W.B.C.S. Notes On – Physics – Spherical Lenses.
- A transparent material (normally glass) bound by two surfaces, of which one or both surfaces are spherical, is known as “spherical lens.”Continue Reading W.B.C.S. Notes On – Physics – Spherical Lenses.
Convex Lens
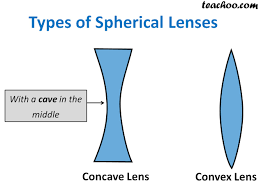
- A lens may have two spherical surfaces, bulging outwards (as shown in the image given below), is known as convex lens or a double convex lens.

- The middle part of this lens is bulged (thicker) and at the both ends, it is narrow.
- Convex lens converges the light rays; therefore, it is also known as converging lens.
Concave Lens
- A lens may have two spherical surfaces, curved inwards (as shown in the image given below), is known as concave lens or a double concave lens.

- The middle part of this lens is narrow (curved inwards) and the both the edges are thicker.
- Concave lens diverges the light rays; therefore, it is also known as diverging lens.
- A lens, either a concave or a convex, has two spherical surfaces and each of these surfaces forms a part of the sphere. The centers of these spheres are known as centers of curvature, represented by English letter ‘C.’
- As there are two centers of curvature, therefore, represented as ‘C1’ and ‘C2.’
- An imaginary straight line, passing through both the centers of curvature of a lens, is known as principal axis.
- Optical center is the central point of a lens. It is represented by ‘O.’
- An aperture is the actual diameter of the circular outline of a spherical lens.
- Principal focus of lens is represented by ‘F.’
- A lens has usually two foci represented as F1 and F2.
- Focal length is the distance between the principal focus and the optical center of a lens. It is represented by ‘f.’
- The following table illustrates, the nature and position of images formed by a convex lens −
| Position of Object | Position of Image | Size of Image | Nature of Image | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At the focus F2 | Highly diminished, pointsized | Real and inverted |  |
| Beyond 2F1 | B/w F2 and 2F2 | Diminished | Real and inverted |  |
| At 2F1 | At 2F2 | Same size | Real and inverted |  |
| B/w F1 & 2F1 | Beyond 2F2 | Enlarged | Real and inverted |  |
| At focus F1 | At infinity | Infinitely large or highly enlarged | Real & inverte d |  |
| B/w focus F1& optical center O | On the same side of the lens as the object | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |  |
- The following table illustrates, the nature and position of images formed by a concave lens −
| Position of Object | Position of Image | Relative Size of Image | Nature of Image | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At infinity | At the focus F1 | Highly diminishe d, pointsized | Virtual and erect |  |
| B/w infinity & optical center O of the lens | B/w F1 & optical center O | Diminishe d | Virtual and erect |  |
Lens Formula
-
- The formula is expressed as −
1v−1u=1f1v−1u=1f
- Lens formula expresses the relationships among the object-distance (i.e. u), image-distance (i.e. v), and focal length (i.e. f) of a lens.
Our own publications are available at our webstore (click here).
For Guidance of WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Preliminary , Main Exam and Interview, Study Mat, Mock Test, Guided by WBCS Gr A Officers , Online and Classroom, Call 9674493673, or mail us at – mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Visit our you tube channel WBCSMadeEasy™ You tube Channel
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website



 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in