Indian Economy – Yearwise Questions – Planning – NITI Aayog – W.B.C.S. Mains Examination.
THE ANSWERS ARE MARKED IN BOLD.Continue Reading Indian Economy – Yearwise Questions – Planning – NITI Aayog – W.B.C.S. Mains Examination.
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2019
- The now defunct Planning Commission was set up on
(A) March 15, 1950
(B) August 6, 1952
(C) September 1, 1951
(D) None of the above - The aim of the Third Five Year Plan (1961 – 66) was
(A) rapid industrialisation.
(B) growth with stability and progress towards self-reliance.
(C) self-reliant and self-generating economy.
(D) removal of poverty and attainment of self-reliance. - ‘Planned Economy for India’ – The book was written by
(A) Sir M. Visvesvarayya
(B) JL. Nehru
(C) SN Agarwal
(D) M.N. Roy - Consider the following statements:
(i) Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister is a non-constitutional,
permanent and independent body.
(ii) It advises the Prime Minister on whole heart of economic issues like inflation, microfinance, industrial output etc.
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
(A) (i) only
(B) (ii) only
(C) Both (i) and (ii)
(D) None of the above - Planning Commission has been scrapped on
(A) January 1, 2015
(B) August 13, 2014
(C) January 22, 2015
(D) July 2, 2015 - Which authority is entrusted with the task of overseeing implementation
of Sustainable Development Goals in India?
(A) NITI AAYOG
(B) PMO
(C) Cabinet
(D) None of the above
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2018
- National Rural Development Institute is situated at
a) Delhi
b) Shimla
c) Hyderabad
d) Mumbai - In context of India’s five year plans, a shift in pattern of industrialization
with lower emphasis on heavy industries and more on infrastructure begin in
a) Fourth Plan
b) Fifth Plan
c) Eight Plan
d) Nineth Plan - The Government of India has established NITI Ayog to replace the
a) Human Rights Commission
b) Finance Commission
c) Law Commissions
d) Planning Commission - Which one of the following is NOT correct?
a) First Five Year Plan : 1951-1956
b) Second Five Year Plan : 1956-1961
c) Third Five Year Plan : 1961-1966
d) Fourth Five Year Plan : 1966-1971 - Which among the following Industrial Policy Resolution/Statement was
based upon the Mahalanobis Model of growth?
a) Industrial Policy Resolution – 1956
b) industry Policy Statement – 1973
c) Industrial Policy Statement – 1977
d) None of the above - In context of India’s five year plans, in which plan was the growth rate
target exceeded?
a) First plan
b) Fifth plan
c) Sixth plan
d) None of the above
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2017
- During which Five Year Plan was the total expenditure on agriculture
the highest ?
(A) 1st
(B) 2nd
(C) 3rd
(D) 4th - What is the duration of the revised 6th National Development Plan ?
(A) 1974-79
(B) 1978-83
(C) 1980-85
(D) 2013-16 - Success of 4th plan was obstructed by
(A) problem of Bengal refugees
(B) war with Pakistan
(C) poor monsoon
(D) All of the above - During which Five year plan did prices show a decline ?
(A) 1st
(B) 3rd
(C) 5th
(D) 6th - In which of the Five Year Plan, the weaker sections of the society got
priority ?
(A) 5th
(B) 4th
(C) 3rd
(D) None of the above - A rolling plan is a plan for
(A) one year
(B) two years
(C) three years
(D) five years - Which five year plan focused on ‘growth with social justice and equity’
?
(A) Ninth Five Year Plan
(B) Eighth Five Year Plan
(C) Seventh Five Year Plan
(D) Sixth Five Year Plan - First five year plan was based on
(A) Harrod – Domar model
(B) P. C. Mahalanobis model
(C) Both of the above
(D) None of the above - The objective of the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005
is
(A) enhance the livelihood & security of rural people by generating
wage employment through works that develop infrastructure base of
that area
(B) to provide financial assistance and technical advice for generation of
employment in rural areas
(C) to impart new technical skill and upgrade the traditional skill of rural
people
(D) to generate employment in health, primary education, drinking water,
housing and rural roads in rural areas
- From which country India adopted the Five Year Plans ?
(A) USSR
(B) USA
(C) Australia
(D) Germany - Which Five-Year-Plan was terminated before the completion of its
period ?
(A) Fifth
(B) Sixth
(C) Seventh
(D) Eighth - Which of the following statement is not correct about INDIA VISION
2020 ?
