Blood Circulation System By WBCS MADE EASY Student At Science Club
Blood Circulation System By WBCS MADE EASY Student At Science Club
Blood Circulation System
(By Amlan Maji WBCS MADE EASY College Street 2023-24 Classroom Foundation Course Batch 2).Continue Reading Blood Circulation System By WBCS MADE EASY Student At Science Club.
In biology, transport is a life process in which a material absorbed (or made) in one part of the body of an organism is carried to other parts in its body. This point will become clear from the following discussion.
We know that all the living organisms (animals and plants) need a continuous supply of different materials such as food, water and oxygen for their survival. These materials must reach the various parts of an organism where they are needed. All the living organisms also produce some waste materials (like carbon dioxide, etc.) as a result of chemical processes occurring in their body cells. These waste materials are harmful and have to be removed from the body. So, it is leans of trans necessary that all the living organisms have some means of transporting (or carrying) materials from one part to another part within their body.
We can now say that: All the living organisms (animals and plants) need a transport system to supply them with food, water and oxygen, and to carry away the harmful waste materials produced in their bodies.
- An essential requirement of all living organism is transportation of materials from the site of formation to the site of requirement.
- Material which required for transportation are: Nutrients, Gases, Metabolic Wastes, Hormones, Enzyme, Antibodies etc.
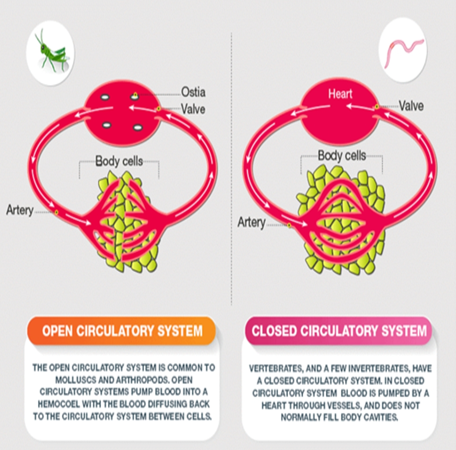
What is closed circulation?
When blood is always confined within heart and blood vessels. Eg.,- Most of the higher animals.
What is open circulation?
– When blood is released within body cavity or haemocoel. Eg., – Insects like Cockroach, Dragon fly, Butterfly, fly, Grasshopper etc.
Human circulatory system consists of:-
- Blood
- Blood vessels
- Heart
Blood (Study of Blood – Hematology)
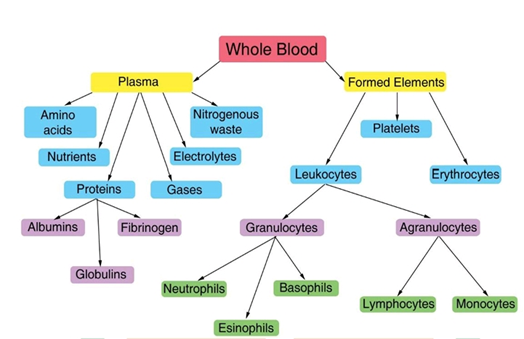
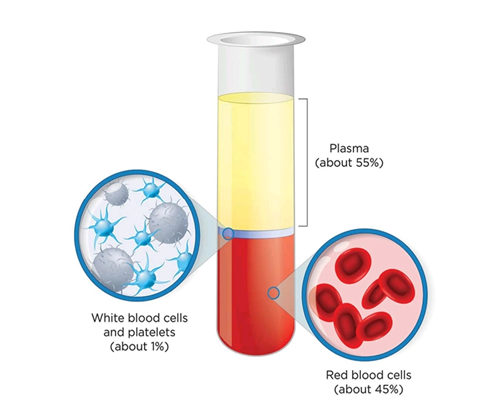
- Blood is fluid Connective tissue containing plasma, red blood cells / corpuscles (RBC), White blood cells (WBC) and platelets (Thrombocytes in non-mammals).
- Blood is the main circulating fluid that helps in the transportation of various substances.
- Blood is accounts for 7% of the body weight in a normal young adult of 70 kg.
