GPS – Geology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
জিপিএস – ভূতত্ত্ব নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
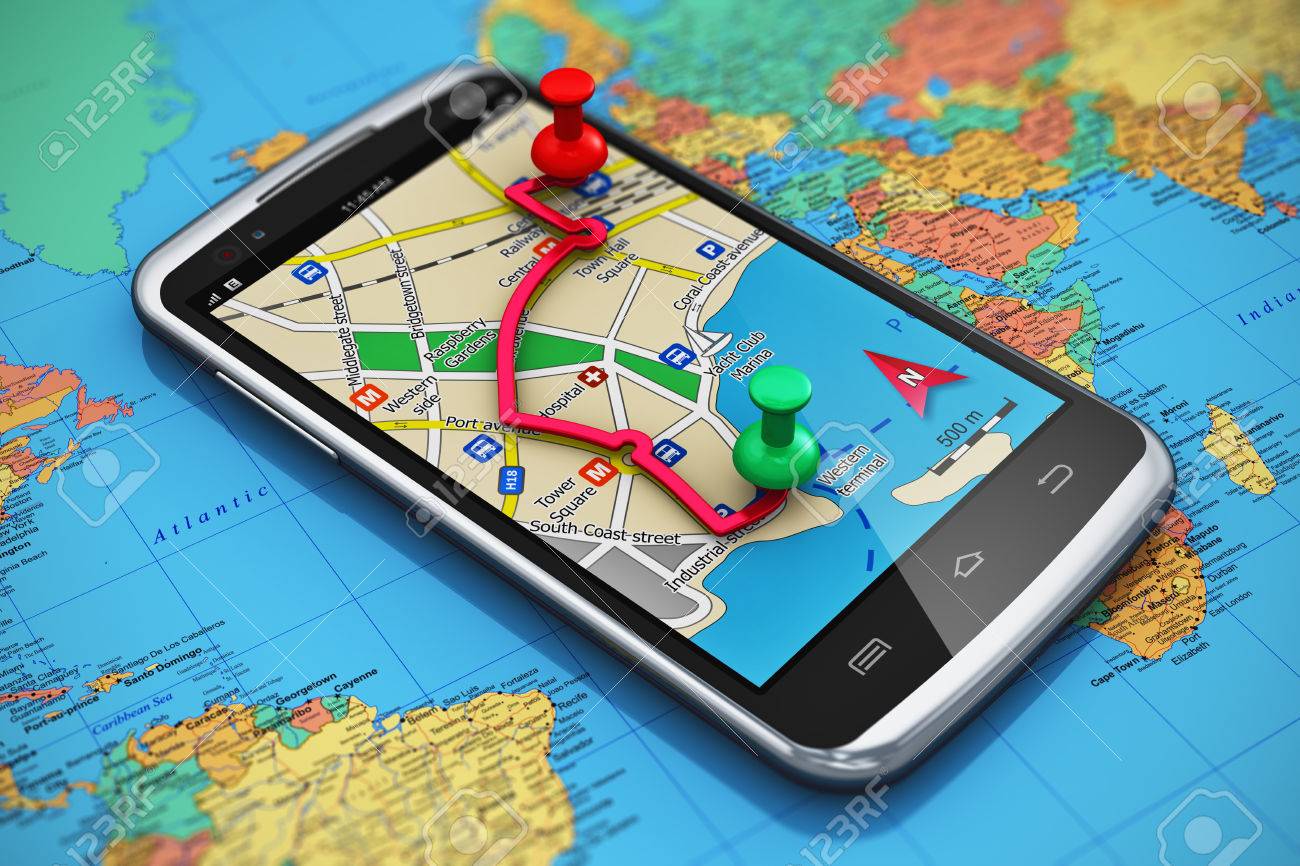
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is actually a constellation of 27 Earth-orbiting satellites (24 in operation and three extras in case one fails). The U.S. military developed and implemented this satellite network as a military navigation system, but soon opened it up to everybody else.Continue Reading GPS – Geology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Each of these 3,000- to 4,000-pound solar-powered satellites circles the globe at about 12,000 miles (19,300 km), making two complete rotations every day. The orbits are arranged so that at any time, anywhere on Earth, there are at least four satellites “visible” in the sky.
A GPS receiver’s job is to locate four or more of these satellites, figure out the distance to each, and use this information to deduce its own location. This operation is based on a simple mathematical principle called trilateration. Trilateration in three-dimensional space can be a little tricky, so we’ll start with an explanation of simple two-dimensional trilateration.
The Global Positioning System (GPS) is a network of about 30 satellites orbiting the Earth at an altitude of 20,000 km. The system was originally developed by the US government for military navigation but now anyone with a GPS device, be it a SatNav, mobile phone or handheld GPS unit, can receive the radio signals that the satellites broadcast.
Wherever you are on the planet, at least four GPS satellites are ‘visible’ at any time. Each one transmits information about its position and the current time at regular intervals. These signals, travelling at the speed of light, are intercepted by your GPS receiver, which calculates how far away each satellite is based on how long it took for the messages to arrive.
Once it has information on how far away at least three satellites are, your GPS receiver can pinpoint your location using a process called trilateration.
GPS satellites have atomic clocks on board to keep accurate time. General and Special Relativity however predict that differences will appear between these clocks and an identical clock on Earth.
General Relativity predicts that time will appear to run slower under stronger gravitational pull – the clocks on board the satellites will therefore seem to run faster than a clock on Earth.
Furthermore, Special Relativity predicts that because the satellites’ clocks are moving relative to a clock on Earth, they will appear to run slower.
The whole GPS network has to make allowances for these effects – proof that Relativity has a real impact.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in