations with constant coefficients.
Formation of partial differential equations. Solutions of 1st order PDE, Lagrange’s method and Charpit’s method.
(6) Statics: Equilibrium of a system of coplanar forces, Astatic equillibrium; Stability of equilibrium, equilibrium of forces in three dimensions. Work and potential energy, friction; Principle of virtual work.
(7) Particle Dynamics: Rectilinear motion, simple harmonic motion. Damped harmonic oscillation. Motion of a particle in a plane. Work and energy, conservation of energy. Orbits under central forces. Planetary motion and Kepler’s laws. Artificial satellite. |
|
| Paper – II : | (1) Classical Algebra
Prime integers. Existence of infinitely many primes. Relatively prime integers. Congruence. Chinese remainder theorem. Fermat’s theorem. Complex numbers; de Moivre’s theorem; complex functions. Polynomial with real coefficients. Fundamental theorem of algebra. Relation between roots and coefficients. Symmetric functions of roots. Descartes’ rule of sign. Cardan’s method of solving a cubic equation. Ferrari’s method of solving a biquadratic equation. Binomial equations and special roots. Inequalities AM ≥ GM ≥ HM and their generalizations. Cauchy Schwarz inequality.
(2) Abstract Algebra Sets and relations; equivalence relations. Groups, subgroups, cyclic groups, cosets, Lagrange’s Theorem, normal subgroups, quotient groups, homomorphism of groups, basic isomorphism theorems, permutation groups, Cayley’s theorem. Rings, subrings and ideals, homomorphisms of rings; Integral domains, principal ideal domains, Euclidean domains and unique factorization domains; Polynomial Rings. Fields, quotient fields. Finite fields Zp, for prime p. |
| (3) Multivariate Calculus & Vector Analysis
Vector valued functions of one real variable. Continuity and differentiability. Velocity and acceleration. Functions of two or three variables: limits, continuity. Directional derivative, partial derivatives, Jacobian. Chain rule. Higher order partial derivatives. Euler’s theorem. Maxima and minima, Lagrange’s method of multipliers. Double and triple integrals; Areas and volumes. Scalar and vector fields. Differentiation of vector fields. Gradient, divergence and curl. Higher order derivatives; Vector identities and vector equations. Line integral, Surface integral. Green’s theorem and Stokes’ theorem.
(4) Metric Space & Complex Analysis: Metric spaces. Open sets and closed sets. Cauchy sequence and convergence. Completeness. Total boundedness. Compactness. Continuity, uniform continuity. Connectedness. Separable metric spaces. Baire category theorem. Examples: Rn, Cn, Space of real valued continuous functions on [a,b]. ep spaces. Extended complex plane, stereographic projection. Differentiability of complex functions; Cauchy-Riemann equations, Analytic functions, harmonic functions; relation between analytic and harmonic functions.
(5) Numerical Analysis and Computer programming: Numerical Analysis: Interpolation. Newton’s (forward and backward) interpolation, Lagrange’s interpolation. Solution of algebraic and transcendental equations of one variable by bisection, fixed point iteration; Regula-Falsi and Newton-Raphson methods; solution of system of linear equations by Gaussian elimination and Gauss-Seidel (iterative) methods. Numerical integration: Trapezoidal rule, Simpson’s 1/3rd rule, Gaussian quadrature formula. Numerical solution of ordinary differential equations: Picard, Euler and Runge- Kutta method (4-th order). Computer Programming: Positional number system, Binary, Octal, Decimal and Hexadecimal systems; Binary arithmetic, Conversion to and from decimal systems. Algorithms and flow charts: important features, Ideas about complexities of algorithm, applications in simple problems. Boolean algebra: Huntington postulates for Boolean algebra, algebra of sets and switching algebra as examples of Boolean algebra, duality principle, disjunctive normal and conjuctive normal forms of Boolean expressions. Design of simple switching circuit. Programming using C.
(6) Probability & Statistics: Probability: Classical and frequency definitions of probability. Axioms of Probability. Multiplication rule of probabilities. Conditional probability, Bayes’ theorem. Independent events. Bernouli trials and binomial law. Probability distribution. Distribution function (Discrete and continuous) of one variable: Binomial, Poisson, Gamma, Uniform and Normal. Transformation of random variables. Two dimensional probability distributions (Discrete and continuous): Uniform and normal. Transformation of random variables. Marginal and Conditional distributions. Mathematical expectation: Mean, variance, moments, central moments. skewness and kurtosis. Median, mode, quartiles. Moment-generating function. Characteristic function. Covariance, Correlation coefficient. Conditional expectation. Regression curves, least square regression lines and parabolas. Chi-square and t-distributions and their important properties. Tchebycheff’s inequality. Convergence in probability. Statements of: Bernoulli’s limit theorem. Law of large numbers. Statement of central limit theorem. Statistics: Sample characteristic and their computation. Sampling distributions of the sample mean and variance. Estimation of parameters: Method of maximum likelihood. Interval estimation for parameters of normal population. Bivariate samples. Sample correlation co-efficient. Least square regression lines and parabolas. Statistical hypothesis. Simple and composite hypothesis. Best critical region of a test. Neyman-Pearson theorem and its application to normal population. Likelihood ratio testing and its application to normal population.