- A healthy human contains about 5-5.6 litres of blood (volume)
- PH of Blood→ 7.35-7.45
Plasma
- Plasma is a straw (a tone of pale yellow) colored, viscous fluid constituting nearly 55% of the blood.
- It contains 90-92% Water, solids (8) % and others
- Fibrinogen, globulin and Albumins are the major protein. Albumin for maintaining osmotic balance, globulin for defense mechanism and fibrinogen for blood clotting
- Albumins and globulins retain water in plasma.
- Serum Albumin is most abundant blood protein.
- Plasma without the clotting factor is called serum.
Red blood cells
- Red blood cells are the most abundant cell of all the cells in blood.
- A healthy adult man has, on an average 5- 5.5 millions of RBC /mm³ of blood.
- RBCs are formed in the red bone marrow in the adult.
- RBCs lack a nucleus and other organelles
- RBCs are circular and biconcave in shape.
Intersting facts about RBC
- Mammals have smallest RBCs in the entire animal Kingdom.
- Among mammals, elephant has largest and musk deer has smallest
- Amphibians (Salamander Proteus and Amphiuma) have largest RBC In the entire animal Kingdom.
- Birds have richest blood in Entire animal Kingdom.
- Richest blood means maximum number of RBC per unit blood.
White blood cells
- They can change their shape like Amoeba and are thus, capable of amoeboid movement. This enables them to squeeze out of blood capillaries into the tissues (extra vascular regions). This process is called diapedesis.
- Number 6000-8000/mm3 of blood.
- eucopenia, and incre Decrease in the number of WBC is called leucopenia, and increase in number is called Leukemia.
- Abnormal increase of WBC is called, Blood Cancer.
- The leucocytes are of two main types: Agranulocytes and granulocytes. Agranulocytes -The granules are not found in the cytoplasm of these cells.
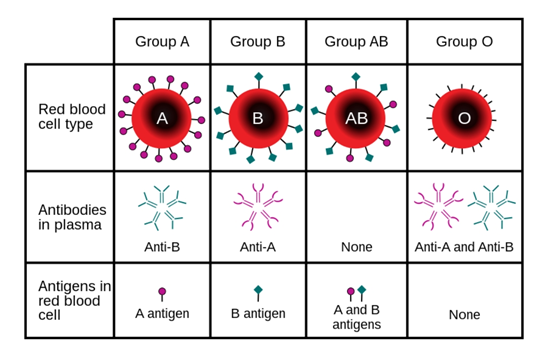
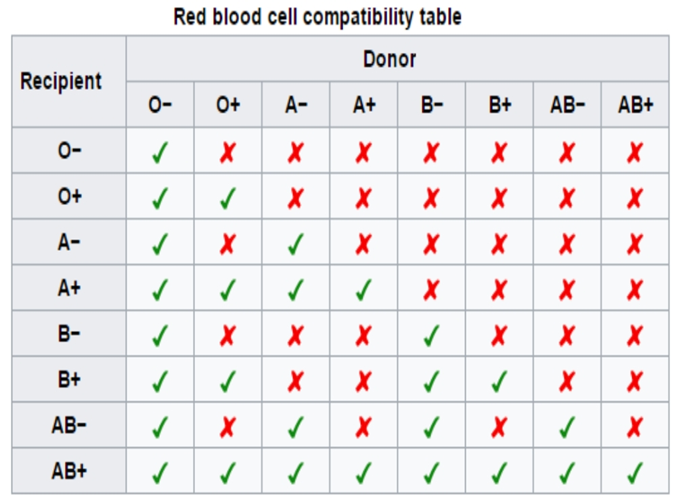
ABO Blood Groups
Karl Landsteiner reported first time ABO blood groups in human beings.
ABO grouping is based on the presence or absence of two surface antigens (chemicals that can induce immune response) on the RBCs namely A and B.
Similarly, the plasma of different individuals contains two natural antibodies (proteins produced in response to antigens).
People whose RBCs display only antigen A have type A blood. Those who have only antigen B are type B Blood. Individuals who have both A and B antigens are type those who have have both A and B antigens are typ neither antigen A nor B are type O
Bombay Phenotype or hh blood group
Bombay blood group, is a rare blood type. This blood phenotype was first discovered in Bombay, now known as Mumbai, in India, by Dr. Y. M. Bhende in 1952. It is mostly found in South Asia (India, Bangladesh, Pakistan) and parts of Middle East such as Iran.