(A) It expects elimination of poverty, unemployment and illiteracy by
2020
(B) It expects that India’s per capita income will get down by 2020
(C) Environment situation will remain as unbalanced as today
(D) It was designed by Dr. Sam Pitroda - In India, the concepts of ‘minimum needs’ and ‘anti-poverty
programmes’ were the innovations of
(A) Fourth Five Year Plan
(B) Fifth Five Year Plan
(C) Sixth Five Year Plan
(D) Eighth Five Year Plan - For internal financing of Five Year Plans, the government depends on
(A) taxation only
(B) public borrowing and deficit financing
(C) taxation and public borrowing
(D) taxation, public borrowing and deficit financing - In the context of India’s Five Year Plans, a shift in the pattern of
industrialisation, with lower emphasis on heavy industries and more on
infrastructure begins in
(A) Tenth Plan
(B) Eighth Plan
(C) Sixth Plan
(D) Fourth Plan - The basic feature of the Rolling Plans was that
(A) revision of the achievement of previous year
(B) no physical target were visualised
(C) no financial target except in the term of annual plans was envisaged
(D) annual fluctuations in prices and major economic developments could
be considered while fixing target - In which one of the following Five Year Plans the actual growth
performance in India in respect of GDP (at factor cost) was less than the
target set ?
(A) Sixth Five Year Plan
(B) Seventh Five Year Plan
(C) Eighth Five Year Plan
(D) Ninth Five Year Plan - Which of the following indicate economic growth through Five Year
Plans ?
(A) Rise in national income and per capita income
(B) Development of railways and roadways
(C) Development of education and health services
(D) Development of industrial towns and industrial estates - India’s economic planning cannot be said to be
(A) Indicative
(B) imperative
(C) limited
(D) democratic - When, for the first time, did the Prime Minister of India announce the
20-point Economic Programme ?
(A) 1973
(B) 1974
(C) 1975
(D) 1976 - Which of the following sector is not covered under the Bharat Nirman
Programme ?
(irrigation, roads, housing, water supply, electrification)
(A) Health & Nutrition
(B) Irrigation
(C) Road
(D) Housing - Abid Hussain Committee is related to
(A) reform in taxes
(B) reform in government projects
(C) reform in small industries
(D) reform in middle level industries
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2016
- What is the main objective of the 12th Five year Plan ?
(A) Faster and inclusive growth
(B) Faster and sustainable growth
(C) Inclusive and sustainable growth
(D) Faster, sustainable and more inclusive growth - Operation Barga in West Bengal was introduced in-
(A) 1977
(B) 1978
(C) 1979
(D) 1980 - What is the estimated rate of growth in the second year of the 12th Five
Year Plan of India ?
(A) 4.7 per cent
(B) 4.9 per cent
(C) 4.5 per cent
(D) 4.3 per cent - Which of the following was not an objective of the 1956 industrial policy
?
(A) Development of co-operative sector
(B) Expansion of public sector
(C) Develop heavy and machine making industries
(D) None of the above - Which of the following was included as part of the land reforms initiated
in India ?
(A) Abolition of intermediaries
(B) Tenancy reforms
(C) Reorganization of agriculture
(D) All of the above - The Second Five Year Plan of India gave special emphasis on-
(A) Labour intensive industries
(B) Heavy and capital goods industries
(C) Consumer goods industries
(D) Small scale and cottage industries - The ceiling on foreign investment was revised in the Industrial Policy
1991 from 40 per cent to-
(A) 49 per cent
(B) 50 per cent
(C) 51 per cent
(D) 52 per cent - When was the Infrastructure Development Finance Company
constituted ?
(A) During the Eighth Five Year Plan
(B) During the Ninth Five Year Plan
(C) During the Tenth Five Year Plan
(D) During the Seventh Five Year Plan - In which among the following years a new ‘Liberalized Industrial Policy’
in India was announced for the first time ?
(A) 1986
(B) 1991
(C) 1992
(D) 1993 - The Industrial Policy of India was first announced in-
(A) 1948 (6th April)
(B) 1936
(C) 1991
(D) 1990 - “Twenty point programme” was launched in the year
(A) 1969
(B) 1975
(C) 1977
(D) 1980 - What has been the average rate of increase in agricultural production in
the Eleventh Five Year Plan ?