(7) Linear Programming: Linear programming problems, Graphical method of solutions; hyperspace, convex sets, extreme points. Basic solution, basic feasible solution and optimal solution; Fundamental theorem of LPP; Simplex method; Duality. Transportation and assignment problems. |
|
| MANAGEMENT : | |
| Paper – I : | UNIT I EVOLUTION AND GROWTH OF MANAGEMENT THOUGHT
Concepts, Theory and Practice, The Evolution of Management Thought — Scientific Management School, The Operational or Management Process approach, Behavioural School, Contemporary School, Recent Contributions, Patterns of Management Analysis, Managerial Roles approach
UNIT II PLANNING AND ORGANISING Planning –Nature, Importance, Types, Process, Concept of MBO, Objectives, Policies, Procedures, |
| Strategies
Decision-Making-Approaches, Decision-Making under Certainty, Risk and Uncertainty, Group Decision Making Guidelines The Nature of Organising -Types of Organisations, Organisational Levels, Process of Organising, Line/Staff Authority, Decentralisation of Authority and Delegation of Authority
UNIT III DIRECTING, COORDINATING AND CONTROLLING Direction — Supervision – Span of Management – Factors determining Span Motivation — Elements – Importance – Methods – Morale Leadership–Theories, Approaches-Power and Authority Coordination – Definition – Characteristics- Objectives – Principles – Techniques Controlling –Control Process, Requirements for effective Control, Critical Control Standards and Techniques, Maintenance vs. Crisis Management, Overall Control Process
UNIT IV ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR Foundations of Individual Behaviour– Personality, Perception, Learning, Attitudes & values Foundations of Group Behaviour–Group Process, Group Tasks, Types, Group Development Conflict Management – Management of Change
UNIT V RECENT DEVELOPMENTS Global Management, Managerial Functions in International Business, Business Process Reengineering, TQM-Six Sigma, Information Technology in Management, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP); Supply Chain Management, Management of Innovation |
|
| Paper – II : | MARKETING MANAGEMENT
Marketing Concept; Marketing Environment; Marketing Mix–4Ps vs 4Cs; Consumer Behaviour–Buying Process, Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning; Product—Types, Product Life Cycle; Pricing—Methods; Distribution—Channels; Promotion—Integrated Marketing Communications; Retailing—Recent Trends; Service Marketing—Features 7Ps; International Marketing—Cultural Dimension; Modes of Entry; e- marketing
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Objectives; Functions; Sources of Finance; Working Capital Management; Cost of Capital; Operating and Financial Leverage; Dividend Policies; Capital Budgeting; Financial Control
HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT Importance; difference between Personnel Management and HRM; Role of a HR Manager Human Resources Planning-Objectives-Importance-Process- Manpower Estimation-Job analysis-Job Description-Job Specification Recruitment-Sources of Recruitment-Selection Process-Placement and Induction Retention of Employees; Training and Development- Objectives and Needs-Training Process-Methods of Training-Tools and Aids-Evaluation of Training Programmes Performance Management System-Definition, Concepts, Different methods of Performance Appraisal Grievance Redressal—Concepts. Mechanisms Productivity Management—Concepts, Employee Involvement, Quality Circles, Kaizen Industrial Relations–Collective Bargaining-Settlement of Disputes
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT Concept, SWOT Analysis, PEST Analysis, Porter’s 5 Forces Framework, BCG Matrix, GE Model; Values and Ethics; Corporate Governance; e-governance
QUANTITATIVE TECHNIQUES Assignment; Transportation; Linear Programming (Graphical and Simplex methods); Network Analysis— PERT and CPM |
| MECHANICAL ENGINEERING : | |
| Paper – I : | Paper – I
Theory of machines : Kinematic and dynamic analysis of planer mechanisms. General description and working principles of Belts, Cams, Gears and Gear trains. Inertia force analysis. Flywheels, Governors, Balancing of rotating masses and in-line engines. Linear vibration analysis of mechanical systems – single degree of freedom. Critical speeds and whirling of shafts.
Mechanics of Solids : Simple stress and strain – plane stress and plane strain, cases, Mohr’s circle. Relation of elastic constants. Stress-strain relations due to uniaxial loading. Thermal stress. Bending Moment and Shear |
| Force diagrams of beams. Bending stress and shear stress in Bending. Deflection of beams. Torsion of circular shafts. Combined stresses – thin wall pressure vessels. Struts and columns. Strain Energy concept. Theories of failure.
Engineering Materials : Basic concepts on structure of solids – crystalline materials. Defects in crystalline materials. Binary phase diagram for selected alloys e.g Copper-Zinc, Copper-tin, Iron-Carbon. Ferrous alloys – structure, properties and applications. Heat treatment of steels. Plastics, Ceramics and composite materials – general character and uses.
Manufacturing Science : Merchant force diagram. Tailors’ tool life equation. Machinability. Rigid, Small and Flexible Automation. CNC concepts. Recent machining concepts — EDM, ECM, Ultrasonic, Laser, Plasma. Introduction to Forming processes—Rolling, Forging, Extrusion. Surface finish measurement.
Manufacturing Management : Production Planning and control, Forecasting-moving average, exponential smoothing. Operations scheduling, assembly line balancing. Concept of Product development. Breakeven analysis, Capacity planning. PERT and CPM. Inventory control – ABC analysis, EOQ model. Materials Requirement Planning. Work measurement. Quality management.
Elements of Computation : Computer Organization, Flow charting. Features of common Computer Languages – C/FORTRAN and elementary programming. |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. Thermodynamics :
Open, closed and isolated systems.
Ideal gas law, Ideal thermodynamics processes – pdv work; Thermodynamic Cycle,
1st law and 2nd law of Thermodynamics; Concepts of Internal Energy, Entropy and Reversibility – simple problems.
Concept of Heat engine and Heat pump – efficiency and COP.
Application of 1st and 2nd laws of thermodynamics in closed and open system (SSFF Equation) – simple problems.
2. Vapour power cycles:- Rankine cycle and Modified Rankine cycle – simple problems.
3. Air standard cycles : Otto, Diesel, Dual, Brayton and Bell-Colman. – pv and TS diagrams, simple problems.
4. Refrigeration : Joule Thomson cooling effect, vapour compression cycle – simple problems.
5. IC Engine : a) S.I and C.I engines – basic principles of working, differences and applications, indicator diagram.
b) 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines: working principles and simple engine performance calculations involving hthermal , hmechanical etc. c) Combustion process, Basic idea about knocking and detonation. Cetane and Octan numbers.
d) Carburetion and Fuel injection-description only.
e) Exhaust gas analysis: ORSAT analysis.
f) Air – Fuel ratio – simple problems.
6. Heat Transfer : a) Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Derivations of unsteady 2-D heat conduction equation.
Numerical problems involving 1-D equation. Concept of Bi-number.
b) Steady state heat conduction in extended surface – derivation of related equation and simple problems.
c) Basic concept of free and forces convections – concept and significance of Nusselt number, Reynolds |
| number and Grashof number.