Rh Factor
Another antigen, the Rh antigen is also observed on the surface of RBCs of majority (nearly 80 85 percent) of humans.
- The term “Rh” was originally an abbreviation of “Rhesus factor.”
- It was discovered in 1937 by Karl Landsteiner and Alexander S. Wiener
- It is the second most important blood group system, after the ABO blood group system.
- It consists of 49 defined blood group antigens, among which antigens D is most important
- Rh(D) status of an individual is normally described with a positive or negative suffix after the ABO type.
- Someone who is A Positive has the A antigen and the Rh(D) antigen,
- Someone who is A Negative lack the Rh(D) antigen.
Erythroblastosis fetalis:–
Erythroblastosis fetalis is hemolytic anemia in the fetus (or neonate, as erythroblastosis neonatorum) caused by transplacental transmission of maternal antibodies to fetal red blood cells. The disorder usually results from incompatibility between maternal and fetal blood groups, often Rho(D) antigens.
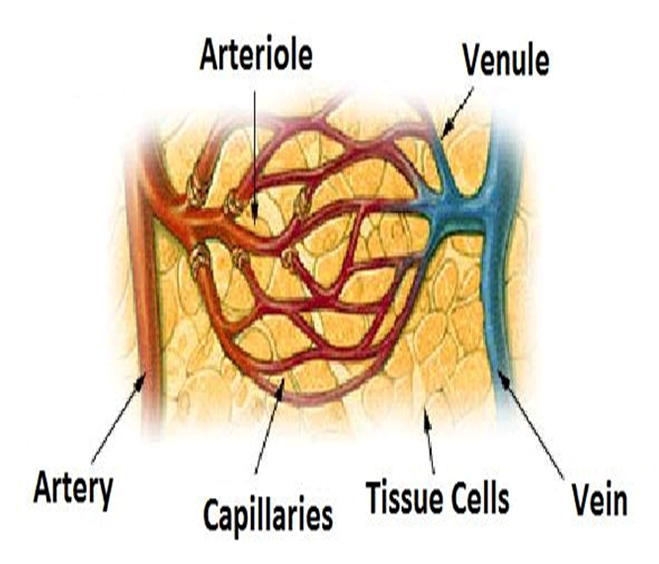
Blood vessels
In blood circulatory system, the blood flows through three types of blood vessels:
(i) arteries, (further division – arterioles) (artery carries blood from the heart to the body organs)
(ii) veins, (further division – venules) (vein carries blood from the body organs back to the heart)
(iii) capillaries
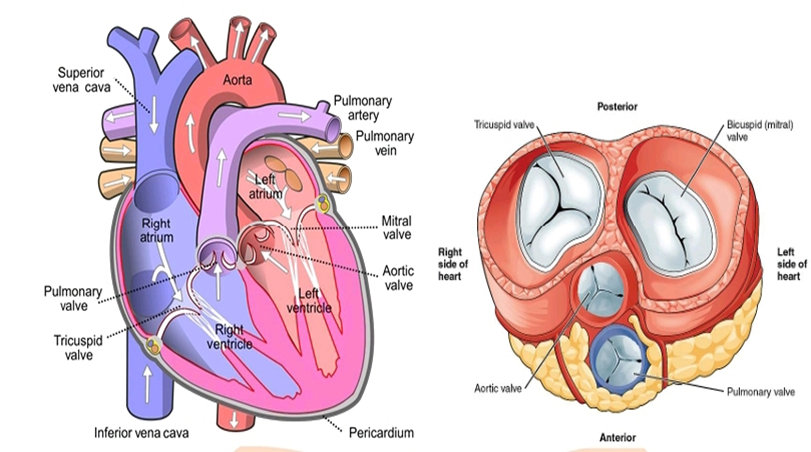
The heart
The heart is roughly triangular in shape.
It is made of special muscle called cardiac muscle.
The size of our heart is about the same as our ‘clenched fist’.
