Current Affairs of 11th June 2023 For IAS And WBCS Examination
Art and Culture
Gulabi meenakari handicraft:

- The Uttar Pradesh state government decided to give GI-tagged Gulabi meenakari handicrafts to visiting delegates from G20 nations.
- Gulabi meenakari handicraft:
- This is one of India’s rarest crafts, practiced in the backstreets of Varanasi near Gai Ghat.
- It is a Persian art technique that involves coloring the surface of metals by fusing different colors.
- During the Mughal dynasty, around the early 17th century, Persian enamellists brought this skill to Varanasi.
- The word ‘mina’ is the feminine form of the Persian word ‘Minoo’ and means ‘heaven’.
- It refers to the azure colour of heaven.
- In Varanasi, it is practised on jewellery and home decor items.
- Minakari work uses very simple instruments such as salai (an etching tool), kiln, metal palette, mortar and pestle, kalam (a tool used to apply enamel), brass dye, small scrubbing brush, forceps and takala (a needle-like tool to apply colours).
- This craft is commonly found in three forms:
- Ek Rang Khula Meena: In this form only gold outlines are exposed and a single transparent colour is used.
- Panch Rangi Meena: In this form the five colours of red, white, green, light blue and dark blue are used.
- Gulabi Meena: In this form pink is the dominant color.
Science and Technology
Tactical LAN Radio

- Context:
- The Indian Army has announced a contract with a Bengaluru-based company to purchase an indigenously produced “tactical LAN radio.”
- It is the Army’s second contract under the framework of Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX).
- Tactical LAN Radio:

- It is cutting-edge high-bandwidth backhaul wireless radio technology for providing reliable and failsafe communication.
- The LAN radio solution provides a wider range of communication options as well as an incorporated frequency hopping mechanism to reduce the possibility of eavesdropping.
- It enables long-distance, high-bandwidth point-to-multipoint communication.
- The system also includes upgraded safety features and can run continuously for 48 hours on a single set without breaking down.
- iDEX (Innovations for Defence Excellence):
- It is the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- iDEX, which introduced in 2018, is an ecosystem that encourages innovation and technology development in defense and aerospace by bringing together innovators and entrepreneurs to give technologically sophisticated solutions for modernizing the Indian military.
- It provides funding/grants for research and development to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), start-ups, individual innovators, R&D (Research and Development) institutes, and universities.
- iDEX will be funded and administered by a ‘Defence Innovation Organization (DIO)’, which has been founded as a ‘not for profit companyas per Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013 by the two founding members, namely, HAL and BEL.
- The iDEX-Prime program intends to assist ever-growing defense start-ups by providing funding for projects requiring more than Rs 1.5 crore up to Rs 10 crore.
- The iDEX portal was designed to increase public awareness and exposure of iDEX activities, as well as to enable more effective running of future challenges through better information management.
- Aims:
- Rapid development of indigenous, inventive technologies.
- Creates a culture of engagement with creative startups in order to stimulate co-creation.
- Achievement: For the year 2021, iDEX has been awarded the prestigious Prime Minister Award for Public Policy in the Innovation Category.
Respiratory syncytial virus
- Context: European regulators have approved the region’s first vaccine for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
- The Arexvy injection, manufactured by the British pharmaceutical company GSK, is designed to protect people aged 60 and up.
- The following are the most important facts regarding Respiratory syncytial virus:
- It is a common respiratory virus that causes mild, cold-like symptoms in most people.
- It is particularly dangerous to newborns and the elderly.
- It is the most common cause of bronchiolitis (inflammation of the small airways in the lung) and pneumonia in children younger than 1 year of age in the United States.
- The virus’s intricate molecular structure and safety problems with prior vaccine trials have impeded efforts to develop a vaccine.
Dimethyl Ether (DME)
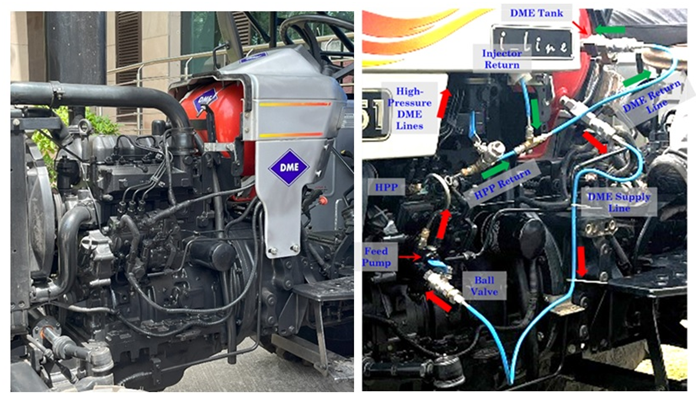
- Context: Recently, IIT Kanpur researchers designed a 100% DME-fueled engine with a mechanical fuel injection system.
- Dimethyl Ether (DME):
- It is a synthetically produced alternative to diesel for use in specially designed compression ignition diesel engines.
- It may be manufactured locally, and many countries, including Japan, the United States, China, Sweden, Denmark, and Korea, are already using DME to power their automobiles.
- Without the use of costly exhaust gas after-treatment systems or complex engine technologies, the DME-fueled engine produced extraordinarily low particle and soot emissions and nearly no smoke.
- It has the potential to be a viable alternative fuel and engine technology to conventional diesel engines utilized in India’s agricultural and transportation sectors.
- Dimethyl Ether has the following properties:
- It has a very high cetane number, which measures the ignitibility of the fuel in compression ignition engines.
- DME is a colorless gas in typical atmospheric circumstances.
- Uses:
- It is widely utilized in the chemical industry as well as as an aerosol propellant.
- It is also used to produce dyes and plastics.
Government Scheme
Operation Amanat