Simple problems with the help of empirical convection correlation for heat transfer. d) Heat exchangers – types and use, Efficiency. Concept of LMTD and NTU method for parallel flow and counter flow heat exchangers – simple problems using LMTD method only.
e) Laws of radiation, Heat exchange between surfaces – black and non-black surfaces, View factor- simple problems.
f) Refrigeration cycles and system components, Choice of Refrigerants, Problems related to performance, COP of refrigeration system.
g) Airconditioning – system components and general description.
Comfort indices. Cooling load calculation using psychrometric chart.
7. Fluid Mechanics :
a) Newton’s law of viscosity: statement and simple problems.
b) Hydrostatic force on submerged flat plate – simple problems
c) Flow parameter measurement – Manometer, Pitot tube, Weir, Venturi meter, Orifice meter – working principles and simple problems.
d) Application of Bernoulli’s principle in simple engineering systems.
e) Head loss in pipe, Darcy – Weisbach equation, Friction factor as function of Reynolds number and relative roughness, Minor loss, Simple system head loss calculations f) Dimensional analysis – various dimensionless quantities, problems involving model tests and their use in prototype performance prediction.
g) Different types of pumps and their applications, Concept of specific speed, System curve and Pump performance curves – operating point.
8. Power plant :
a) Thermal and Hydraulic Power plant components – description only.
b) Different types of hydraulic and steam turbines and their areas of application.
c) Modern High pressure, high duty boilers – description.
d) I.D., F.D and balanced draft boilers – description and simple problems, Dust removal systems – description only.
e) Heat balance, Station and plant heat rates, Plant load factor, Load curve; Station economics – simple problems. |
|
| MEDICAL SCIENCE : | |
| Paper – I : | Human Anatomy : Human Physiology : Biochemistry : Pathology : Microbiology : Pharmacology : Forensic Medicine and Toxology. |
| Paper – II : | General Medicine : General Surgery : Obstetrics and Gynaecology including Family Planning : Preventive and Social Medicine. |
| PHILOSOPHY : | |
| Paper – I : | Problems of Philosophy (European and Indian)
1. Plato and Aristotle : Ideas, Substance; Form and Matter; Causation; Actuality and Potentiality. 2. Rationalism (Descartes, Spinoza, Leibnitz) : Cartesian Method and Certain Knowledge; Substance; God; Determinism and Freedom. 3. Empiricism (Locke, Berkeley, Hume) : Theory of Knowledge; Substance and Qualities; Self and God; Scepticism. 4. Kant : Possibility of Synthetic a priori judgments; Space and Time; Categories. 5. Moore, Russell and Early Wittgenstein : Defence of Common sense; Refutation of Idealism; Logical Atomism; Picture Theory of Meaning. 6. Logical Positivism : Verification Theory of Meaning; Rejection of Metaphysics. |
| 7. Cârvâka : Theory of Knowledge; Metaphysics and Ethics.
8. Jainism : Anekântavâda,; Saptabhanginaya. 9. Buddhism : Four Noble Truths; Pratîtyasamutpâda, Kşaņikavâda, Nairâtmyavâda. 10. Nyâya – Vaiśesika : Theory of Categories; Theory of Pramâna; Self; Theory of Causation; Atomistic Theory of Creation. 11. Sâmkhya : Prakŗti; Puruşa; Causation; Theory of Evolution. 12. Yoga : Citta; Cittavŗtti. 13. Mîmâmsâ : Epistemology; Theory of Validity. 14. Vedânta : Views of Śamkara and Râmânuja on Brahman; Îśvara; Âtman; Jîva; Jagat; Mâyâ; Avidyâ; Adhyâsa. 15. Swâmi Vivekânanda : Practical Vedânta. 16. Sri Aurobindo : Evolution; Involution; Integral Yoga. 17. Rabindranath Tagore: Nature of Man; Surplus in Man. |
|
| Paper – II : | Socio – Political Philosophy and Psychology
1. Social and Political Ideals : Equality, Justice, Liberty: Views of Mill, Locke, Rawls. 2. Individual and State : Rights, Duties and Accountability. 3. Political Ideologies : Anarchism, Marxism, Socialism and Democracy. 4. Humanism; Secularism; Multiculturalism. 5. Social Change : Gandhi, Ambedkar. 6. Mind – Body Problem : Dualism, Philosophical Behaviourism, Person Theory of Strawson. 7. Levels of Mind; Proofs for the existence of the unconscious; Freud’s theory of dream, citta, cittavŗtti (Yoga).
Ethics and Philosophy of Religion
8. Standards of Morality : Utilitarianism (Bentham and Mill), Deontological Theories. 9. Virtue Ethics : Aristotle. 10. Human Rights and Discrimination. 11. Feminism : Liberal and Radical. 12. Environmental Ethics : Bio-centric ethics and Eco-centric ethics. 13. Theories of Punishment; Capital Punishment. 14. Terrorism and Just war. 15. Indian Ethics : Puruşârtha, Concept of Liberation, Anuvrata and Mahâvrata (Jainism), Brahmavihâra (Buddhism). 16. Proofs for the existence of God : Descartes, St. Anselm, Naiyâyikas. 17. Religion without God, Religion and Morality. 18. Religious Pluralism. 19. Nature of Religious Language : Cognitive and Non-cognitive, Analogical and Symbolic. |
| PHYSIOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | 1. Biophysical Principles :
Definition and example of osmosis and buffers; Definition of pH.
2. Biochemical Principles : Definition and chemistry of monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL, LDL, VLDL; amino acides, nucleotides.
3. Metabolism : Glycolysis, TCA Cycle, β-oxidation, deamination, transamination.
4. Nutrition & Dietetics : Definition of food groups, Balanced diet and ACU. Source, functions and deficiency symptoms of vitamin A, B1, B6, B12, C, D, E, and Fe, Zn, Na, K, Ca, I.
5. Blood : Formed elements of blood, functions of hemoglobin; plasma protein. ABO and Rh Blood groups. Overview of innate and acquired immunity.
6. Heart and circulation : Properties of cardiac muscle, cardiac cycle, definition and determination of cardiac output, normal ECG waves.
