Different Ranks In Society – Anthropology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
সমাজের বিভিন্ন পদমর্যাদা / বর্গ – নৃতত্ত্ব নোটস – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
Indian population is a product of different races. People who came to India merged with the Indian race. It is difficult to trace the history of ancient races who came to India.Continue Reading Different Ranks In Society – Anthropology Notes – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Aryans entered India around 1500 B.C. They emigrated to India from Cyria, Asia minor, Mesopotamia and Iran. The Aryans were followed by Mongoloids from East. They settled in eastern parts of India such as Bengal and Assam. In spite of such racial differences Indians have a strong sense of Psychological identity which is termed as “Indianness”. India is regarded as a land of unity in diversity which has increased the sense of psychological security and identity.
Unity in diversity in India:
It is a unique feature of India. It is reflected in the following aspects.
Linguistic diversity:
India is a land of diverse languages. Each language has its own dialects. Out of so many languages ’14’ major languages are recognised as official languages. They Include:
i. Assamee
ii. Bengali
iii. Gujarati
iv. Hindi
v. Kashmiri
vi. Marathi
vii. Malayalam
viii. Oriya
Religious Diversity and Unity:
India is the land of almost all the major religions of the world. The major religions followed by the country are as follows:
Hinduism:
It is the religion of the majority in India. Hindus believe in doctrine of Karma, Dharma, idolworship, salvation etc.
Islam:
It originated in Arabia and came to India in 12th Century the followers of Islam are called Muslims. Islam believes in god Allah, five times prayers a day and pilgrimage to Mecca.
Christianity:
Came to India through the followers of Jesus. Christians believe that Jesus is the messenger of God who was sent to earth to reconcile men and God.
Christians are scattered all over the country.
Sikhism:
Was founded by Guru Nanak. According to Sikhism God is form- less, timeless. Gurudwara is a place of worship for Sikhs.
Buddhism:
It originated in India during the 6th century B.C. It imposes self restriction and curbing the desire.
Jainism:
It was founded by Mahaveera. It preachers nonviolence and hard penance. Apart from these major religions casteism is also dominating Indian society. Clashes among different castes, instances of religious disharmony quite often disturb Indian society. In spite of such differences bonds of unity are noticed. All religions are existing side by side in India. Unity in diversity is found in the field of religion, certain practices such as institution of pilgrimage, tradition of interdependence emotional bonds are common to all religions.
Geographical Diversity and Unity:
The boundaries of India vary from Kashmir to Kanyakumari. Climatic conditions vary to a large extent in different parts of India. Parts of Rajastan is a desert area and gangetic plane is a fertile land. The nature of soil, extent of rainfall differ throughout the country. In spite of such geographical differences. India is treated as a single country under the rule of one particular government.
Cultural Unity:
The cultural unity finds its expression in the literature and thought of different communities. Cultural ideology is common to all Indians. Celebration of functions, dance music are common throughout the country.
Political diversity and unity:
The typical feature of Indian democracy is the existence of multi-party system. Different states may have different governments. But all the states are controlled by the Central government. Fundamental rights are granted to all the citizens of India. Universal adult franchise is a typical feature which promotes a strong sense of unity.
Economic diversity and unity:
There are various sectors of economy like agriculture, Industry etc. Each sector makes contribution to national income in different proportions. But all the sectors of the economy are treated equally. Investments are made in all sectors. Taxation rules are applied to all sectors. Indian government is striving to achieve a socialistic pattern of economy. Thus various aspects of unity in diversity has promoted a strong sense of psychological security and identity.
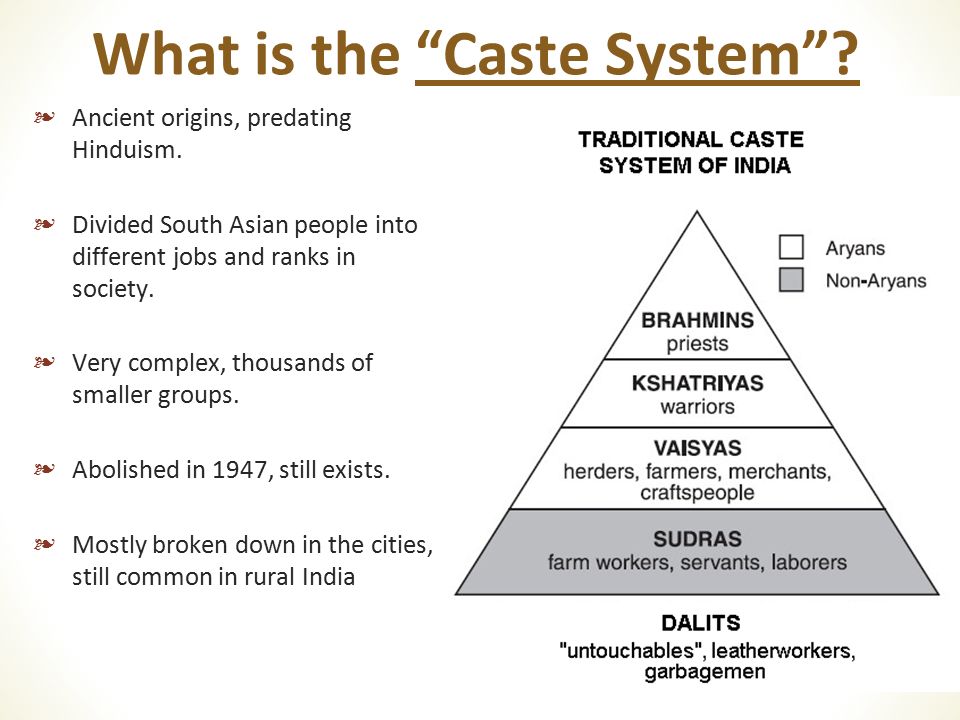
Social Stratification in India:
Stratification is an indispensable factor of any society. It is a process of differentiation which places some people in a rank which is higher than others. The concept of stratification is based on the concept of inequality.Inequalities are inherent in the nature of human beings. Human beings are differentiated on the basis of socially approved criteria such as age, sex, kinship occupation etc. Social inequality is usually found in property, power, wealth, income and status. Social stratification can be considered as patterned inequality.
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website


 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in