Continuous Random Variables – Statistics Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
অবিচ্ছিন্ন দৈব চালক – স্ট্যাটিসটিক্স নোট – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
Continuous Random Variables
A continuous random variable is a random variable where the data can take infinitely many values. For example, a random variable measuring the time taken for something to be done is continuous since there are an infinite number of possible times that can be taken.Continue Reading Continuous Random Variables – Statistics Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
For any continuous random variable with probability density function f(x), we have that:
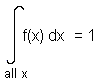
This is a useful fact.
Example
X is a continuous random variable with probability density function given by f(x) = cx for 0 ≤ x ≤ 1, where c is a constant. Find c.
If we integrate f(x) between 0 and 1 we get c/2. Hence c/2 = 1 (from the useful fact above!), giving c = 2.
Cumulative Distribution Function (c.d.f.)
If X is a continuous random variable with p.d.f. f(x) defined on a ≤ x ≤ b, then the cumulative distribution function (c.d.f.), written F(t) is given by:
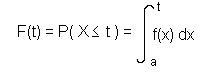
So the c.d.f. is found by integrating the p.d.f. between the minimum value of X and t.
Similarly, the probability density function of a continuous random variable can be obtained by differentiating the cumulative distribution.
The c.d.f. can be used to find out the probability of a random variable being between two values:
P(s ≤ X ≤ t) = the probability that X is between s and t. But this is equal to the probability that X ≤ t minus the probability that X ≤ s.
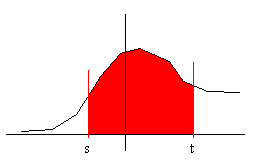
Hence:
- P(s ≤ X ≤ t) = P(X ≤ t) – P(X ≤ s) = F(t) – F(s)
Expectation and Variance
With discrete random variables, we had that the expectation was S x P(X = x) , where P(X = x) was the p.d.f.. It may come as no surprise that to find the expectation of a continuous random variable, we integrate rather than sum, i.e.:
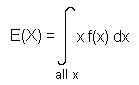
As with discrete random variables, Var(X) = E(X2) – [E(X)]2
Our own publications are available at our webstore (click here).
For Guidance of WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Preliminary , Main Exam and Interview, Study Mat, Mock Test, Guided by WBCS Gr A Officers , Online and Classroom, Call 9674493673, or mail us at – mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Visit our you tube channel WBCSMadeEasy™ You tube Channel
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website



 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in


















































































