In humans, the heart is located between the lungs, middle compartment of the chest but it is slightly tilled towards left.
The Heart is a muscular organ in most animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system.
- The heart has four compartments called chambers inside it. The upper two chambers of heart are called atria (singular atrium), and the Lower two chambers of heart are called ventricles.
- The two atria receive blood from the two main veins. And the two ventricles transport blood to the entire body and the lungs.
The heart beats non-stop all the time.
The heart beat is due to the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscles which make up the atria and the ventricles.
- Please note that the two atria (left atrium and right atrium) contract together and relax together. Similarly, the two ventricles (left ventricle and right ventricle) contract tion of two atria is imm together and relax together. The contraction of two atria is immediately followed by the contraction of the two ventricles.
- The heart beats (or beating of heart) circulates the blood in the human body.
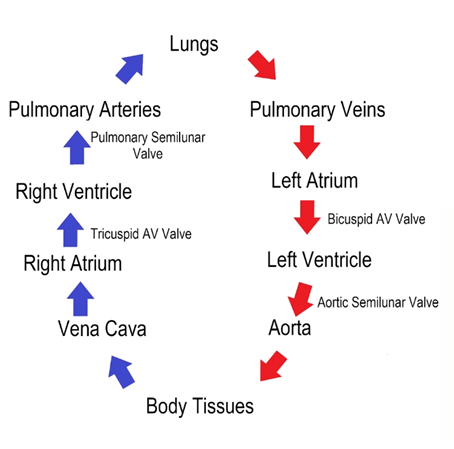
The blood circulatory system in human beings is an example of double circulation.
- The pathway of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called pulmonary circulation; and the pathway of blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart is called the systemic circulation.
- These two types of circulation taken together make double circulation.
Heartbeat
One complete contraction and relaxation of the heart is called a heartbeat.
- The heart usually beats about 70 to 72 times in a minute when we are resting. This means that the heart pumps out blood to the arteries about 70 to 72 times per minute.
- The number of heartbeats increase too much during and after a physical exercise or when a person is excited.
- we count our hearther fter running for a while For example, if we count our heartbeats after running for a while, we will find it to be more than 100 per minute. During rigorous exercise it can be as high as 150 to 200 beats per minute.
Stroke volume (SV)
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat.
The term stroke volume can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although it usually refers to the left ventricle. The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 70 mL in a healthy 70-kg man.
Blood pressure
• The pressure at which blood is pumped around the body by the heart is called blood pressure. The blood pressure of a person is always expressed in the form of two values called ‘systolic pressure and ‘diastolic pressure’.
The phase of the heart beat when the heart contracts and pumps the blood into arteries is called ‘systole And the phase of heart beat when the heart relaxes (or expands) and allows the chambers to fill with blood is called ‘diastole’.
The maximum pressure at which the blood leaves the heart through the main artery (aorta) during contraction phase, is called the systolic pressure. The minimum pressure in the arteries during the relaxation phase of heart is called the diastolic pressure.
The blood pressure of a person is expressed in terms of millimeters of mercury (which is written as mm Hg). a person is ex
The normal blood pressure values are:
Systolic pressure : 120 mm Hg
Diastolic pressure : 80 mm Hg
This is usually written as 120/80
The blood pressure values vary from person to person and from time to time. They also vary with age For example, a young person may have blood pressure of 110/75 but at the age of 60 years it could be 145/90. High blood pressure is called hypertension.
High blood pressure is caused by the constriction (narrowing) of very small arteries (called arterioles) which results in increased resistance to blood flow.. Very high blood pressure can lead to rupture of an artery and internal bleeding.
Blood pressure is measured by using an instrument called sphygmomanometer. Two readings of blood pressure are taken: systolic pressure (when the heart is contracting and pumping out blood), and diastolic pressure (when the heart relaxes and fills with blood).
