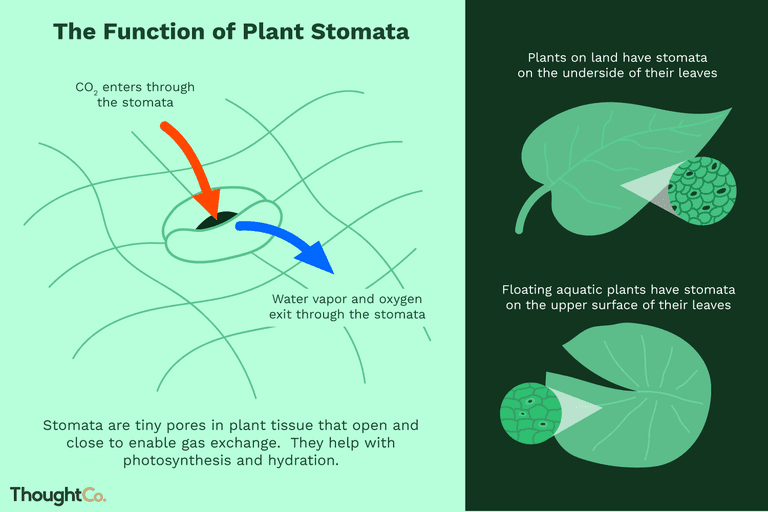
Stomata – Types – Botany Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
স্টোমাটার প্রকার – উদ্ভিদ বিদ্যা নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
The dicotyledons stomata were firstly classified into 4
types by Yesque in the year 1889. The names for your types
were given after the family in which these types were first
studied. The four types as defined by Yesque (1889) are as
follows:Continue Reading Stomata – Types – Botany Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
(i) Ranunculaceous type: Stoma mother cell is cut off by a
simple U-shaped wall; mature stomata are surrounded by
several irregularly disposed epidermal cells.
(ii) Cruciferous type: The stoma mother cell is cut off in the
primordial cell by three or more cell walls inclined to
one another at an angle of about 60°; mature stomata are
surrounded by three subsidiary cells, of which one is,
smaller than the other two.
(iii) Caryophyllaceous or Labiateous type: Stoma mother cell
is cut off into the primordial cell by two U-shaped cell
walls oriented in opposite directions, the second being
attached to the concavity of the first, mature stomata are
suspended in the middle of an epidermal cell by two cell
walls perpendicular to the pore.
(iv) Rubiaceous type: Stoma mother cell is cut off in the
primordial cell by two parallel walls; mature stomata are
accompanied by two subsidiary cells parallel to the longaxis of the pore.
In order to remove the impression that the particular
type of stomata are not restricted to certain families only;
Metcalfe and Chalk (1950) replaced these terms by more general
descriptive ones: “anomocytic” for Mranunculaceous”, “anisocytic”
for “Cruciferous”; “diacytic” for “Caryophyllaceous” or
“labiateous” and “paracytic” for “rubiaceous”.
Since Metcalfe and Chalk (1950) proposed these terms;
they have been in use in most research papers to indicate the
structure and position of the epidermal or subsidiary cells. The
different terms of Metcalfe and Chalk (1950) are defined as
under:
(i) Anomocytic (irregular-celled)type: The stoma is surrounded
by a definite number of cells that are not different from
the remainder of the epidermis.
/
(ii) Anisoeytic (unequal celled) type: The stoma is surrounded
by three cells of which one is distinctly smaller than the
other two.
(iii) Diacytic (Cross-celled) type: The stoma is enclosed by
a pair of subsidiary cells whose common wall is at right
angles to the guard cells.
(iv) Paracytic (parallel celled) type: The stoma is accompanied
on either side by one or more subsidiary cells parallel tothe long axis of the pore and guard cells.
The following morphological terms have been added to this list:
(v) Actinoc.ytic type: The stoma is surrounded by a circle of
radiating cells (Metcalfe and Chalk, 1950).
(vi) Cyclocytic type: The stoma is surrounded by 4 or more cells
forming a narrow ring around the guard cells (Stace, 19650*
(vii) Tetracytic type: The stoma is surrounded by four
subsidiary cells, 2 lateral and 2 polar, the polar sometimes
smaller and roundish (Metcalfe,1961).
(viii) Stoma with a single subsidiary cell; : The stoma is
accompanied by a single subsidiary cell either shorter or
longer than the guard cells and which mostly lie parallel
to the long axis of the pore. Van Cotthem (1970) designated
this as a hemiparacytic.
B. MORPHOGENETIC OR ONTOGENETIC CLASSIFICATION:
The stoma mother cell or stomatal initial called the
meristemoid is cut off from a cell of the protoderm. The
stomatal initial undergoes one or more divisions to give rise
to a stoma. A stomatal meristemoid which divides to form two
equal guard cells is called a guard mother cell.
I. Prantl^ classification (1872); It was Prantl (1872) who
firstly recognised two main ontogenetic types of stomata as under(i) Direct type: The stoma initial undergoes only two divisions,
cutting off a mesogene neighbouring cell during the first
division before the second segment form the two guard cells
during the second division.
(ii) Indirect type; The stomata initial divides three or more
times to give rise to two or more mesogene neighbouring and
encircling cells before forming the guard cells.
II. Florin’s classification (1931. 1955): The gymnosperm stomata
were classified into two following ontogenetic types by
Florin (1931, 1933):
(i) Haplocheilic type: A stoma mother cell directly dunctions
as a guard mother cell which divides to produce a pair of
guard cells only without cutting off any subsidiary cells..
(ii) Syndetocheilic type: A stomatal initial functions as a guard
mother cell after cutting off one or more subsidiary cells.
Our own publications are available at our webstore (click here).
For Guidance of WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Preliminary , Main Exam and Interview, Study Mat, Mock Test, Guided by WBCS Gr A Officers , Online and Classroom, Call 9674493673, or mail us at – mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Visit our you tube channel WBCSMadeEasy™ You tube Channel
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website



 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in