7. Respiratory System : Carriage of oxygen and carbondioxide, definition of lung volumes and capacities, hypoxia. |
|
8. Renal Physiology : Structure of nephron, formation of urine, non excretory functions of kidney. |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. Nerve-Muscle Physiology: Structure and functions of skeletal muscle & nerve fibre, classification of nerve fibres, neuromuscular junction, neuromuscular transmission, synaptic transmission, origin and propagation of nerve impulse, degeneration and regeneration in nerve fibres.
2. Nervous system : Basic anatomical organization of the neurons system, ascending and descending tracts, reflex arc, classification and properties of reflexes, functions of sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons system, sleep, memory, learning and aphasia.
3. Sensory physiology: Eye-structure of retina, accommodation, myopia, hypermetropia and astigmatism; Ear-structure of middle and inner ear, transmission of sound wave through ear; structure of taste buds and smell receptors.
4. Skin and body temperature regulation: structure and functions of skin and sweat glands, neural and hormonal control of body temperature.
5. Endocrine system: structure and functions of pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas and adrenal gland diseases associated with hypo and hypersecretion of these glands.
6. Reproductive physiology: Histology of testis and ovary, spermatogenesis, ovulation, menstrual cycle. 7. Work physiology: Definition of 02 debt, 02max, static work, dynamic work and physical fitness index (PFI), Body Mass Index (BMI).
8. Environmental and social physiology: Air, water and noise pollution, mass immunization, ORS and concept of safe drinking water. |
| PHYSICS : | |
| Paper – I : | 1. Mechanics:
a) Particle dynamics: Laws of motion, conservation principles. Inertia and inertial frame, Centripetal and Coriolis acceleration. Motion under a central force, Kepler’s laws. Gravitational Field and potential – simple examples. System of particles, centre of mass and laboratory reference frame. Elastic and inelastic collision.
Generalised coordinate, degrees of freedom. Lagrange’s and Hamilton’s equations- simple applications. Hamilton’s principle.
b) Rigid body dynamics: Degrees of freedom of a rigid body. Euler angle. Moment of Inertia, parallel and perpendicular axes theorem.
c) Properties of matter & fluid dynamics: Elasticity. Surface Tension. Viscosity. Equation of continuity. Bernoulli’s equation.
2. Special Relativity: Michelson-Morley experiment. Lorentz transformation, length contraction, time dilation, addition of velocities. Doppler effect, relativistic kinematics, mass energy relation. Four vector and covariance.
3. Waves and Oscillations:
a) Oscillation: Simple harmonic motion, damped oscillation, forced oscillation and resonance. Fourier series and its simple applications. Superposition, beats. b) Waves: Equation of progressive wave, wave packets, phase and group velocities. Stationary waves, reflection and refraction from Huygen’s principle. c) Geometrical Optics: Fermat’s principle and laws of reflection and refraction. Matrix method in paraxial optics, thin lens formula, nodal points, two thin lenses separated by a distance. Chromatic and spherical aberration (qualitative). d) Physical Optics: Spatial and temporal coherence. Interference of light, Young’s experiment. Stoke’s law, thin films. Newton’s ring. Michelson interferometer. Fraunhofer diffraction – single slit, double slit, diffraction grating. Fresnel diffraction, Zone plate. e) Polarization: Linear and circularly polarized light, double refraction, quarter wave plate. Optical activity. Polarimeter. f) Laser: Einstein A and B coefficients. Ruby and He-Ne lasers.
4. Electricity and Magnetism:
a) Electrostatics & Magnetostatics: Gauss and Stoke’s theorem. Laplace and Poisson equations and boundary value problems. System of charges, multipole expansion of scalar potential. Method of images and its applications. Dipole field and potential. Dipole in an external field. Dielectrics, polarization. Boundary value problems for conducting & dielectric spheres in a uniform field. |
| Magnetic shell, uniformly magnetized sphere. Ferro-, para- and diamagnetic substances. Hysteresis in ferromagnetic materials.
b) Current electricity: Kirchhoff’s laws and their applications, Biot-Savart law, Ampere’s law, Faraday’s law, Lenz’s law. Self and mutual inductances. Mean and rms values in AC circuits. DC & AC circuits with R, L and C components. Series and parallel resonances. Q-factor. Basic principle of transformer.
c) Electromagnetic theory: Displacement current and Maxwell’s equations. Wave equations in vacuum, Poynting theorem. Vector and Scaler potentials. Normal and anomalous dispersion.
5. Thermodynamics: Laws of thermodynamics, change of entropy in different processes. Maxwell’s relations and its applications. Clausius – Claperyon equation. Gibbs’ phase rule and chemical potential. Joule-Thomson effect and liquification of gasses. |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. Quantum Mechanics:
Wave-particle duality, Schrödinger equation and expectation value, uncertainty principle, Solutions of the one-dimensional Schrödinger equation for a free particle (Gussian wave-packet) particle in a box, particle in a finite well, linear harmonic oscillator, Reflection and transmission by a step potential and by a rectangular barrier. Particle in a three dimensional box. Angular momentum. Hydrogen atom. Spin. Spin half particle, properties of Pauli spin matrices.
Stern – Gerlach experiment, electron spin, fine structure of hydrogen atom, L-S coupling, J-J coupling, Spectroscopic notation of atomic states, Zeeman effect, Raman Effect and molecular structure, Laser Raman spectroscopy.
2. Statistical Physics:
Macro and micro states. Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac distributions. Partition function. Distribution of molecular velocities in ideal gasses, equipartition theorem. Specific heat of solids, Einstein and Debye theory. Blackbody radiation, Planck’s law, Stefan Boltzmann law. Rayleigh- Jeans formula and Wein’s displacement law. Specific heat of electrons at low temperature.
