Geography Notes On – Composition Of Biosphere – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
ভূগোল নোট – জীব মণ্ডলের গঠন – WBCS পরীক্ষা।
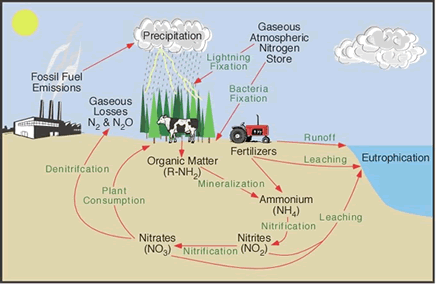
Biosphere, relatively thin life-supporting stratum of Earth’s surface, extending from a few kilometres into the atmosphere to the deep-sea vents of the ocean. The biosphere is a global ecosystem composed of living organisms (biota) and the abiotic (nonliving) factors from which they derive energy and nutrients.Continue Reading Geography Notes On – Composition Of Biosphere – For W.B.C.S. Examination.
Before the coming of life, Earth was a bleak place, a rocky globe with shallow seas and a thin band of gases—largely carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, molecular nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, and water vapour. It was a hostile and barren planet. This strictly inorganic state of the Earth is called the geosphere; it consists of the lithosphere (the rock and soil), the hydrosphere (the water), and the atmosphere (the air). Energy from the Sun relentlessly bombarded the surface of the primitive Earth, and in time—millions of years—chemical and physical actions produced the first evidence of life: formless, jellylike blobs that could collect energy from the environment and produce more of their own kind. This generation of life in the thin outer layer of the geosphere established what is called the biosphere, the “zone of life,” an energy-diverting skin that uses the matter of the Earth to make living substance.
The biosphere is a system characterized by the continuous cycling of matter and an accompanying flow of solar energy in which certain large molecules and cells are self-reproducing. Water is a major predisposing factor, for all life depends on it. The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and sulfur, when combined as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, provide the building blocks, the fuel, and the direction for the creation of life. Energy flow is required to maintain the structure of organisms by the formation and splitting of phosphate bonds. Organisms are cellular in nature and always contain some sort of enclosing membrane structure, and all have nucleic acids that store and transmit genetic information.
All life on Earth depends ultimately upon green plants, as well as upon water. Plants utilize sunlight in a process called photosynthesis to produce the food upon which animals feed and to provide, as a by-product, oxygen, which most animals require for respiration. At first, the oceans and the lands were teeming with large numbers of a few kinds of simple single-celled organisms, but slowly plants and animals of increasing complexity evolved. Interrelationships developed so that certain plants grew in association with certain other plants, and animals associated with the plants and with one another to form communities of organisms, including those of forests, grasslands, deserts, dunes, bogs, rivers, and lakes. Living communities and their nonliving environment are inseparably interrelated and constantly interact upon each other. For convenience, any segment of the landscape that includes the biotic and abiotic components is called an ecosystem. A lake is an ecosystem when it is considered in totality as not just water but also nutrients, climate, and all of the life contained within it. A given forest, meadow, or river is likewise an ecosystem. One ecosystem grades into another along zones termed ecotones, where a mixture of plant and animal species from the two ecosystems occurs. A forest considered as an ecosystem is not simply a stand of trees but is a complex of soil, air, and water, of climate and minerals, of bacteria, viruses, fungi, grasses, herbs, and trees, of insects, reptiles, amphibians, birds, and mammals.
Stated another way, the abiotic, or nonliving, portion of each ecosystem in the biosphere includes the flow of energy, nutrients, water, and gases and the concentrations of organic and inorganic substances in the environment. The biotic, or living, portion includes three general categories of organisms based on their methods of acquiring energy: the primary producers, largely green plants; the consumers, which include all the animals; and the decomposers, which include the microorganisms that break down the remains of plants and animals into simpler components for recycling in the biosphere. Aquatic ecosystems are those involving marine environments and freshwater environments on the land. Terrestrial ecosystems are those based on major vegetational types, such as forest, grassland, desert, and tundra. Particular kinds of animals are associated with each such plant province.
For Guidance of WBCS (Exe.) Etc. Preliminary , Main Exam and Interview, Study Mat, Mock Test, Guided by WBCS Gr A Officers , Online and Classroom, Call 9674493673, or mail us at – mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
Visit our you tube channel
WBCSMadeEasy™ You tube Channel
Please subscribe here to get all future updates on this post/page/category/website




 Toll Free 1800 572 9282
Toll Free 1800 572 9282  mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in
mailus@wbcsmadeeasy.in