- The Railway Protection Force (RPF) recently completed a successful operation called “Amanat,” which resulted in the recovery of lost or abandoned luggage and valuable items.
- The Railway Protection Force has developed an innovative step as part of the Operation Amanat campaign to make it easier for travelers to retrieve their lost luggage.
- It aids in the recovery of passengers’ lost possessions.
- RPF troops from the different Divisions contribute information about misplaced bags, including images.
- The information is available on the webportal https://wr.indianrailways.gov.in/ in the tab of divisions under the link “Mission Amanat – RPF”.
- Passengers can check lost Property Offices at stations to check if their luggage that went missing or was misplaced in railway premises or trains is still available.
- Railway Protection Force:
- The RPF contingent is a part of the Union of India’s Armed Forces. It is a security force owned by Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways.
- It is headed by the Director General (DG). However, the post of Director-General of RPF is held on deputation by a senior Indian Police Service (IPS) officer.
- The RPF’s history begins in 1882, when individual railway corporations recruited their own guards to defend railway property.
- The force was declared as statutory force in the year 1957 by an enactment of Parliament subsequently declared as an Armed Force of the Union of India in the year 1985.
- The RPF Rules were passed in 1959, and the RPF Regulations were issued in 1966. The Railway Property (Unlawful Possession) Act, 1966, granted on the Force some limited authority to apprehend and prosecute offenders involved in railway property.
- RPF has been primarily entrusted with ensuring the safety of railway property. However, while the provisions of the RPF Act were soon found to be insufficient for the maintenance of an efficient and disciplined Force, the RPF Rules and Regulations were also found to be judicially unsound.
- Parliament amended the RPF Act of 1957 in 1985 to ensure the Force’s continued existence as an armed force of the Union.
- This Force recruits its troops from all around the country and takes pride in displaying a really national character and image. Since its birth, the Force has garnered notoriety and glory.
National Training Conclave

- Context: The Prime Minister will launch the first National Training Conclave at the International Exhibition and Convention Centre Pragati Maidan in New Delhi.
- National Training Conclave:
- The conclave is part of the ‘Mission Karmayogi’ National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB).
- Goal: To promote collaboration among civil service training institutes and to develop the country’s training infrastructure for civil servants.
- The Capacity Building Commission is hosting the Conclave.
- The conclave will be attended by about 1500 delegates from various training institutes, including Central Training Institutes, State Administrative Training Institutes, Regional and Zonal Training Institutes, and Research Institutes.
- Civil servants from the central government, state governments, and local governments, as well as private-sector professionals, will participate in the deliberations.
- The Conclave will feature eight panel talks, each concentrating on a different issue concerning Civil Services training institutes, such as faculty development, training impact assessment, and content digitisation.
- Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmyogi, also known as the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB), intends to train civil servants for the future by increasing their creativity, constructiveness, and innovation through transparency and technology.
- This unique program will assist create the groundwork for the country’s public workers.
- In addition to “off-site learning,” there will be a greater focus on “on-site learning.”
- It will be steered by four new bodies.
- The new entities will be a Prime Minister’s Public Human Resources Council, a Capacity Building Commission, a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that will own and operate the digital assets and technological platform for online training, and a Coordination Unit, which will be headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
Indian Economy
Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)