3. Nuclear and Particle Physics:
Basic nuclear properties – size, binding energy, angular momentum, parity, magnetic moment; Semi- empirical mass formula and applications, mass parabolas; Shell model of the nucleus-successes and limitations; Violation of parity in beta decay; Q-value of nuclear reactions; Nuclear fission and fusion, energy production in stars;
Classification of elementary particles and their interactions; Conservation laws;
4. Solid State Physics:
Crystalline and amorphous structure of matter; Different crystal systems. Methods of determination of crystal structure; X-ray diffraction; Band theory of solids-conductors, insulators and semiconductors; Magnetism; dia, para and ferromagnetism; Elements of superconductivity,
5. Electronics:
Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors, p-n-p and n-p-n transistors, Amplifiers, Oscillators-Hartley, Weinbridge and crystal oscillators, Op-amps, FET, JFET and MOSFET. Digital electronics-Boolean identities. De Morgan’s laws. Logic gates and truth tables. Simple logic circuits. |
| POLITICAL SCIENCE : | |
| Paper – I : | Group – A
Western Political Thought – Plato, Aristotle, Machiavelli, Rousseau, Bentham, J. S. Mill, Marx.
Indian Political Thought – Kautilya, Rammohan Roy, Vivekananda, Syed Ahmed Khan, Rabindranath, Gandhi, Ambedkar.
Political Concepts – State, Civil Society, Government, Governance, Power, Authority, Nation, Nationalism, Internationalism.
Political Ideas – Rights, Duties, Liberty, Equality, Justice, Rule of Law, People Participation. Political Ideologies – Liberalism, Democratic Socialism, Feminism, Terrorism. Different aspects of Democracy – Meaning and Theories of Democracy; Direct vs Representative Democracy; Electoral System; Electoral Reforms.
Political Process – Party System, Single Party, Bi Party, and Multi Party Systems; National Parties and Regional Parties; Lobbyists and Pressure Groups.
Forms of Government – Dictatorial vs Democratic; Totalitarian vs Liberal. Presidential vs Parliamentary, |
| Unitary vs Federal.
Social Movements – Environmental movements, Women’s movements, Human rights movements. Group-B
Basic features of Indian Constitution – Constituent assembly, Salient Features of the Indian Constitution, Nature of Indian Federation, Centre-State relations, Legislative, Executive and Financial-Fiscal dimensions, Evolving political trends.
Fundamental Rights – Directive Principles & Fundamental duties – Constitutional provisions and judicial interpretations regarding fundamental rights.
Union Legislature – Composition, Powers and Functions of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha, Functioning of the Committee System.
Union Executive – President, Vice President – Election, Position, Functions, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, Relationship between President and Prime Minister.
The Judiciary – Supreme Court and the High Courts, Composition and Functions, Judicial review and Judicial activism, Public interest litigations, Judicial reforms.
Government in the States – Governor, Chief Minister and Council of Ministers, Position and Functions. State Legislature – Composition and Functions. Local Government and Politics – Panchayati Raj: Evaluation, Structure, Powers and Functions, Municipal Government; Significance of 73rd and 74th amendments; Role of women, SCs & STs in Local Government.
Bureaucracy – Classical administration and Development Administration; Changing role of bureaucracy in Post-Colonial India, “Representative” bureaucracy, Issues of bureaucratic accountability.
Social Processes – Role of Peasants and Workers in Indian Politics; Role of Interest / Pressure Groups; Regionalism, Casteism, Linguism and Communalism in Indian Politics; Issues of Criminalisation, Corruption; Citizens’ movements. |
|
|
Paper – II : |
Public Administration and International Relations Group – A Public Administration
Theories of Administration – Scientific Management, Classical Theory, Weber’s theory of bureaucracy, Riggsian Model of Echological Approach to Public Administration.
Forms of Public Organizations – Ministries and Departments; Corporations, Boards and Commissions.
Principles of Organization – (a) Hierachy (b) Unity of Command (c) Span of Control (d) Authority (e) Centralization, Decentralization and Delegation, (f) Line and Staff.
Processes of administration – (a) Decision – making and Policy Formulation (b) Communication and Control (c) Leadership (d) Co-ordination.
Accountability and Control – Legislative, Executive and Judicial Control over administration; Role of Civil Society; Public opinion and Media; Right to Information; Administrative Corruption; Grievance Redressal Machineries like Ombudsman.
Development Administration – Evolution of the Concept; Basic features.
Control of Public Expenditure – Parliamentary Control, Control of Parliamentary Committees; Indian Administration – Continuity and Charge – brief historical outline. Recruitment and Training of Civil Servants in India – Role of Union and State Public Service Commissions and Training Institution.
Organization of the Union Government in India – PMO, Cabinet Secretariat, Secretariat Administration.
Organization of the State Governments in India – Chief Secretary – Relationship between Secretariats and Directorates.
District Administration in India – Changing role of District Officers, Sub-divisional Officers & Block Officer; their interfaces with Local Self Government.
Group-B
International Relations |
| Some Basic Concepts of International Relations – (a) Balance of Power (b) Collective Security (c) Bi- polarity and Unipolarity (d) Neo-Colonialism (e) Globalization.
Foreign Policy – Concept and Techniques; Determinants of foreign policy. Evolution of World Politics – League of Nations; United Nations; Cold War; Detente; Collapse of the Soviet Union; Regional Integrations; International Terrorism.
Non-Alignment – Evolution of the Movement and Role of India.
Major Issues in Indian Foreign Policy – Sino-Indian relations, Indo-Pak conflicts and the liberation of Bangladesh, developments in Sri Lanka, Indian role in promoting regional cooperation through S.A.A.R.C., the Kashmir question and India becoming a nuclear power. India and South East Asia; India’s relations with U.S.A., China, Japan & Russia. India on the question of nuclear weapon. India and the U.N. system-India’s role in U.N. peace keeping and global disarmament. India and the emerging international economic order.