(A) 3%
(B) 4%
(C) 4.1%
(D) 3.7% - Rapid industrialisation is the basic objective of –
(A) Second Five Year Plan
(B) Third Five Year Plan
(C) Fourth Five Year Plan
(D) Fifth Five Year Plan - India’s economic crisis in 1991 was mainly the outcome of the following
–
(A) Acute Fiscal deficit crisis
(B) Balance of Payments crisis
(C) High rate of inflation
(D) All of the above - In India the concept of ‘minimum needs’ and ‘directed antipoverty
programmes’ were innovation of-
(A) Fourth Five Year Plan
(B) Fifth Five Year Plan
(C) Sixth Five Year Plan
(D) Seventh Five Year Plan - Which of the following planning is executed at the grass root level ?
(A) Centralised planning
(B) Decentralised planning
(C) Fixed planning
(D) Imperative planning - In the First Five Year Plan of India, priority was given to –
(A) Food and agricultural
(B) Industrial production
(C) Reducing unemployment
(D) None of the above - National Food Security Mission was introduced in the –
(A) Tenth Five Year Plan
(B) Eleventh Five Year Plan
(C) Twelfth Five Year Plan
(D) Ninth Five Year Plan - New National Food Security Mission (NFSM) with an expenditure of Rs.
4882 crore in the 11th plan aims at ensuring adequate supply of –
(A) rice, cereals, pulses
(B) wheat, cereals, pulses
(C) rice, wheat, pulses
(D) rice, cereals, wheat
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2015
- Which of the statements is not correct
(A) National Food Security Mission was launched in 2007-2008
(B) It (NFSM) aimed at increase in production of rice, wheat and pulses
(C) The basic strategy is to promote and extend improved technologies
(D) It did not lay emphasis on soil management - Integrated Rural Development Programme (IRDP) came during
(A) Fourth plan
(B) Fifth plan
(C) Sixth plan
(D) Rolling plan - The strategy of direct attack on poverty was taken in this plan
(A) Plan four
(B) Plan five
(C) Plan six
(D) Plan nine - Attitude of Industrial Policy 1991 toward foreign direct investment was
one of
(A) Total rejection
(B) Increase in the share of FDI
(C) Decrease in the share of FDI
(D) None of the above - India suffered serious foreign exchange crisis in this year
(A) 1989
(B) 1990
(C) 1991
(D) 1995 - Disinvestment of PSE-s was required because of this
(A) Increase in competitiveness
(B) Increasing subsidy
(C) Increase in capacity unutilisation
(D) All of the above - Consider the following :
1. Growing public sector was emphasized in first eighth plans
2. Planning in India derives its objectives and social premises from the
Directive Principles of State Policy
3. The Planning Commission was set-up in March, 1952 by a Resolution of
the Government of India
(A) 1 & 3 are true
(B) 2 & 3 are true
(C) 1 & 2 are true
(D) All are true - Consider the following statement
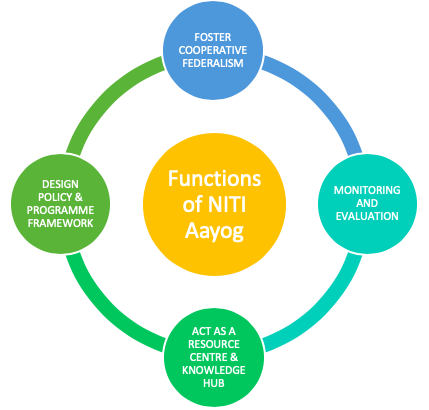
1. Niti Aayog is a policy think tank
2. It aims at greater participation in the economic policy by the State
Governments
3. First meeting of the Aayog was held on 18th February, 2015
(A) 1 & 2 are true
(B) 1, 2 & 3 are true
(C) 2 & 3 are true
(D) 1 is true - The Eighth Plan could not take off in 1990 due to
(A) Extreme financial crisis
(B) Fast changing political situation
(C) The concept of Annual Plan was brought in
(D) Planning Commission advised so - The National Urban Transport Policy has the following focus-
(A) Move fast
(B) Move people not vehicle
(C) Reduction in public transport
(D) Discouraging non-motorised modes of travel - The second meeting of the Governing Council of NITI Aayog
emphasized on :
(A) Eradication of poverty
(B) State units should be the focus of all development efforts
(C) Clearance of all pending projects
(D) (A) & (B) - The basic thrust of two Annual Plans, 1990-91 and 1991-92 are
(A) Maximisation of employment
(B) Ensuring social transformations
(C) Securing self-sustaining growth
(D) (A) & (B) both - Consider the following statement
1. The Ninth Plan was launched in the fiftieth year of India’s independence
2. It lay emphasis on five basic minimum needs
3. It achieved a growth rate of 5.5 per cent per annum in GDP
(A) 1 & 3 are true
(B) 1 & 2 are true
(C) 2 & 3 are true
(D) All of the above are true - Consider the following statements :
1. The tenth Five Year Plan (2002-07) was approved by NDC in December,
2002
2. The plan aimed at creating 50 million job opportunities
3. It recognizes that Governance is one of the most important factors for
realizing the objectives of the plan
(A) 1 & 2 are true
(B) 2 & 3 are true
(C) 1 & 3 are false
(D) All are true - Development of basic capital goods industries took place during –
(A) First plan
(B) Second plan
(C) Sixth plan
(D) Eighth plan - First two decades of planning witnessed foreign exchange position to
be
(A) Very satisfactory
(B) Unsatisfactory
(C) Moderate
(D) None applies - Early phase of Indian planning experience observed this.