- Context: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) proposes mandating audits of Insolvency Resolution Process Costs (IRPC) in resolution cases where the assets of the corporate debtor (CD) exceed Rs 100 crore.
- Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India:
- Under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (Code), the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India was set up in 2016.
- It is a key pillar of the ecosystem responsible for the Code’s implementation, which consolidates and amends the laws relating to the reorganization and insolvency resolution of corporate persons, partnership firms, and individuals in a time-bound manner in order to maximize the value of such persons’ assets, promote entrepreneurship, credit availability, and balance the interests of all stakeholders.
- Functions:
- The IBBI regulates both professionals and processes.
- It has regulatory authority over insolvency professional agencies, entities, insolvency professionals, and information utilities.
- Under the IBC, it enforces rules for corporate insolvency resolution, individual insolvency resolution, corporate liquidation, and individual bankruptcy.
- It sets the minimum eligibility standards for registration of insolvency professional agencies, insolvency professionals, and information utilities, as well as the curriculum for the insolvency professionals’ qualifying examination for enrolment.
- It gathers and maintains insolvency and bankruptcy records, as well as disseminates information about such situations.
- Constitution: The following members are appointed by the Central Government to the Board:
- A Chairperson.
- Three members chosen from among Central Government officers with the rank of Joint Secretary or higher. Each of the three members will serve as an ex-officio representative of the Ministries of Finance, Corporate Affairs, and Law.
- The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) appoints one member as an ex-officio member.
- Five more members appointed by the Central Government, at least three of whom must be full-time members.
- The Chairperson and members (other than ex-officio members) serve for five years or until they reach the age of sixty-five, whichever comes first, and are eligible for re-appointment.
Five Significant Decisions For Strengthening Primary Agricultural Credit

- Context:The Government of India has made five major decisions concerning Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), a fundamental unit and the smallest cooperative credit institution in India that operates at the grassroots (gram panchayat and village level).
- The five decisions were made during a meeting in New Delhi between Amit Shah, the Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation, and Mansukh Mandaviya, the Minister of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- Five decisions:
- There are approximately 1 lakh Primary Agricultural Credit Cooperative Societies in India. PACS that are not currently operating as fertiliser retailers will be identified and encouraged to operate as retailers on the basis of feasibility in a phased manner.
- PACS that are not now operating as Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samridhi Kendras (PMKSK) would be placed under the purview of PMKSK.
- iii. PACS will be associated with the marketing of organic fertilizers, particularly fermented organic manure (FoM), liquid fermented organic manure (LFOM), and phosphorus-enriched organic manure (PROM).
- PACS can also be employed as drone entreprerieurs for spraying fertilisers and pesticides. Drones can also be used for property surveys.
- Under the Department of Fertilisers’ Market Development Assistance (MDA) scheme, fertilizer companies will act as an aggregator for small bio-organic producers to market the end product. PACS will also be included as wholesalers/retailers in this supply and marketing chain of bio-organic fertilisers.
Important One-Liner:
- Shivraj Singh Chouhan, the Chief Minister of Madhya Pradesh, is preparing to start a Learn and Earn program that would provide young people with skills that are in great demand by companies.The program’s goal is to train at least one lakh youth, and registration for training providers and interested youth will begin on June 7th and 15th, respectively.
- To address the problem of nutrient imbalance, the Commission on Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) has proposed that the Centre include urea in the nitrogen-based subsidy (NBS) scheme.
- According to a new study undertaken by the Indian Council of Medical Research-India Diabetes (ICMR-INDIAB), India has around 101 million diabetics and 136 million pre-diabetics.According to the report, Goa has the greatest population of diabetic patients. Diabetes affects around 26.4% of the Goan population.The ICMR-INDIAB study was published in the monthly publication “The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology,” which focuses on diabetes, endocrinology, and metabolism.
- The Central Council of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), India’s largest professional accounting body, has approved the renewal of the existing MRA/MoU with CPA Canada (Chartered Professional Accountants of Canada) and CPA Ireland, formerly the Institute of Certified Public Accountants in Ireland.ICAI has also approved the renewal of Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) with the South African Institute of Chartered Accountants (SAICA), the Bahrain Institute of Banking and Finance (BIBF), the National Board of Accountants and Auditors (Tanzania), and the Qatar Financial Centre Authority.
- Brihanmumbai Electric Supply and Transport (BEST) Undertaking, a civic transport and electricity provider public body based in Mumbai, Maharashtra, has won the UITP (Union Internationale des Transports Publics) Awards 2023 for its project “BEST Green Travel Initiative: Creating Sustainable Public Transportation.”
- The Central Government has established a peace committee in Manipur, chaired by Governor Anusuiya Uikey.The committee’s members include the Chief Minister, a few state government officials, MPs, MLAs, and leaders from poetical parties, former public servants, educationists, litterateurs, artists, social workers, and representatives from various ethnic groups.Its goal is to aid the peace-making process among the state’s numerous ethnic groups, between opposing groups, and to strengthen social cohesiveness, mutual understanding, and courteous communication.


 +919674493673
+919674493673  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in






































































