Recent Global Issues – Egypt, Lebanon and Lybia. |
|
| PSYCHOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | Basic psychological processes and development
Scope and Methods of Psychology – Biological basis of behaviour
2. Cognitive Processes: A) Sensation: attributes of sensation, psychophysics (weber-Fechner Law), Methods of Pscychophysics B) Attention: determinants of attention, fluctuation of attention, selectivity of attention C) Perception: Movement, space, depth and time perception, perceptual organization, Gestalt View
3. Learning.: Conditions of Learning Ø Theory of classical conditioning Ø Theory of operant conditioning Ø Trial and error theory Ø Theory of insight learning Ø Programmed learning
4. Memory: Encoding, storage, retrieval Ø Types of Memory (STM & LTM, ICONIC, Echoic & Procedural) Ø Forgetting curve Ø Theories of forgetting
5. Motivation and Emotion: Physiological and psychological basis of motivation and emotion Ø Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation – factors influencing intrinsic motivation Ø Theories of motivation – Maslow, Mcclelland Ø Theories of Emotion – James-Lange Theory, Canon-Bard and Schachter-Singer Theory Ø Effects of Motivation and emotion on behaviour
6. Intelligence Ø Spearman’s two factor theory Ø Thurstone’ s theory Ø Guilford’s structure of intellect Ø Gardner’s theory Ø Measurement of intelligence – IQ & deviation IQ, Tests of intelligence – Stanford Binet Ø Types of intelligence – Social, abstract, concrete, emotional, artificial, spiritual Ø Gifted and mentally challenged children
7. Thinking Ø Piaget’s theory of cognitive development ~ Problem solving Ø Creative thinking – Nature and stages
8. Attitude, Values and Interest Ø Definition of attitude, values and interests Ø Value – concept, development and measurement Ø Attitude – formation, measurement and change concept Ø Stereotype, prejudice, discrimination Ø Measurement, reduction of prejudice |
| 9. Interest – concept and measurement
10. Development of behaviour : From birth to adolescence Ø Physical development Ø Emotional development Ø Moral development Ø Social development |
|
| Paper – II : | 1. Personality
Ø Theories of personality – Freud, Erikson, Eysenck and Rogers
2. Individual Difference: Nature – Nurture controversy Ø Nature – nurture controversy Ø Character and construction of standardized psychological tests, types of tests
3. Mental health & adjustment – concept of mental health & wellbeing Ø Stress & health – nature, types, causes and consequence of stress Ø Adjustment – criteria of adjustment Ø Management of stress
4. Psychological Disorders Ø Causes of abnormal behaviour Ø Anxiety disorders Ø Mood disorders Ø Schizophrenia Ø Substance abuse disorders
5 .. Psychotherapy Ø Psychoanalysis Ø Cognitive Behaviour therapy Ø Client centered therapy
6. Organizational psychology Ø Personal selection, job analysis methods Ø Job Satisfaction Ø Theories of motivation, Herzberg, Alderfer Ø Conflict in organization – sources, types Ø Organizational culture and climate Ø Occupational health hazards 7. Group Ø Types of group Ø Group versus team – Influence of primary and secondary group on society Ø Structure and functions of group Ø Leadership – Characteristics of a good leader with special reference to trans actual and transformational leadership
8. Social problems Ø Problems of social integration caste, class and religion Ø Delinquency and crime Ø Psychosocial problems related to old age
9. Application of Psychology to different fields a) Rehabilitation – concept, primary, secondary and tertiary prevention b) Education – Psychology, principles underlying effective teaching-learning c) Motivating and training people for entrepreneurship and economic development
10. Psychology and Methodology Ø Normal probability curve Ø Parametric and non-parametric statistics – characteristics Ø Hypothesis formation Ø Research variables and their control |
| Ø Techniques of sampling | |
| SOCIOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | Fundamentals of Sociology :
a) Modernity and social changes in Europe and emergence of Sociology.
b) Scope of the subject and comparison with other social sciences.
c) Sociology and common sense.
Pathfinders of Sociology :
a) Karl Marx – Historical materialism, mode of production, alienation, class struggle.
b) Emile Durkheim, Social fact, collective consciousness and social solidarity, suicide, religion and society.
c) Max Weber – Social action, ideal types, types of authority and bureaucracy. Protestant ethic and the spirit of capitalism.
d) Simmel : Formal Sociology : Forms & Types; Subjective & Objective Culture, Money; Metropolis.
e) Contemporary interpretations of Modern Sociology: Talcolt Parsons – Social system and its four major problems, pattern variables. Robert K. Merton – Latent and manifest function and dysfunction, conformity and deviance, reference groups.
f) Social System : Equilibrium, status, role, culture, heredity and environment, social control, conformity & deviance, forms of interaction, social interaction and everyday life. Types of human groups. Personality and socialization. Power, authority, legitimacy, sociology of political life. Religion in relation to solidarity and social conflict, magic, science and morality. Social aspects of production, distribution, exchange and consumption.
g) Individual & groups : Personality & Socialization, classification of groups & their contemporary significance.
Inequality, Stratification & Mobility :
a) Concepts – equality, inequality, hierarchy, exclusion, poverty and deprivation.
b) Social mobility – open and closed systems, types of mobility, sources and consequences of mobility.
Economy & Society :
a) Social aspects of production, distribution, exchange & consumption, Social organization of work in different types of Society – slave society, feudal society, industrial / capitalist society, post – industrial society.
b) Formal and informal organization of work.
c) Labour & Society.
Politics and Society :
a) Power elite, bureaucracy, pressure groups and political parties.
b) Nation – state, citizenship, democracy, civil society, ideology.
c) Protest, agitation, social movements, collective action, revolution.
Religion & Society :
a) Religion in modern society: religion and science, secularization, religious revivalism, fundamentalism, pluralism.
b) Magic, religion & morality and science.
Science & Technology :
a) Ethos of science;
b) Scientific temper;
c) Social responsibility of science; |
|
d) Social control of science;
e) Social consequences of science and technology;
f) Technology and social change.
Social research and methods of enquiry:
a) Importance of social research.
b) Survey Method – Questionnaires and interviews as technique.
c) Field Method – Observation (participant and non-participant) as technique.
d) Experimentation in Sociology.
Social & cultural change in modern society :
a) Development and dependency,
b) Agents of social change,
c) Education & social change,
d) Science, Technology & social change,
e) Dominant Culture,
f) Celebrity Culture. |
|
| Paper – II : | Society & Culture in India :
Unity & diversity, modernity and tradition, contestation.
Approaches to the study of Indian Society :
Indological (Ghurye); Structural-functional (Srinivas); Marxist / Dialectical (Desai) ; Dalit (Ambedkar).
Major Social Groups :
Religious groups, linguistic and regional groups, castes & tribes.
