Medical Science Notes On – Haemothorax – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
মেডিকেল সায়েন্স নোটস – হেমোথোরাক্স – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
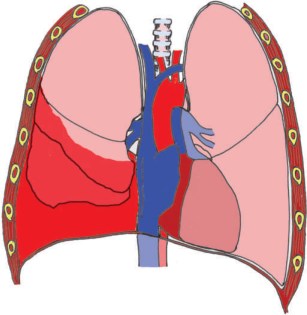
Haemothorax is a problem commonly encountered in medical practice and
is most frequently related to open or closed chest trauma or to invasive
procedures of the chest. Spontaneous haemothorax is less common and can
have various causes, such as the use of anticoagulants, neoplasia, and
rupture of pleural adhesions. Identification by radiography and
thoracentesis is indicated and treatment of the underlying trauma should
start immediately.Continue Reading Medical Science Notes On –
Haemothorax – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
After insertion of a large chest tube, antibiotic prophylaxis in trauma
patients should be administered for 24 h.
Further treatment depends on the haemodynamic stability of the patient,
the volume of evacuated blood and the occurrence of persistent blood loss.
Surgical exploration by VATS or thoracotomy is necessary if >1.500 ml of
blood has accumulated and/or an ongoing production of >200 ml of blood
per hour is observed. If the haemorrhage is less severe, careful
investigation into the underlying cause must be performed and blood
should be evacuated by tube thoracostomy.
If clotted blood retained in spite of tube thoracostomy, intrapleural
fibrinolytic therapy can be applied to breakdown clots and adhesions. If
conservative treatment is insufficient, a surgical approach with VATS or
thoracotomy is indicated to prevent subsequent complications.
Spontaneous haemothorax (SH) is a subcategory of haemothorax that
involves the accumulation of blood within the pleural space in the abscence
of trauma or other causes. The clinical presentation is variable and include
a rapid progression of symptoms of chest pain and dyspnea that can be life
threatening when hemodynamic instability and hypovolemic shock occurs.
Despite haemothorax, SH is much less common with data limited to case
reports and case series. A literature review has been performed to identify
and summarise all potentials causes leading to this clinical entity.
Haemothorax is a clinical entity that in most cases can be caused by trauma
, coagulopathy, or iatrogenic causes through procedures such as central line
insertion, thoracocentesis, pleural biopsies. It is defined as a pleural fluid
with hematocrit greater than 50% of the patient’s blood, although in cases
of long standing haemothorax due to haemodilution, hematocrit level can
be lower mimicking a hemorrhagic exudation. Therefore a hematocrit of
25-50% of the patients blood can raise the suspicion of haemothorax.
Spontaneous haemothorax (SH) is a subcategory of haemothorax that
involves the accumulation of blood within the pleural space in the absence
of trauma or other causes. The clinical presentation is variable and include
s a rapid progression of symptoms of chest pain and dyspnea that can be
life threatening when hemodynamic instability and hypovolemic shock
occurs.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in