(A) Import substitution
(B) Free trade regime
(C) Import liberalization
(D) Both (B) and (C) - Find the incorrect statement.
Structural adjustment implies this
(A) Increasing import restriction
(B) Import liberalization
(C) Opening domestic market to free trade
(D) Bringing flexible exchange rate - Which one of the following does not come under liberalization
programme ?
(A) Removal of Industrial licensing
(B) Reservation of small scale industries items
(C) Reduction in MRTP restrictions
(D) Increasing limit of foreign direct investment - Zamindary abolition in West Bengal came in this year
(West Bengal estate acquisition act 1953)
(A) 1951
(B) 1953
(C) 1960
(D) 1961 - Devaluation of Indian currency in 1991 was required to bring
(A) Increase in Imports
(B) Decrease in Exports
(C) Increase in Exports
(D) Both Exports and Imports to fall - The first Industrial policy in India was introduced in the year
(A) 1947
(B) 1948 (6th April)
(C) 1950
(D) 1951 - Freight equalisation policy affected industrial development in West
Bengal in the following way
(A) Beneficially
(B) Adversely
(C) Neutrally
(D) None applies - Industrial Reforms Policy took this approach to monopolies
(A) Remove MRTP restrictions
(B) Tighten such restrictions
(C) Neutral attitude
(D) Partly regulate the monopolies - Number of public sector enterprise (PSE) under New Economic
Policy
(A) Increased
(B) Decreased
(C) Remained same
(D) First increased then decreased - Find out the incorrect statement
Chelliah Committee recommended regarding tax reforms –
(A) To simplify rules of tax
(B) To reduce rate of income tax
(C) To raise the rate of customs duties
(D) Both (A) and (B) - Economic reforms policy gives utmost emphasis on
(A) Import restriction
(B) Export promotion and import liberalisation
(C) Import substitution
(D) None applies - Trickle down process in India has become
(A) Successful highly in generating all round growth
(B) Not at all successful
(C) Partly successful
(D) Uncertain
WBCS Main Question Paper – 2014
- The first Five Year Plan in India was launched in the year :
(A) 1951
(B) 1949
(C) 1953
(D) 1947 - The outline of second Five Year Plan was made by –
(A) B.N. Gadgil
(B) V.K.R. V. Rao
(C) P. C. Mahalanabish
(D) C. K. Vakil - The Planning Commission was set up :
(A) Under the Government of India Act, 1935
(B) as per the provisions of the Constitution of India
(C) by a Cabinet resolution
(D) as per the recommendations of the National Development Council - In LERMS (Liberalisation Exchange Rate Management System) –
(A) 60% of Foreign currency holding was permitted to be converted
on the market rate, whereas remaining 40% on official rate
(B) 40% on Market rate and 60% on official rate
(C) 100% on official rate
(D) None of the above - Growth with Equity and Distributive Justice was the main objective in
(A) 7th Five Year plan
(B) 8th Five Year plan
(C) 9th Five Year plan
(D) 11th Five Year plan - The time period for the 7th Five Year Plan was –
(A) 1986-91
(B) 1985-90
(C) 1980-85
(D) 1991-96
To know more about W.B.C.S. Preliminary Examination Mock Test – Click Here.
To know more about W.B.C.S. Main Examination Mock Test – Click Here.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in