Some Major Institutions :
Marriage, family, kinship patterns and changes affecting those; gender socialization; division of labour and economic interdependence, decision-making, centres of power and political participation; religion and society; Education, inequality, social change, contemporary trends.
Social Inequality :
Nature and types; traditional concepts of hierarchy, caste and class; the Backward Classes; concepts of equality and social justice in relation to traditional hierarchies; education, occupation; changing patterns of stratification.
Social change in modern India :
Westernization, Sanskritisation and secularization; directed and undirected change; legislative and executive measures; social reforms; social movements; industrialization & urbanization; associations and pressure groups.
Women & children :
Demographic profile of women; special problems – dowry, atrocities, discrimination; existing programmes for women and their impact. Situational analysis of children; child welfare programmes.
Globalisation & ecological crisis in India :
Ecological and Environmental movements in India.
Social problems in India :
1) Poverty in rural and urban areas, 2) Child labour, 3) Problem of youth, 4) Drug addiction, 5) Juvenile delinquency, 6) Problems relating to old age, 7) Population problem, |
| 8) Mass illiteracy,
9) Problem of violence. |
|
| STATISTICS : | |
| Paper – I : | Probability theory:
Definition of probability: Classical and relative-frequency approach to probability, Kolmogorov’s Axiomatic definition (detailed discussion on discrete space only), limitations of Classical definition. Probability of union and intersection of events, Conditional probability and Independence of events, Bayes’ Theorem and its applications Random Variables : Definition of discrete and continuous random variables, cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.) and its properties (with proof), probability mass function (p.m.f.) and probability density function (p.d.f.), Expectation and Moments, Joint distribution of two random variables, marginal and conditional distributions, Statistical Independence. Convergence in Probability, Weak Law of Large Numbers and its applications, Convergence in Distribution, Chebyshev’s inequality, Statement of Central Limit Theorem (i.i.d. case) & its applications.
Statistical Inference: Point & Interval Estimations and Testing of Hypothesis: Point estimation: Requirements of a good estimator – notions of Mean Square Error, Consistency, Unbiasedness: Minimum Variance Unbiasedness and Best Linear Unbiasedness. Sufficiency and factorization theorem, Rao-Balckwellisation, Methods of estimation- moments, least square, maximum likelihood and minimum chi-square
Elements of Hypothesis Testing : Null and Alternative hypotheses, Simple and Composite hypotheses, Critical Region, Type I and Type II Errors, Level of Significance and Size, p-value, Power. MP and UMP tests, Neyman Pearson lemma, Likelihood ratio tests. Interval Estimation: Confidence intervals, Concepts of Uniformly Most Accurate (UMA) confidence sets, relationship with tests of hypotheses.
Multivariate Analysis: Multivariate data – multiple regression, multiple correlation and partial correlation – their properties and related results. Random Vector: Probability mass and density functions, Distribution Function, Mean vector and Dispersion matrix, Marginal and Conditional Distributions, Ellipsoid of Concentration, Multiple Regression, Multiple Correlation, Partial Correlation, Multonomial and Multivariate Normal Distributions.
Sample Survey: Concepts of a Finite Population and a Sample, Need for Sampling, Complete Enumeration and Sample Surveys. General Ideas: Planning and execution of sample surveys, analysis of data and reporting, Biases and Errors. Judgement and probability sampling. Tables of Random Numbers and their uses Simple Random Sampling with and without replacement, Determination of sample size in simple random sampling, Stratified random sampling, Systematic sampling, Cluster and multistage sampling, ratio and regression methods of estimation.
Analysis of variance and Design of Experiments: Heterogeneity and Analysis of Variance and Covariance, Linear Hypothesis, Orthogonal splitting of total variation, applications of the ANOVA technique to: one-way classified data, two-way classified data with equal number of observations per cell (fixed effects model only).
Principles of experimental design: Randomization, Replication and Local Control, Uniformity trials, Shapes and Sizes of Plots and Blocks. Standard Designs and their Analyses: Completely Randomized Design (CRD), Randomized Block Design (RBD) and Latin Square Design. Factorial Designs- 22 and 23 experiments. |
| Paper – II : | Industrial Statistics:
Introduction: Concepts of Quality and Quality Control, Process Control and Product Control. Process Control: Control Charts and their uses, Choice of Subgroup sizes, Construction of control charts – by attributes (p, c, np) (including unequal subgroup size) and variables ( X , R). Interpretation of non- random patterns of points.
Product Control: Producer’s Risk, Consumer’s Risk, Acceptance Sampling Plan, Single and Double sampling plans by attributes, their OC, ASN ( and ATI ), LTPD and AOQL , Sequential sampling plan- OC and ASN.
Concept of Reliability, failure rate and reliability functions, reliability of series and parallel systems. |
|
Economic Statistics: Index Numbers: Price, Quantity and Value indices. Price Index Numbers: Construction, Uses, Limitations, Tests for index numbers,Various formulae and their comparisons, Chain Index Number.
Some Important Indices: Consumer Price Index, Wholesale Price Index and Index of Industrial Production – methods of construction and uses.
Measurement of income inequality: Gini’s coefficient, Lorenz curves, Application of Pareto and Lognormal as income distributions.
Population Statistics: Introduction: Sources of Population Data – Census data, Registration data and the errors in such data. Rates and ratios of vital events.
Measurements of Mortality: Crude Death rate, Specific Death Rate, Standardized death Rate, Case fatality rate and Cause of Death Rate, Infant Mortality Rate, Neonatal and Perinatal Mortality Rates.
Life tables: Descriptions of Complete and Abridged Life Tables and their uses, Cohort vs. Current Life Tables, Stable population and Stationary population, Construction of complete life table from population and death statistics.
Measurements of Fertility: Crude Birth Rate, General Fertility Rate, Age Specific Fertility Rate, Total Fertility Rate. Growth Curve models.
Time Series Analysis: Introduction: Examples of time series from various fields, Components of a times series, Additive and Multiplicative models. Trend and Seasonal Components: Estimation of trend by linear filtering (simple and weighted moving- averages ) and curve fitting ( polynomial, exponential ), Estimation of seasonal component by ratio to moving-average method, ratio to trend method, some special processes-: Moving Average process, Auto Regressive processes of orders one and two, Exponential smoothing method of forecasting.