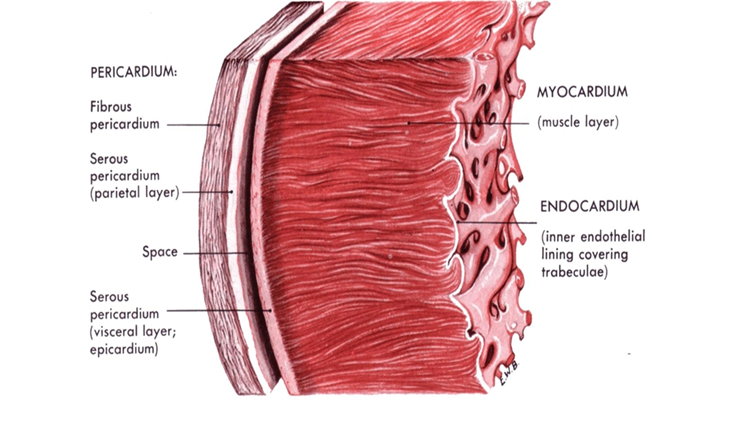
The heart wall
- The heart wall is made up of three layers: the inner endocardium, middle myocardium and outer epicardium.
- These are surrounded by a double-membraned sac called the pericardium.

Previous Years’ Solved Questions
Prelims:-
1)Which can bind O2 molecules?
(A) Red blood cells
(B) White blood cells
© Vitamin B12
(D) Vitamin E
2)Amounts of O2 normally carried by 100 ml of pure human blood, is
(a) 40 ml
(b) 10 ml
© 20 ml
(d) 30 ml
3)Normal human blood is
(A) Acidic
(B) Alkaline
© Neutral
(D) Variable
Mains:-
1)The normal blood pressure of human beings should remain in the range of
a) 120/80 mm
b) 110/70 mm
c) 140/80 mm
d) 110/60 mm
2)Universal recipient blood group is
1)AB
2)O
3)B
4)A
3)The heart rate of adult persons should remain in the Range of
A) 50-60 times per minute
B) 70-80 times per minute
C) 40-50 times per minute
D) 90-100 times per minute
4)Blood is filtered in the body through
a) Liver
b) Kidney
c) Lungs
d) None of the above
5)Blood pressure is under control of
(adrenal gland)
(A) Adrenal
(B) Pituitary
(C) Thyroid
(D) Aldosterone
6) The blood cells that defend the body against infections are
(A) White blood cells
(B) Red blood cells
(C) Platelets
(D) Erythrocytes
WBCS MADE EASY CONTACT DETAILS
Toll free no 1800 572 9282
Head Office
8274048710
9051834864
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Garia Center
8274048710
City Office (College Street)
8585843673 collegestreet@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Medinipur Office
8274972589 medinipur@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Siliguri Office 9051265991 siliguri@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Grievance officer
8777076749
Academics
academics@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Personality & Development Lab
Personalityanddevelopmentlab@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Current Affairs Club
currentaffairsclub@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Website www.wbcsmadeeasy.in
Download WBCS MADE EASY App from this link http://on-app.in/app/rrnvu
www.youtube.com/wbcsmadeeasytm
www.facebook.com/wbcsmadeeasy
www.linkedin.com/in/wbcsmadeeasy
??
Download WBCS MADE EASY App from here to get free material and videos: http://on-app.in/app/home?orgCode=rrnvu
Courses available : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/courses/
Online Foundation Course : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/wbcs-onli…
Classroom Foundation Course : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/courses/w…
Prelims Mock Test : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/courses/w…
Mains Mock Test : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/courses/w…
Optional Subject Guidance : https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/crash-cou…
General Combined Course has been newly introduced: https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in/courses/g…
Thank you Visit https://www.wbcsmadeeasy.in email: mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in TOLL FREE PHONE NUMBER 1800 5 72 92 82 (Only serious candidates contact please) Other numbers 9674493673, 9051834864, 8274048710 Disclaimer: These mock interview sessions are for practice purpose and has no bearing with actual interview in PSC,WB. Views / answers expressed here by individuals are of their own and WBCS MADE EASY has no responsibility of that.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in






































































