Linear Programming: Formulation of LP problems, Simple LP model and its graphical solution, Simplex algorithm.
Official statistics: The Statistical system in India: The Central and State Government organizations, the functions of the Central Statistical Organization (CSO), National Sample Survey Organization (NSSO) and West Bengal Bureau of Applied Economics and Statistics.
National Income statistics: Income, expenditure and production approaches. Their applications in various sectors in India. |
|
| ZOOLOGY : | |
| Paper – I : | Group A : Short/objective questions.
This group will cover the whole content of the Paper (I)
Group B : Non-Chordata & Chordata 01. Outline classifications of Protozoa upto Phyla 02. Outline classifications of Porifera to Hemichordata upto classes. 03. Classification of chordata upto orders.
Non Chordata Locomotion in Protozoa Annelida, Insecta & Mollusca, Excretion and Osmoregulation in Annelida, Arthropoda & Mollusca. Sense organs in Mollusca and Arthropoda.
Specialized Features: Conjugation in ciliates Polymorphism in Siphonophora Coral reefs: types and formation Evolutionary position of Onychophora, Limulus Social Organisation in insects – Honey bee & Termites
Chordata Specialized Features: Ciliary mode of feeding in lower chordates. |
| Integumentary derivatives in mammals.
Comparative anatomy of heart, aortic arches & Kidney Respiratory structure and function in fish, bird and mammals. Ruminant stomach. Evolutionary position of Sphenodon and Monotremata Poison apparatus, Biting mechanism and types of poison in snakes. Retrogressive metamorphosis, Neoteny and paedogenesis. Migration of Birds Aerodynamics in birds flight. Echolocation in Chiroptera and Caetacea
Group C : Ecology, Biodiversity and Ethology Energy flow, Population Dynamics — Growth forms, mortality, natality, population density regulation. Niche concept and resource Partitioning Ecological succession.
Pollution : Green house effect, Pollutants types and nature. Acute and chronic toxicity due to air and water pollution. Innate and learned behaviour, FAP (Fixed Action Plan), Selfishness, Co-operation, Altruism and Kinship
Biodiversity : Definition, Levels, values, in-situ and Ex-situ conservation, Hot spots, megadiversity countries, Biopiracy. Wildlife management strategies with reference to Tiger, Rhino and Elephant, Elementary concept on remote sensing for sustainable diversity.
Systematics and Quantitative Biology Codes of Zoological nomenclature, species concept, phenetics and cladistics. Measure of Central Tendency, Probability, Student t test Chi square, ANOVA, Goodness of fit. |
|
| Paper – II : | Group A : Short/objective questions.
This group will cover the whole content of the Paper (II)
Group B :
Cell Biology & Genetics : Ultra structure & functioning of – Plasmamembrane, Golgi complex, Mitochondria, ER, Lysosome, Chromosome, Nucleosome, Cell cycle. Allele : Types, ABO blood group, Bombay phenotype, 3 point chromosome mapping in diploid with problems. Autosomal & sex linked inheritance in Drosophila & Man, Sex determinations in Drosophila & Man. Replication, Transcription and m RNA processing & Translation in prokaryots. Operon concept – Lac & Tryptophan, Mutations & Mutagenesis, Down, Klinefelter and Turner syndrome, Albinisim, Sickle cell anaemia, Thalassemia, Recombinant DNA : Vector, Principle of cloning, Restriction Endonucleases Transgenic animals. Role of protooncogene & Tumor Supressor Genes. Human Genome Project.
Histology & Endocrinology : Histology : Cell types and functions. Pituitary, endocrine pancreas, gonads, Thyroid, adrenal. Mechanism of hormone action, Basic concept of cell signalling. Hormonal control of reproductive cycles in mammals. General idea of insect endocrine glands and their function.
Physiology & Biochemistry : Enzymes : Classes, kinetics and factors affecting enzyme action. Osmoregulation : Types and mechanism in aquatic vertebrates. Macromolecules : Protein, fat & carbohydrates. Glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, Transamination & oxidative and non-oxidative deamination. Role of haemoglobin in oxygen & carbon di oxide transport, Foetal haemoglobin, Physiology of nerve impulse and propagation, Muscular contraction, Vitamines. Principles and use of instruments – Spectrophotometer, TLC, RAPD, RFLP, PCR, ELISA , DNA finger printing.
Group C :
Developmental Biology Gametogenesis, fertilization, IVF basic concept, cleavage-types and examples. Gastrulation in frog and chick. Organizer, induction and competence. Placenta : Types and formation. Organogenesis : Eye and heart.
Evolution & adaptation : Origin of life, natural selection : modern view, Neutral theory. |
|
Evolution : Elephant, Horse & Man. Hardy Weinberg equilibrium and factors affecting it. Fossilization, Zoogeographical realms, continental drift, Adaptive features of Aquatic, Volant and desert animals. Mimicry and colouration. . .
Economic Zoology : Pisciculture, Apiculture, Sericulture & Poultry. Types of cattle breed in India. Common pests of paddy, wheat and jute – damage & control, IPM.
Parasitology & Immunology : Morphology, Life-cycle, Pathogenecity and control of Plasmodium, Leishmania, Taenia, Fasciola, Ancylostoma & Wuchereria. Immunoglobulin classification, T & B cell cooperation. T cell receptors, cytokines, complements. Antigen-antibody reaction. Principles and importance of vaccination. Pathophysiology of Tuberculosis, Types of virus. |
Please call 9674493673, 9051834864 or 8274048710 or mail us at mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in for details.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website
For Guidance of WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Preliminary , Main Exam and Interview, Study Mat, Mock Test, Guided by WBCS Gr A Officers , Online and Classroom, Call 9674493673, 9051834864 or 8274048710, or mail us at – mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in







































































































